Cardiovascular VIVA`s
... What are the long term consequences of essential hypertension Major risk factor for development of atherosclerosis leading to: 1. Coronary artery disease 2. Cerebrovascular disease 3. Aortic dissection 4. Renal failure 5. Cardiac hypertrophy 6. Cardiac failure 7. Multi infarct dementia 8. Retinal ch ...
... What are the long term consequences of essential hypertension Major risk factor for development of atherosclerosis leading to: 1. Coronary artery disease 2. Cerebrovascular disease 3. Aortic dissection 4. Renal failure 5. Cardiac hypertrophy 6. Cardiac failure 7. Multi infarct dementia 8. Retinal ch ...
TETRALOGY OF FALLOT
... The most common of cyanotic congenital defects. The primary cause is the misalignment of the truncoconal septum (separating the aorta from the pulmonary trunk) with the muscular ventricular septum. The truncoconal septum is displaced to the right resulting in pulmonary stenosis and an overriding aor ...
... The most common of cyanotic congenital defects. The primary cause is the misalignment of the truncoconal septum (separating the aorta from the pulmonary trunk) with the muscular ventricular septum. The truncoconal septum is displaced to the right resulting in pulmonary stenosis and an overriding aor ...
Human blood type review
... in an accident. Soon, a man shows up to claim their fortune saying that he is their only son who ran away from home as a boy. Other relatives dispute the claim. Hospital records show that the deceased couple were type AB and O. The claimant to the fortune was type O. Could he be their son? Explain w ...
... in an accident. Soon, a man shows up to claim their fortune saying that he is their only son who ran away from home as a boy. Other relatives dispute the claim. Hospital records show that the deceased couple were type AB and O. The claimant to the fortune was type O. Could he be their son? Explain w ...
Short QT syndrome
... palpitations and dizziness with high tendency to paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) episodes, short QT interval on ECG (QTc ≤ 300 ms) that doesn't significantly change with heart rate, tall, narrow-based ...
... palpitations and dizziness with high tendency to paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AF) episodes, short QT interval on ECG (QTc ≤ 300 ms) that doesn't significantly change with heart rate, tall, narrow-based ...
Congenital Heart Disease
... Life expectancy for a Down Syndrome sufferer with mild/moderate disability = 55 yrs ...
... Life expectancy for a Down Syndrome sufferer with mild/moderate disability = 55 yrs ...
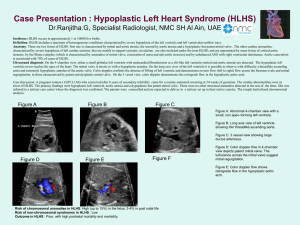
A case of hypoplastic left heart syndrome
... regurgitation, in those characterized by patent and dysplastic mitral valve . On the 3 vessel view, color doppler demonstrates the retrograde flow in the hypoplastic aortic arch. Case discussion: A pregnant women ( G2P1L1A0) who conceived after 8 years of secondary infertility came for a routine ant ...
... regurgitation, in those characterized by patent and dysplastic mitral valve . On the 3 vessel view, color doppler demonstrates the retrograde flow in the hypoplastic aortic arch. Case discussion: A pregnant women ( G2P1L1A0) who conceived after 8 years of secondary infertility came for a routine ant ...
backgrounder
... experienced cardiologists, cardiac surgeons and other medical specialists who collaborate to determine the most appropriate care for each patient. Medications do not cure aortic stenosis; however, medications are sometimes prescribed to help control symptoms, maximize heart function, control blood p ...
... experienced cardiologists, cardiac surgeons and other medical specialists who collaborate to determine the most appropriate care for each patient. Medications do not cure aortic stenosis; however, medications are sometimes prescribed to help control symptoms, maximize heart function, control blood p ...
Swyer syndrome in a woman with pure 46,XY gonadal dysgenesis
... Therefore, females with Swyer syndrome required close follow up because of the high risk of neoplastic transformation in the dysgenetic gonads. In this case, after estrogen therapy patient had her first menstruation cycle but menstruation was disappeared when she stopped pills and the histopathology ...
... Therefore, females with Swyer syndrome required close follow up because of the high risk of neoplastic transformation in the dysgenetic gonads. In this case, after estrogen therapy patient had her first menstruation cycle but menstruation was disappeared when she stopped pills and the histopathology ...
Beals syndrom
... which are highly similar but distinct genes situated in 5q23-31 and 15q15-21.3 chromosome, respectively ...
... which are highly similar but distinct genes situated in 5q23-31 and 15q15-21.3 chromosome, respectively ...
Marfan Syndrome - Birmingham Women`s Hospital
... What is Marfan syndrome? Marfan syndrome is an inherited condition which can affect many parts of the body including the skeleton, lungs, eyes, heart and blood vessels. The condition is caused by a change in the gene which makes fibrillin. Fibrillin is a fine fibre which acts like a scaffolding wit ...
... What is Marfan syndrome? Marfan syndrome is an inherited condition which can affect many parts of the body including the skeleton, lungs, eyes, heart and blood vessels. The condition is caused by a change in the gene which makes fibrillin. Fibrillin is a fine fibre which acts like a scaffolding wit ...
amyloidosis
... right renal artery; saphenous-vein bypass graft had failed, resulting in a poorly functioning right kidney 1976 - developed angina pectoris 1981 - diabetes mellitus was discovered, successfully managed with insulin therapy 1995 - urea nitrogen level 12 mmol/l, creatinine 114.9 umol/l 1997 - coronary ...
... right renal artery; saphenous-vein bypass graft had failed, resulting in a poorly functioning right kidney 1976 - developed angina pectoris 1981 - diabetes mellitus was discovered, successfully managed with insulin therapy 1995 - urea nitrogen level 12 mmol/l, creatinine 114.9 umol/l 1997 - coronary ...
Anesthetic considerations for patients with Down syndrome
... lar defect occur in 30% to 60% of all patients with Down syndrome.11 Patent ductus arteriosus (12%) and tetralogy of Fallot (8%) occur less frequently but are also of significance.10 Although many children with Down syndrome undergo repair of cardiac defects repaired, there is an increased incidenc ...
... lar defect occur in 30% to 60% of all patients with Down syndrome.11 Patent ductus arteriosus (12%) and tetralogy of Fallot (8%) occur less frequently but are also of significance.10 Although many children with Down syndrome undergo repair of cardiac defects repaired, there is an increased incidenc ...
PDF file - Via Medica Journals
... — biphasic or deeply inverted T waves in leads V2 and V3, and occasionally in leads V1, V4, V5, and V6; — no or minimal elevation of cardiac enzymes; — no or minimal ST-segment elevation (< 1 mm); — no loss of precordial R-wave progression; — no pathological precordial Q wave; — a history of angina. ...
... — biphasic or deeply inverted T waves in leads V2 and V3, and occasionally in leads V1, V4, V5, and V6; — no or minimal elevation of cardiac enzymes; — no or minimal ST-segment elevation (< 1 mm); — no loss of precordial R-wave progression; — no pathological precordial Q wave; — a history of angina. ...
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome | SpringerLink
... Chromosomal aberrations account for about 6% of all congenitally malformed hearts. Many genetic and hereditary diseases are associated with such congenital malformations, although the causative mechanism is unknown. Prospective studies using chromosomal analysis have suggested that some malformation ...
... Chromosomal aberrations account for about 6% of all congenitally malformed hearts. Many genetic and hereditary diseases are associated with such congenital malformations, although the causative mechanism is unknown. Prospective studies using chromosomal analysis have suggested that some malformation ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
... Difficulty in determining if a given axial computed tomographic (CT) image is still in the aorta or passing partially through the aorta and the left ventricular outflow track. This factor can lead to gross misinterpretations of aortic diameter. A and B differ by only one CT level, yet they yield mar ...
... Difficulty in determining if a given axial computed tomographic (CT) image is still in the aorta or passing partially through the aorta and the left ventricular outflow track. This factor can lead to gross misinterpretations of aortic diameter. A and B differ by only one CT level, yet they yield mar ...
Cardiometabolic Syndrome (2)
... – Conclusively proved the increased risk of CVD with long-term sustained hypertension – Demonstrated a 10 year risk of cardiovascular disease in treated patients vs non-treated patients to be 0.40. – 40% reduction in stroke with control of HTN Precedes literature on Metabolic Syndrome ...
... – Conclusively proved the increased risk of CVD with long-term sustained hypertension – Demonstrated a 10 year risk of cardiovascular disease in treated patients vs non-treated patients to be 0.40. – 40% reduction in stroke with control of HTN Precedes literature on Metabolic Syndrome ...
Familial Subvalvular Aortic Stenosis in the Rottweiler Outline SAS in
... – Dogs that pass are unlikely to have SAS – Dogs that fail may or may not have SAS – Echocardiography can help differentiate dogs with functional murmurs from those with SAS ...
... – Dogs that pass are unlikely to have SAS – Dogs that fail may or may not have SAS – Echocardiography can help differentiate dogs with functional murmurs from those with SAS ...
WMC_Cardio_1011Final_REV1.indd - New York Center for Aortic
... “This saves a patient from a lifetime of taking anticoagulant medications, which are necessary to prevent blood ...
... “This saves a patient from a lifetime of taking anticoagulant medications, which are necessary to prevent blood ...
Tetralogy of Fallot with Quadricuspid Aortic Valve
... cyanosis with bilateral clubbing (grade III) was evident on fingers and toes. However ‘a’ wave in jugular venous pulse was not prominent. Apex beat was subxiphoid in location and retractile formed by right ventricle. There was a palpable thrill in left third and fourth intercostal space parasternall ...
... cyanosis with bilateral clubbing (grade III) was evident on fingers and toes. However ‘a’ wave in jugular venous pulse was not prominent. Apex beat was subxiphoid in location and retractile formed by right ventricle. There was a palpable thrill in left third and fourth intercostal space parasternall ...
Familial Subvalvular Aortic Stenosis in Rottweilers
... Auscultation Screening • Auscultation screening is a good first step – Dogs that pass are unlikely to have SAS – Dogs that fail may or may not have SAS – Echocardiography can help differentiate dogs with functional murmurs from those with SAS ...
... Auscultation Screening • Auscultation screening is a good first step – Dogs that pass are unlikely to have SAS – Dogs that fail may or may not have SAS – Echocardiography can help differentiate dogs with functional murmurs from those with SAS ...
Marfan Syndrome - Malaysian Rare Disorders Society
... Can I expect him to exhibit exactly the same symptoms that I do? No. Marfan Syndrome is one of several disorders said to show variable expressivity. This means that symptoms and severity vary from patient to patient, even among those from the same family. Your son may be more or less severely affect ...
... Can I expect him to exhibit exactly the same symptoms that I do? No. Marfan Syndrome is one of several disorders said to show variable expressivity. This means that symptoms and severity vary from patient to patient, even among those from the same family. Your son may be more or less severely affect ...
congenital heart diseases
... •CHD occurs in 0.3% of all live births •Most patients are recognized in infancy or childhood and appropriately treated •Most patients with CHD who have been surgically corrected or palliated will reach adulthood or child-bearing age •Embryology of the formation of the heart and cardiovascular system ...
... •CHD occurs in 0.3% of all live births •Most patients are recognized in infancy or childhood and appropriately treated •Most patients with CHD who have been surgically corrected or palliated will reach adulthood or child-bearing age •Embryology of the formation of the heart and cardiovascular system ...
Cardiometabolic Syndrome
... o “…too much clinically important information is missing to warrant its designations as a syndrome.” o Unclear pathogenesis, Insulin resistance is not a consistent finding in some definitions. o CVD risks has not shown to be greater than the sum of it’s individual components. *ADA ...
... o “…too much clinically important information is missing to warrant its designations as a syndrome.” o Unclear pathogenesis, Insulin resistance is not a consistent finding in some definitions. o CVD risks has not shown to be greater than the sum of it’s individual components. *ADA ...
Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS) also known as Ullrich–Turner syndrome, gonadal dysgenesis, and 45,X, is a condition in which a female is partly or completely missing an X chromosome. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected. Often, a short and webbed neck, low-set ears, low hairline at the back of the neck, short stature, and swollen hands and feet are seen at birth. Typically they are without menstrual periods, do not develop breasts, and are unable to have children. Heart defects, diabetes, and low thyroid hormone occur more frequently. Most people with TS have normal intelligence. Many, however, have troubles with spatial visualization such as that needed for mathematics. Vision and hearing problems occur more often.Turner syndrome is not usually inherited from a person's parents. No environmental risks are known and the mother's age does not play a role. Turner syndrome is due to a chromosomal abnormality in which all or part of one of the X chromosomes is missing or altered. While most people have 46 chromosomes, people with TS usually only have 45. The chromosomal abnormality may be present in just some cells in which case it is known as TS with mosaicism. In these cases, the symptoms are usually fewer and possibly none occur at all. Diagnosis is based on physical signs and genetic testing.No cure for Turner syndrome is known. Treatment, however, may help with symptoms. Human growth hormone injections during childhood may increase adult height. Estrogen replacement therapy can promote development of the breasts and hips. Medical care is often required to manage other health problems with which TS is associated.Turner syndrome occurs in between one in 2000 and one in 5000 females at birth. All regions of the world and cultures are affected about equally. People with TS have a shorter life expectancy, mostly due to heart problems and diabetes. Henry Turner first described the condition in 1938. In 1964, it was determined to be due to a chromosomal abnormality.