Impedance, Balance, and Output/Input Connections for Digital Audio
... output and input. To some extent, you can simply be guided by the shapes of the input and output jacks. Should the impedance of the output and input match? The impedance of output and input don’t have to match exactly. In general, the audio output (e.g., the mic) should have lower impedance than the ...
... output and input. To some extent, you can simply be guided by the shapes of the input and output jacks. Should the impedance of the output and input match? The impedance of output and input don’t have to match exactly. In general, the audio output (e.g., the mic) should have lower impedance than the ...
Dual impedance digital multimeters
... today for testing industrial, electrical, and electronic systems have high impedance input circuits greater than 1 megohm. In simple terms this means that when the DMM is placed across a circuit for a measurement, it will have little impact on circuit performance. This is the desired effect for ...
... today for testing industrial, electrical, and electronic systems have high impedance input circuits greater than 1 megohm. In simple terms this means that when the DMM is placed across a circuit for a measurement, it will have little impact on circuit performance. This is the desired effect for ...
atf-54143_100-500mhz..
... inexpensive method of accomplishing this is to use two PNP bipolar transistors arranged in a current mirror configuration as shown in Fig. 1. Due to resistors R1 and R3 this circuit is not a true current mirror, but if the voltage drops across R1 and R3 are kept identical, the current through R3 is ...
... inexpensive method of accomplishing this is to use two PNP bipolar transistors arranged in a current mirror configuration as shown in Fig. 1. Due to resistors R1 and R3 this circuit is not a true current mirror, but if the voltage drops across R1 and R3 are kept identical, the current through R3 is ...
AD8629S: Zero-Drift, Single-Supply Rail-to-Rail Input/Output Operational Amplifier Aerospace Data Sheet (Rev E, 10/2012)
... The AD8629 is a single-supply, ultrahigh precision rail-to-rail input and output operational amplifier. The typical offset voltage of less than 1 μV allows this amplifier to be easily configured for high gains without risk of excessive output voltage errors. The extremely small temperature drift ens ...
... The AD8629 is a single-supply, ultrahigh precision rail-to-rail input and output operational amplifier. The typical offset voltage of less than 1 μV allows this amplifier to be easily configured for high gains without risk of excessive output voltage errors. The extremely small temperature drift ens ...
Analog Lock-In Amplifiers - Stanford Research Systems
... the front-panel Ref Out BNC connector. Both sine and square waveforms are selectable, and the output amplitude can be set between 100 nV and 10 V. The reference is also available on the rear panel of the SR124. Four phase-shifted 1 Vrms outputs at 0°, 90°, 180° and 270° can used for a variety of app ...
... the front-panel Ref Out BNC connector. Both sine and square waveforms are selectable, and the output amplitude can be set between 100 nV and 10 V. The reference is also available on the rear panel of the SR124. Four phase-shifted 1 Vrms outputs at 0°, 90°, 180° and 270° can used for a variety of app ...
Power Supply
... Use twisted-pair cable. DeviceNet® thick shielded twisted pair cable is recommended. Network terminators: These are supplied with the controller. Place terminators at each end of the CANbus network. Resistance must be set to 1%, 121Ω, 1/4W. Connect ground signal to the earth at only one point, near ...
... Use twisted-pair cable. DeviceNet® thick shielded twisted pair cable is recommended. Network terminators: These are supplied with the controller. Place terminators at each end of the CANbus network. Resistance must be set to 1%, 121Ω, 1/4W. Connect ground signal to the earth at only one point, near ...
Ionfsat - dept.aoe.vt.edu
... maximum. The outer conductor or shield is connected at the voltage null, and the center conductor is tapped out to the match point. As the feed point is moved further away from the voltage null, the input current at the feed point decreases, resulting in an increase in the antenna input impedance [3 ...
... maximum. The outer conductor or shield is connected at the voltage null, and the center conductor is tapped out to the match point. As the feed point is moved further away from the voltage null, the input current at the feed point decreases, resulting in an increase in the antenna input impedance [3 ...
MAX2611 DC-to-Microwave, Low-Noise Amplifier _______________General Description ____________________________Features
... MAX2611 is easy to use. Input and output series capacitors may be necessary to block DC bias voltages (generated by the MAX2611) from interacting with adjacent circuitry. These capacitors must be large enough to contribute negligible reactance in a 50Ω system at the minimum operating frequency. Use ...
... MAX2611 is easy to use. Input and output series capacitors may be necessary to block DC bias voltages (generated by the MAX2611) from interacting with adjacent circuitry. These capacitors must be large enough to contribute negligible reactance in a 50Ω system at the minimum operating frequency. Use ...
Mar 2003 Triple and Quad RGB Amplifiers Deliver Full Performance on 3.3V
... The LT6550 and LT6551 3.3V triple and quad high speed amplifiers make it possible to create compact solutions for driving RGB and component video cables. These voltage feedback amplifiers drive either 50Ω or 75Ω double terminated cables and are preconfigured for a fixed gain of two, thus eliminating ...
... The LT6550 and LT6551 3.3V triple and quad high speed amplifiers make it possible to create compact solutions for driving RGB and component video cables. These voltage feedback amplifiers drive either 50Ω or 75Ω double terminated cables and are preconfigured for a fixed gain of two, thus eliminating ...
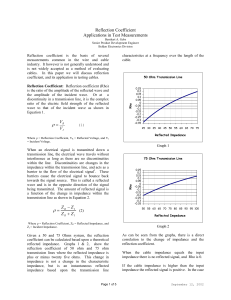
Reflection Coefficient Applications in Test Measurements
... of an open circuit the impedance is infinitely high and the reflected signal is equals the input signal and has the same polarity. Thus VR and VI are equal in magnitude and of the same polarity so the resultant Rho is 1. If the cable impedance is lower than the input impedance the reflected signal ...
... of an open circuit the impedance is infinitely high and the reflected signal is equals the input signal and has the same polarity. Thus VR and VI are equal in magnitude and of the same polarity so the resultant Rho is 1. If the cable impedance is lower than the input impedance the reflected signal ...
E1 power amplifier
... High-gain voltage amplifiers are widely available for instrumentation and other applications in a single integrated circuit, usually called an 'operational amplifier'. However, commonly used types have limited output currents, about 15 mA, precluding their use in higher power applications, such as a ...
... High-gain voltage amplifiers are widely available for instrumentation and other applications in a single integrated circuit, usually called an 'operational amplifier'. However, commonly used types have limited output currents, about 15 mA, precluding their use in higher power applications, such as a ...
Document
... motor rated voltage is grid voltage, low VTR will lead to output electromagnetic torque and motor load capacity decreased. It is seen as a disadvantage of the MC. Under the same output power condition as that for a back-to-back converter, the output current of the MC will be higher than the back-t ...
... motor rated voltage is grid voltage, low VTR will lead to output electromagnetic torque and motor load capacity decreased. It is seen as a disadvantage of the MC. Under the same output power condition as that for a back-to-back converter, the output current of the MC will be higher than the back-t ...
Ground Current Measurement
... Instrumentation amplifiers are not, of course, free from noise. The AD620 has a little over 1 µV r.m.s. input referred noise when used with a gain of 1,000. This means that the oscilloscope trace will not be a fine line but a fuzzy line several mV wide (referred to the oscilloscope input). Neverthel ...
... Instrumentation amplifiers are not, of course, free from noise. The AD620 has a little over 1 µV r.m.s. input referred noise when used with a gain of 1,000. This means that the oscilloscope trace will not be a fine line but a fuzzy line several mV wide (referred to the oscilloscope input). Neverthel ...
20/2 Data Sheet - Mescon Technologies, Inc.
... referenc e c ompensation. M odel 20/2L also provides input li nearization to correct for the inherent Thermocouple non-linearity. An optional LCD indicator is available to indicate actual temperatu re in ¡C or ¡ F. The 20/2 can be easily ranged without requiring special tools or board modifications. ...
... referenc e c ompensation. M odel 20/2L also provides input li nearization to correct for the inherent Thermocouple non-linearity. An optional LCD indicator is available to indicate actual temperatu re in ¡C or ¡ F. The 20/2 can be easily ranged without requiring special tools or board modifications. ...
Review of Circuits as LTI Systems
... directly through the filter and show up at the output. Faster components of the input induce displacement current within the capacitor, and so they get attenuated through the resistor. So Vout is a “slower” version of Vin . ...
... directly through the filter and show up at the output. Faster components of the input induce displacement current within the capacitor, and so they get attenuated through the resistor. So Vout is a “slower” version of Vin . ...
FIN1531 5V LVDS 4-Bit High Speed Differential Driver FI N1531 5V
... LVTTL Output Enable Time from Z to LOW See Figure 4 and Figure 5 (Note 7) ...
... LVTTL Output Enable Time from Z to LOW See Figure 4 and Figure 5 (Note 7) ...