Director`s Foreword The Many Meanings of the Cyrus Cylinder
... the Iranian throne, he addressed Cyrus as his great precursor. He asked the British Museum to lend the Cyrus Cylinder to Tehran as part of the festivities, and its presence in Iran was commemorated by the striking of a gold medal showing the Shah on one side, and the Cyrus ...
... the Iranian throne, he addressed Cyrus as his great precursor. He asked the British Museum to lend the Cyrus Cylinder to Tehran as part of the festivities, and its presence in Iran was commemorated by the striking of a gold medal showing the Shah on one side, and the Cyrus ...
sswhhl08na_bio101020..
... historical documents indicate that an Akkadian ruler named Sargon took over Sumerian territory. The city of Akkad was located north of Sumer along the Euphrates River. As ruler of Akkad, Sargon formed the world’s first permanent army. It is thought that at this time, Sargon named himself Sharrum-kin ...
... historical documents indicate that an Akkadian ruler named Sargon took over Sumerian territory. The city of Akkad was located north of Sumer along the Euphrates River. As ruler of Akkad, Sargon formed the world’s first permanent army. It is thought that at this time, Sargon named himself Sharrum-kin ...
Mesopotamia
... headwaters in the Armenian Highlands. Both rivers are fed by. Get information, facts, and pictures about Mesopotamia at Encyclopedia.com. Make research projects and school reports about Mesopotamia easy with credible articles. Ancient Mesopotamia saw the rise of the first civilization in world histo ...
... headwaters in the Armenian Highlands. Both rivers are fed by. Get information, facts, and pictures about Mesopotamia at Encyclopedia.com. Make research projects and school reports about Mesopotamia easy with credible articles. Ancient Mesopotamia saw the rise of the first civilization in world histo ...
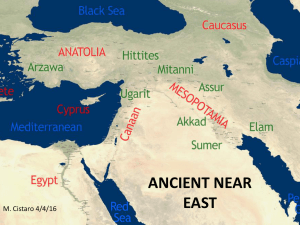
ancient near east - Mr. C at Hamilton
... of imperial powers following one another in succession: first the Assyrians, then the Babylonians and Medes, and now the Persian empire, the largest state in the history of the Ancient World. This now covers the entire region and beyond. The Lydians, Phrygians and Ionian Greeks of Asia Minor, the Ph ...
... of imperial powers following one another in succession: first the Assyrians, then the Babylonians and Medes, and now the Persian empire, the largest state in the history of the Ancient World. This now covers the entire region and beyond. The Lydians, Phrygians and Ionian Greeks of Asia Minor, the Ph ...
Catal Huyuk Catal Huyuk was a Neolithic village in
... multiple groups such as the Hittites, Kassites, and Assyrians. After the Assyrian empire fell, the Neo-Babylonian Empire was formed by a Chaldean named Nabopolassar who took the throne. His son, Nebuchadnezzar II renovated and expanded the city, often bragging about the beautiful architecture of Mes ...
... multiple groups such as the Hittites, Kassites, and Assyrians. After the Assyrian empire fell, the Neo-Babylonian Empire was formed by a Chaldean named Nabopolassar who took the throne. His son, Nebuchadnezzar II renovated and expanded the city, often bragging about the beautiful architecture of Mes ...
the word “Mesopotamia?”
... 5. What is the name of the geographic region in which Mesopotamia was located? ...
... 5. What is the name of the geographic region in which Mesopotamia was located? ...
mesopotamia webquest
... 5. What is the name of the geographic region in which Mesopotamia was located? ...
... 5. What is the name of the geographic region in which Mesopotamia was located? ...
Primary Gods and Goddesses
... Music-Cuneiform sources reveal an orderly organized system of diatonic scales, depending on the tuning of stringed instruments in alternating fifths and fourths. Instruments of Ancient Mesopotamia include harps, lyres, lutes, reed pipes and drums. The vocal tone or timbre was probably similar to the ...
... Music-Cuneiform sources reveal an orderly organized system of diatonic scales, depending on the tuning of stringed instruments in alternating fifths and fourths. Instruments of Ancient Mesopotamia include harps, lyres, lutes, reed pipes and drums. The vocal tone or timbre was probably similar to the ...
3_Mesopotamia
... 15. The thing about Territorial kingdoms is that they relied on the poorest people to pay taxes, and provide ____________ and serve in the ____________, all of which made you not like your king very much so if you saw any nomadic invaders coming by you might just be like "Hey nomadic invaders! Come ...
... 15. The thing about Territorial kingdoms is that they relied on the poorest people to pay taxes, and provide ____________ and serve in the ____________, all of which made you not like your king very much so if you saw any nomadic invaders coming by you might just be like "Hey nomadic invaders! Come ...
File
... 15. The thing about Territorial kingdoms is that they relied on the poorest people to pay taxes, and provide ____________ and serve in the ____________, all of which made you not like your king very much so if you saw any nomadic invaders coming by you might just be like "Hey nomadic invaders! Come ...
... 15. The thing about Territorial kingdoms is that they relied on the poorest people to pay taxes, and provide ____________ and serve in the ____________, all of which made you not like your king very much so if you saw any nomadic invaders coming by you might just be like "Hey nomadic invaders! Come ...
#3—Crash Course World History Mesopotamia 1. So 5,000 years
... 15. The thing about Territorial kingdoms is that they relied on the poorest people to pay taxes, and provide ____________ and serve in the ____________, all of which made you not like your king very much so if you saw any nomadic invaders coming by you might just be like "Hey nomadic invaders! Come ...
... 15. The thing about Territorial kingdoms is that they relied on the poorest people to pay taxes, and provide ____________ and serve in the ____________, all of which made you not like your king very much so if you saw any nomadic invaders coming by you might just be like "Hey nomadic invaders! Come ...
Ancient Mesopotamia and Hammurabi`s Code
... 15. The thing about Territorial kingdoms is that they relied on the poorest people to pay taxes, and provide ____________ and serve in the ____________, all of which made you not like your king very much so if you saw any nomadic invaders coming by you might just be like "Hey nomadic invaders! Come ...
... 15. The thing about Territorial kingdoms is that they relied on the poorest people to pay taxes, and provide ____________ and serve in the ____________, all of which made you not like your king very much so if you saw any nomadic invaders coming by you might just be like "Hey nomadic invaders! Come ...
AP World History Summer Assignment 2015
... It is with great pleasure I welcome you to AP World History. I am excited that you have chosen to take this challenging but rewarding course. AP World History is a college-‐level course, whi ...
... It is with great pleasure I welcome you to AP World History. I am excited that you have chosen to take this challenging but rewarding course. AP World History is a college-‐level course, whi ...
Teacher Answer Sheet
... 1. Why is Mesopotamia often called the “Cradle of Civilization”? Mesopotamia is where some of the first large cities formed thousands of years ago 2. What does the word Mesopotamia mean? "the land between rivers" 3. What two rivers flow through or near the area of Mesopotamia? Tigris and Euphrates R ...
... 1. Why is Mesopotamia often called the “Cradle of Civilization”? Mesopotamia is where some of the first large cities formed thousands of years ago 2. What does the word Mesopotamia mean? "the land between rivers" 3. What two rivers flow through or near the area of Mesopotamia? Tigris and Euphrates R ...
Fertile Crescent • Mesopotamia • Polytheism • Cuneiform
... Be able to create a timeline Be able to explain the development of writing from Pictograph to Cuneiform Why was Hammurabi’s Code so important for Babylon, Mesopotamia, and the rest of the world? ...
... Be able to create a timeline Be able to explain the development of writing from Pictograph to Cuneiform Why was Hammurabi’s Code so important for Babylon, Mesopotamia, and the rest of the world? ...
Ancient Mesopotamia (FOH 10)
... 6. Make a list of the various groups of people living in ancient Mesopotamia (during different historical periods), as mentioned in our sources. - Try to list them in order of their appearance in the history of this region. - Can you relate any of these groups to places on your map of Mesopotamia? ...
... 6. Make a list of the various groups of people living in ancient Mesopotamia (during different historical periods), as mentioned in our sources. - Try to list them in order of their appearance in the history of this region. - Can you relate any of these groups to places on your map of Mesopotamia? ...
huma 1301 Pre test 1
... 12. The earliest discovered inscribed clay tablets come from a. Sumer. b. Africa. c. Egypt. d. Babylon. 13. The first literary epic developed in a. India. b. Egypt. c. Mesopotamia. d. China. 14. The Great Temple at Karnak was a. dedicated to the sun-god Amon-Ra. b. a landmark of Egypt’s Old Kingdom. ...
... 12. The earliest discovered inscribed clay tablets come from a. Sumer. b. Africa. c. Egypt. d. Babylon. 13. The first literary epic developed in a. India. b. Egypt. c. Mesopotamia. d. China. 14. The Great Temple at Karnak was a. dedicated to the sun-god Amon-Ra. b. a landmark of Egypt’s Old Kingdom. ...
WORD
... time. 1. The THREE ancient civilizations of Mesopotamia are: _____________________________, _________________________________ and ____________________________________. 2. Over the course of 6000 years, the rich land of the ______________________ Crescent, cradled between the _______________________ ...
... time. 1. The THREE ancient civilizations of Mesopotamia are: _____________________________, _________________________________ and ____________________________________. 2. Over the course of 6000 years, the rich land of the ______________________ Crescent, cradled between the _______________________ ...
The Assyrians and The Persians
... to the Indus. Civilization within this area would more and more be a matter of interplay, borrowing and cosmopolitanism. The framework for this was provided by the great political change of the middle of the first millennium BC, the rise of a new power, Persia, and the final collapse of the Egyptia ...
... to the Indus. Civilization within this area would more and more be a matter of interplay, borrowing and cosmopolitanism. The framework for this was provided by the great political change of the middle of the first millennium BC, the rise of a new power, Persia, and the final collapse of the Egyptia ...
Babylon

Babylon (Akkadian: Bābili or Babilim; Arabic: بابل, Bābil) was a significant city in ancient Mesopotamia, in the fertile plain between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. The city was built upon the Euphrates and divided in equal parts along its left and right banks, with steep embankments to contain the river's seasonal floods.Babylon was originally a small Semitic Akkadian city dating from the period of the Akkadian Empire c. 2300 BC. The town attained independence as part of a small city state with the rise of the First Amorite Babylonian Dynasty in 1894 BC. Claiming to be the successor of the more ancient Sumero-Akkadian city of Eridu, Babylon eclipsed Nippur as the ""holy city"" of Mesopotamia around the time Amorite king Hammurabi created the first short lived Babylonian Empire in the 18th century BC. Babylon grew and South Mesopotamia came to be known as Babylonia.The empire quickly dissolved after Hammurabi's death and Babylon spent long periods under Assyrian, Kassite and Elamite domination. After being destroyed and then rebuilt by the Assyrians, Babylon became the capital of the Neo-Babylonian Empire from 609 to 539 BC. The Hanging Gardens of Babylon was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. After the fall of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, the city came under the rules of the Achaemenid, Seleucid, Parthian, Roman and Sassanid empires.It has been estimated that Babylon was the largest city in the world from c. 1770 to 1670 BC, and again between c. 612 and 320 BC. It was perhaps the first city to reach a population above 200,000. Estimates for the maximum extent of its area range from 890 to 900 hectares (2,200 acres).The remains of the city are in present-day Hillah, Babil Governorate, Iraq, about 85 kilometers (53 mi) south of Baghdad, comprising a large tell of broken mud-brick buildings and debris.