CVS EXAM
... Pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary stenosis Tricuspid stenosis LARGE v-waves: TRICUSPID REGURG “should never be missed” ...
... Pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary stenosis Tricuspid stenosis LARGE v-waves: TRICUSPID REGURG “should never be missed” ...
Postural Tachycardia Syndrome and Hypermobility Syndrome
... 2. Arthralgia for longer than 3 months in 4 or more joints MINOR CRITERIA: 1. Beighton score of 1,2 or 3/9 (0,1,2 or 3 if aged 50+ 2. Arthralgia (>3 months) in 1-3 joints or back pain (>3 M) spondylosis, spondylosis/spondyloisthesis 3. Dislocation/subluxation in more than one joint 4. Soft tissue rh ...
... 2. Arthralgia for longer than 3 months in 4 or more joints MINOR CRITERIA: 1. Beighton score of 1,2 or 3/9 (0,1,2 or 3 if aged 50+ 2. Arthralgia (>3 months) in 1-3 joints or back pain (>3 M) spondylosis, spondylosis/spondyloisthesis 3. Dislocation/subluxation in more than one joint 4. Soft tissue rh ...
Richner-Hanhart Syndrome: A case report of an 11 month old female
... recessive disorder resulting from the deficiency of the enzyme tyrosine aminotransferase (TAT)1, which is located on chromosome 16q22.1-q22.3. Ocular lesions, painful palmo-plantar hyperkeratosis and occasionally mental retardation are the cardinal features of this disease. High blood levels of tyro ...
... recessive disorder resulting from the deficiency of the enzyme tyrosine aminotransferase (TAT)1, which is located on chromosome 16q22.1-q22.3. Ocular lesions, painful palmo-plantar hyperkeratosis and occasionally mental retardation are the cardinal features of this disease. High blood levels of tyro ...
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome | SpringerLink
... univentricular palliation typically includes three operations. The first stage of palliation, or the Norwood operation, is performed at birth. The second stage is a bidirectional Glenn operation, usually undertaken at 6 to 8 months of age. The third, and final, stage is the Fontan operation, which c ...
... univentricular palliation typically includes three operations. The first stage of palliation, or the Norwood operation, is performed at birth. The second stage is a bidirectional Glenn operation, usually undertaken at 6 to 8 months of age. The third, and final, stage is the Fontan operation, which c ...
differential diagnosis of chest pain
... depending on which segment of aorta is involved Most common in men older than age 60 Hypertension is the most important risk factor Marfan's syndrome, congenital bicuspid and unicommissural aortic valves, aortic coarctation Preexisting aortic aneurysm (due to vasculitic conditions such as giant cell ...
... depending on which segment of aorta is involved Most common in men older than age 60 Hypertension is the most important risk factor Marfan's syndrome, congenital bicuspid and unicommissural aortic valves, aortic coarctation Preexisting aortic aneurysm (due to vasculitic conditions such as giant cell ...
Bavasi, A
... http://www.aao.org/bcscsnippetdetail.aspx?id=daa80517-a4c1-4ef2-842e59dd8e3666ce http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1325/ http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/joubert/joubert.htm http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/462135 http://jcn.sagepub.com/content/14/9/583.short Conclusion: o While th ...
... http://www.aao.org/bcscsnippetdetail.aspx?id=daa80517-a4c1-4ef2-842e59dd8e3666ce http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1325/ http://www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/joubert/joubert.htm http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/462135 http://jcn.sagepub.com/content/14/9/583.short Conclusion: o While th ...
Chest Pain - UNC School of Medicine
... Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is defined by EITHER acute myocardial infarction OR unstable angina. These patients are divided into 3 subsets: ST elevation myocardial infarction non-ST elevation MI Unstable angina ...
... Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) is defined by EITHER acute myocardial infarction OR unstable angina. These patients are divided into 3 subsets: ST elevation myocardial infarction non-ST elevation MI Unstable angina ...
Aortic valve stenosis
... the heart. Their function is to make sure that blood flows in one direction through the heart. The aortic valve sits between the main left heart chamber called the left ventricle (pictured on the right), and the main artery in the chest called the aorta, which distributes the blood to your whole bod ...
... the heart. Their function is to make sure that blood flows in one direction through the heart. The aortic valve sits between the main left heart chamber called the left ventricle (pictured on the right), and the main artery in the chest called the aorta, which distributes the blood to your whole bod ...
patient information leaflet about aortic valve stenosis
... the heart. Their function is to make sure that blood flows in one direction through the heart. The aortic valve sits between the main left heart chamber called the left ventricle (pictured on the right), and the main artery in the chest called the aorta, which distributes the blood to your whole bod ...
... the heart. Their function is to make sure that blood flows in one direction through the heart. The aortic valve sits between the main left heart chamber called the left ventricle (pictured on the right), and the main artery in the chest called the aorta, which distributes the blood to your whole bod ...
A common clinical problem
... • Shortness of breath with exertion • Syncope (usually with exertion) • Echocardiographic evidence of severe aortic stenosis • Peak aortic velocity > 4 m/s (> 64 mm Hg) ...
... • Shortness of breath with exertion • Syncope (usually with exertion) • Echocardiographic evidence of severe aortic stenosis • Peak aortic velocity > 4 m/s (> 64 mm Hg) ...
Iridocorneal endothelial syndrome: iris naevus (Cogan
... The purpose is to present a case of iridocorneal endothelium Syndrome with glaucoma and discuss clinical presentation and management strategies. A 45 year old female presented with redness, pain and diminision of vision in left eye. The patient was completely evaluated for the complaints. Slit lamp ...
... The purpose is to present a case of iridocorneal endothelium Syndrome with glaucoma and discuss clinical presentation and management strategies. A 45 year old female presented with redness, pain and diminision of vision in left eye. The patient was completely evaluated for the complaints. Slit lamp ...
backgrounder
... experienced cardiologists, cardiac surgeons and other medical specialists who collaborate to determine the most appropriate care for each patient. Medications do not cure aortic stenosis; however, medications are sometimes prescribed to help control symptoms, maximize heart function, control blood p ...
... experienced cardiologists, cardiac surgeons and other medical specialists who collaborate to determine the most appropriate care for each patient. Medications do not cure aortic stenosis; however, medications are sometimes prescribed to help control symptoms, maximize heart function, control blood p ...
26 Somatic-neurological syndromes
... then lateral funiculus of spinal cord. It is clinically reveals as mielopathy (funicular myelosis). The disease develops gradually and it is characterized by pain, paresthesias in lower extremities, bathyesthesia, sensitive ataxia, lowering of deep knee-jerk reaction and Achilles reflex. Brain membr ...
... then lateral funiculus of spinal cord. It is clinically reveals as mielopathy (funicular myelosis). The disease develops gradually and it is characterized by pain, paresthesias in lower extremities, bathyesthesia, sensitive ataxia, lowering of deep knee-jerk reaction and Achilles reflex. Brain membr ...
PDF - Molecular Vision
... particularly helpful clinical feature that is highly specific to this syndrome. Ocular features are more diverse and include microphthalmia, lacrimal duct obstruction, and coloboma [2]. Since the original description, 81 cases have been reported, and while the phenotype was believed by many to be qu ...
... particularly helpful clinical feature that is highly specific to this syndrome. Ocular features are more diverse and include microphthalmia, lacrimal duct obstruction, and coloboma [2]. Since the original description, 81 cases have been reported, and while the phenotype was believed by many to be qu ...
Clinical and cytogenetic profile of Down syndrome at King Hussein
... with Down syndrome especially hypothyroidism which usually has subtle presentation and can be particularly challenging to detect in these patients because of the symptoms of hypothyroidism may overlap with features of Down syndrome.(14,15) Infants with Down syndrome, especially boys, showed elevated ...
... with Down syndrome especially hypothyroidism which usually has subtle presentation and can be particularly challenging to detect in these patients because of the symptoms of hypothyroidism may overlap with features of Down syndrome.(14,15) Infants with Down syndrome, especially boys, showed elevated ...
A Turkish Adulthood Joubert Syndrome and Review of the Literature
... an abnormal breathing pattern (1,2). Additional deformities such as extra fingers and toes, cleft lip or palate, tongue abnormalities, and seizures may also occur. Many patients die in infancy or childhood, but some survive into adulthood with variable cognitive and motor impairments, depending on w ...
... an abnormal breathing pattern (1,2). Additional deformities such as extra fingers and toes, cleft lip or palate, tongue abnormalities, and seizures may also occur. Many patients die in infancy or childhood, but some survive into adulthood with variable cognitive and motor impairments, depending on w ...
Short QT syndrome
... 6) Cerrone M, Noujaim S, Jalife J. The short QT syndrome as a paradigm to understand the role of potassium channels in ventricular fibrillation. J Intern ...
... 6) Cerrone M, Noujaim S, Jalife J. The short QT syndrome as a paradigm to understand the role of potassium channels in ventricular fibrillation. J Intern ...
Sympathetic denervation in the treatment of fatal arrhythmias in long
... with long QT syndrome have been reported in the literature, the concomitance of restrictive cardiomyopathy with long QT syndrome has not been reported, yet.[5,6] The coexistence of long QT syndrome with restrictive cardiomyopathy is an extremely rare. Restrictive cardiomyopathy and pulmonary hyperte ...
... with long QT syndrome have been reported in the literature, the concomitance of restrictive cardiomyopathy with long QT syndrome has not been reported, yet.[5,6] The coexistence of long QT syndrome with restrictive cardiomyopathy is an extremely rare. Restrictive cardiomyopathy and pulmonary hyperte ...
Korsakoff Syndrome Topic Sheet
... to identify because it may be masked by symptoms of other conditions common among those who misuse alcohol, including intoxication or withdrawal, infection or head injury. Experts recommend that a medical workup for memory loss or other cognitive changes always include questions about an individual’ ...
... to identify because it may be masked by symptoms of other conditions common among those who misuse alcohol, including intoxication or withdrawal, infection or head injury. Experts recommend that a medical workup for memory loss or other cognitive changes always include questions about an individual’ ...
Sick Sinus Syndrome and Atrial Standstill
... occur, ECGs are done more frequently. Other monitoring is based on the underlying disease. Following implantation of a pacemaker, recheck visits are usually scheduled at 1 and 3 months. After the pacemaker has received its final adjustments, you will be asked to monitor the heart rate weekly and to ...
... occur, ECGs are done more frequently. Other monitoring is based on the underlying disease. Following implantation of a pacemaker, recheck visits are usually scheduled at 1 and 3 months. After the pacemaker has received its final adjustments, you will be asked to monitor the heart rate weekly and to ...
Mitral valve replacement
... - fibrosis & deformity of valve leaflets. - shortening of chordae tendinae . 2. Dilatation of the LV & mitral valve ring (functional) 3. Dysfunction of papillary muscles: due to ischemia , infarction. 4. Less common causes as: - congenital abnormalities. - endocarditis. - HOCM ...
... - fibrosis & deformity of valve leaflets. - shortening of chordae tendinae . 2. Dilatation of the LV & mitral valve ring (functional) 3. Dysfunction of papillary muscles: due to ischemia , infarction. 4. Less common causes as: - congenital abnormalities. - endocarditis. - HOCM ...
Aortic Valve
... performed routinely as determined by age, symptoms, and coronary risk factors. Cardiac catheterization and angiography may also be helpful when there is discordance between clinical findings and echocardiography. “Stable” refers to stable echocardigraphic measurements. In some centers, serial follow ...
... performed routinely as determined by age, symptoms, and coronary risk factors. Cardiac catheterization and angiography may also be helpful when there is discordance between clinical findings and echocardiography. “Stable” refers to stable echocardigraphic measurements. In some centers, serial follow ...
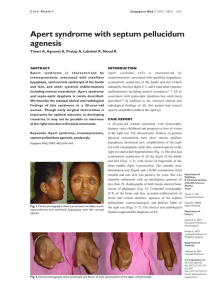
Apert syndrome with septum pellucidum agenesis
... Fig. 4 Radiograph of both hands shows bony fusion of the phalanges of adjacent digits. ...
... Fig. 4 Radiograph of both hands shows bony fusion of the phalanges of adjacent digits. ...
Post-Cardiac Injury Syndrome after Permanent Pacemaker
... days after pacemaker implantation (mean 21.5 days), and all patients had pericardial effusion identified via echocardiography and CT scan of the chest. The outcomes of these cases were good and most of them (n = 7, 63.6%) could be treated conservatively without surgical intervention. Recently, Hsu e ...
... days after pacemaker implantation (mean 21.5 days), and all patients had pericardial effusion identified via echocardiography and CT scan of the chest. The outcomes of these cases were good and most of them (n = 7, 63.6%) could be treated conservatively without surgical intervention. Recently, Hsu e ...
Marfan syndrome

Marfan syndrome (also called Marfan's syndrome) is a genetic disorder of connective tissue. It has a variable clinical presentation, ranging from mild to severe systemic disease. The most serious manifestations involve defects of the heart valves and aorta, which may lead to early death if not properly managed. The syndrome also may affect the lungs, eyes, dural sac surrounding the spinal cord, the skeleton, and the hard palate. People with Marfan syndrome tend to be unusually tall, with long limbs and long, thin fingers and toes.The syndrome is caused by the misfolding of fibrillin-1, a glycoprotein which forms elastic fibers in connective tissue and contributes to cell signaling activity by binding to and sequestering transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β). The mutated fibrillin binds poorly to TGF-β, which results in an accumulation of excess TGF-β in the lungs, heart valves, and aorta. This in turn causes abnormal structure and function of vascular smooth muscle and reduced integrity of the extracellular matrix, which weaken the tissues and cause the features of Marfan syndrome.Named after Antoine Marfan, the French pediatrician who first described the condition in 1896, the disease is an autosomal dominant disorder. Management often includes the use of angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs) and beta blockers.