Romeo and Juliet - Multiple Critical Perspective
... the work itself. This view is in direct contrast to the Formalist approach to literature. In order to understand a work, one must fully understand the author’s life and emotional stance, and vice versa. Though a work might not be blatantly autobiographical, psychoanalysts argue that there is always ...
... the work itself. This view is in direct contrast to the Formalist approach to literature. In order to understand a work, one must fully understand the author’s life and emotional stance, and vice versa. Though a work might not be blatantly autobiographical, psychoanalysts argue that there is always ...
Chapter 1 Psychology and Life
... d. can be broken into smaller elemental units which can be studied. 4. Which technique used to examine mental processes is most associated with structuralism? a. magnetic resonance imaging b. introspection c. survey administration d. biofeedback 5. This school of psychological thought was an outgrow ...
... d. can be broken into smaller elemental units which can be studied. 4. Which technique used to examine mental processes is most associated with structuralism? a. magnetic resonance imaging b. introspection c. survey administration d. biofeedback 5. This school of psychological thought was an outgrow ...
social influence - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... person to respond in a particular way to objects, other people, and events. ...
... person to respond in a particular way to objects, other people, and events. ...
Social Psychology
... person to respond in a particular way to objects, other people, and events. ...
... person to respond in a particular way to objects, other people, and events. ...
Unit 5: Micro-Inequities - American Bar Association
... Micro-inequities are the ways in which individuals are either singled out, overlooked, ignored or otherwise discounted based on an unchangeable characteristic such as race or gender. – Usually take form in a slight difference of language, gesture, treatment or even tone of voice. – Are often subcons ...
... Micro-inequities are the ways in which individuals are either singled out, overlooked, ignored or otherwise discounted based on an unchangeable characteristic such as race or gender. – Usually take form in a slight difference of language, gesture, treatment or even tone of voice. – Are often subcons ...
Theories of Behavior Change
... that behaviors are often linked with one’s personal motivation.8 This suggests that it may be important to present information to help shape positive attitudes towards the behavior and stress subjective norms or opinions that support the behavior. • For perceived behavioral control to influence beh ...
... that behaviors are often linked with one’s personal motivation.8 This suggests that it may be important to present information to help shape positive attitudes towards the behavior and stress subjective norms or opinions that support the behavior. • For perceived behavioral control to influence beh ...
Sociocultural Psychology
... Feeling the attraction To test this in the context of interpersonal attraction they had male students hold conversations with female students they'd just met through microphones and headsets. One of the quickest ways that people who've just met stereotype each other is by appearance. People automati ...
... Feeling the attraction To test this in the context of interpersonal attraction they had male students hold conversations with female students they'd just met through microphones and headsets. One of the quickest ways that people who've just met stereotype each other is by appearance. People automati ...
The Consumer and Conformity
... Informal rules that explain how most individuals respond in particular situation. ...
... Informal rules that explain how most individuals respond in particular situation. ...
Leading Through Motivation
... on cognitive explanations of behavior, reinforcement theory focuses instead on the impact which external environmental consequences have on behavior. The law of effects states that behavior followed by pleasant consequences is likely to be repeated; behavior followed by unpleasant consequences is n ...
... on cognitive explanations of behavior, reinforcement theory focuses instead on the impact which external environmental consequences have on behavior. The law of effects states that behavior followed by pleasant consequences is likely to be repeated; behavior followed by unpleasant consequences is n ...
The Effects of Laissez-Faire Leadership
... he theme for the 2012 Administrative Issues Journal Academic Conference is “Seizing Opportunities” which suggests the importance of being proactive. People high in proactive personality “identify opportunities and act on them, show initiative, take action, and persevere until meaningful changes occu ...
... he theme for the 2012 Administrative Issues Journal Academic Conference is “Seizing Opportunities” which suggests the importance of being proactive. People high in proactive personality “identify opportunities and act on them, show initiative, take action, and persevere until meaningful changes occu ...
Applying Behavioral Economics to Weight
... pursue an outcome that is liked best when it is gained, from among all available options. ► Revealed preference ► Opportunity set (e.g., a large number of TV channels increase life satisfaction) ...
... pursue an outcome that is liked best when it is gained, from among all available options. ► Revealed preference ► Opportunity set (e.g., a large number of TV channels increase life satisfaction) ...
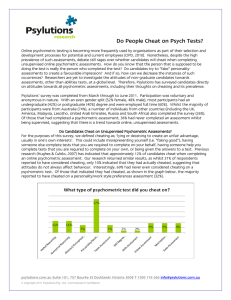
Do People Cheat on Psych Tests?
... there is only a very small percentage that are willing to hand over the responsibility for their assessments to someone else, and organisations should be more concerned about candidates trying to create a favourable impression on personality/work style preferences assessments. ...
... there is only a very small percentage that are willing to hand over the responsibility for their assessments to someone else, and organisations should be more concerned about candidates trying to create a favourable impression on personality/work style preferences assessments. ...
Understanding Psychology 5th Edition Morris and Maisto
... thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of an individual are influenced by the real or imagined behavior of others. Main areas Social cognition Attitudes Social influence Social action ...
... thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of an individual are influenced by the real or imagined behavior of others. Main areas Social cognition Attitudes Social influence Social action ...
Advanced Placement Psychology Mrs. Kerri Hennen Study Guide
... legislation, Wanda opposed it. Her present attitude favoring such legislation can best be explained by: A) attribution theory. B) cognitive dissonance theory. C) social exchange theory. D) evolutionary psychology. E) two-factor theory. 8. According to cognitive dissonance theory, dissonance is most ...
... legislation, Wanda opposed it. Her present attitude favoring such legislation can best be explained by: A) attribution theory. B) cognitive dissonance theory. C) social exchange theory. D) evolutionary psychology. E) two-factor theory. 8. According to cognitive dissonance theory, dissonance is most ...
Chapter 8
... an eating disorder characterized by binges of extreme overeating followed by self induced vomiting, misuse of laxatives or other inappropriate methods to purge the excessive food and prevent weight gain ...
... an eating disorder characterized by binges of extreme overeating followed by self induced vomiting, misuse of laxatives or other inappropriate methods to purge the excessive food and prevent weight gain ...
Operant Conditioning 001
... Consequences that increase the frequency of a behavior, are referred to as ―reinforcers,‖ whereas events that decrease the frequency of behavior are called ―punishments.‖ Most operant behavior is signaled or guided by antecedent stimuli, which ―evoke‖ given responses. In contrast to elicited stimuli ...
... Consequences that increase the frequency of a behavior, are referred to as ―reinforcers,‖ whereas events that decrease the frequency of behavior are called ―punishments.‖ Most operant behavior is signaled or guided by antecedent stimuli, which ―evoke‖ given responses. In contrast to elicited stimuli ...
a PowerPoint Presentation of Module 43
... Attribution: Identifying causes Attribution: a conclusion about the cause of an observed behavior/event. Attribution Theory: We explain others’ behavior with two types of attributions: Situational Attribution (factors outside the person doing the action, such as peer pressure), or Dispositional ...
... Attribution: Identifying causes Attribution: a conclusion about the cause of an observed behavior/event. Attribution Theory: We explain others’ behavior with two types of attributions: Situational Attribution (factors outside the person doing the action, such as peer pressure), or Dispositional ...
Module 43 Powerpoint
... Attribution: Identifying causes Attribution: a conclusion about the cause of an observed behavior/event. Attribution Theory: We explain others’ behavior with two types of attributions: Situational Attribution (factors outside the person doing the action, such as peer pressure), or Dispositional ...
... Attribution: Identifying causes Attribution: a conclusion about the cause of an observed behavior/event. Attribution Theory: We explain others’ behavior with two types of attributions: Situational Attribution (factors outside the person doing the action, such as peer pressure), or Dispositional ...
PSY325: Summer 2007
... they are beautiful We use the attractive quality as the basis around which we make all other attributions In many ways we like to be around them which can lead us to act positively toward them This can lead to a self fulfilling prophecy in that we think they are special, treat them like their specia ...
... they are beautiful We use the attractive quality as the basis around which we make all other attributions In many ways we like to be around them which can lead us to act positively toward them This can lead to a self fulfilling prophecy in that we think they are special, treat them like their specia ...
Operant Conditioning
... Most operant behaviors originate as emitted responses. (e.g., An newborn produces a unique type of cry when hungry & receives milk in response. This strengthens the behavior, making it more likely the infant will produce the unique cry when hungry. ...
... Most operant behaviors originate as emitted responses. (e.g., An newborn produces a unique type of cry when hungry & receives milk in response. This strengthens the behavior, making it more likely the infant will produce the unique cry when hungry. ...
Social Psychology - IB-Psychology
... activated when we make direct eye contact with a physically attractive person (fMRI study) ...
... activated when we make direct eye contact with a physically attractive person (fMRI study) ...
Psych 2 Principles of Psychology Christopher Gade Office: 5315
... Most of us believe that our attitudes influence our behaviors, however, that’s not true all of the time. Cognitive dissonance: A change in behavior alters a change in attitude. In other words, sometimes what we do influences what we think. Festinger’s cog turning task ...
... Most of us believe that our attitudes influence our behaviors, however, that’s not true all of the time. Cognitive dissonance: A change in behavior alters a change in attitude. In other words, sometimes what we do influences what we think. Festinger’s cog turning task ...