4. Structure of the Atom
... The planetary atom will emit light of a particular frequency. An electron in an orbit will emit a light wave at the orbital frequency. ...
... The planetary atom will emit light of a particular frequency. An electron in an orbit will emit a light wave at the orbital frequency. ...
2. Many-electron systems
... What is the problem? We also have to consider Pauli principle, which says that two electrons can not be in the same state. If we consider this, too, the following states will be allowed: ...
... What is the problem? We also have to consider Pauli principle, which says that two electrons can not be in the same state. If we consider this, too, the following states will be allowed: ...
Bohr Model of the Atom
... Neils Bohr thought that Rutherford’s model had merit, but needed to include some of the newly developing quantum theory to make it work (Bohr studied in Rutherford’s lab in 1912) Planck and Einstein had shown that the energy of oscillating charges must change in discrete amounts. Einstein argued tha ...
... Neils Bohr thought that Rutherford’s model had merit, but needed to include some of the newly developing quantum theory to make it work (Bohr studied in Rutherford’s lab in 1912) Planck and Einstein had shown that the energy of oscillating charges must change in discrete amounts. Einstein argued tha ...
density of quantum states in periodical structures
... New quantum effects have been studied in thin nanograting layers. Nanograting on the surface imposes additional boundary conditions on the electron wave function and reduces the density of states. When the dimensions of the nanograting are close to the De Broglie wavelength the density of states red ...
... New quantum effects have been studied in thin nanograting layers. Nanograting on the surface imposes additional boundary conditions on the electron wave function and reduces the density of states. When the dimensions of the nanograting are close to the De Broglie wavelength the density of states red ...
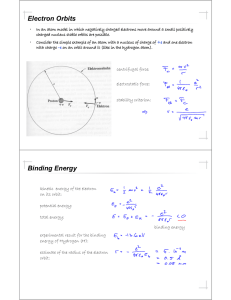
Electron Orbits
... with the state of knowledge we had at that time, understand spectral line emission, so that if somebody published a paper about it, one assumed, "Probably it is not right." So we did not know it. But we made that experiment (and got the result that confirmed Bohr's theory) because we hoped that if w ...
... with the state of knowledge we had at that time, understand spectral line emission, so that if somebody published a paper about it, one assumed, "Probably it is not right." So we did not know it. But we made that experiment (and got the result that confirmed Bohr's theory) because we hoped that if w ...
Mid Term Examination 2 Text
... mixture of normal Hydrogen with a small fraction of Deuterium. How the line series of the emitted light will look like if the Deuterium contribution can be detected? Depict the situation for one (any) of the spectroscopic lines. Be specific! 4. Molecular Orbital Theory: In a diatomic molecule AB , a ...
... mixture of normal Hydrogen with a small fraction of Deuterium. How the line series of the emitted light will look like if the Deuterium contribution can be detected? Depict the situation for one (any) of the spectroscopic lines. Be specific! 4. Molecular Orbital Theory: In a diatomic molecule AB , a ...
Electromagnetic Mediums PowerPoint
... Reflection occurs when a wave strikes an object or surface and bounces off. Light waves reflecting off an object allow you to see that object. Light reflected from any surface always follows a simple rule: the angle with which the ray of light hits the surface is the same with which the ray of l ...
... Reflection occurs when a wave strikes an object or surface and bounces off. Light waves reflecting off an object allow you to see that object. Light reflected from any surface always follows a simple rule: the angle with which the ray of light hits the surface is the same with which the ray of l ...
Electromagnetic Waves: Mediums
... Reflection occurs when a wave strikes an object or surface and bounces off. Light waves reflecting off an object allow you to see that object. Light reflected from any surface always follows a simple rule: the angle with which the ray of light hits the surface is the same with which the ray of l ...
... Reflection occurs when a wave strikes an object or surface and bounces off. Light waves reflecting off an object allow you to see that object. Light reflected from any surface always follows a simple rule: the angle with which the ray of light hits the surface is the same with which the ray of l ...
Final Questions
... 82. What happens when a rubber rod is rubbed with a piece of fur, giving it a negative charge? 83. A repelling force occurs between two charged objects when 84. An attracting force occurs between two charged objects when 85. What is an electric insulator? 86. What is induction? (Draw a picture) 87. ...
... 82. What happens when a rubber rod is rubbed with a piece of fur, giving it a negative charge? 83. A repelling force occurs between two charged objects when 84. An attracting force occurs between two charged objects when 85. What is an electric insulator? 86. What is induction? (Draw a picture) 87. ...
History of Atomic Theory PowerPoint
... Most α-particles passed through, but some were deflected ...
... Most α-particles passed through, but some were deflected ...
quantum number
... What this means is that it is not possible to assign a definite position for a particle in a system. All that can be given is the probability of finding the particle at a particular location. This is why, for example, we describe the electrons in an atom as a “cloud” of charge surrounding the ...
... What this means is that it is not possible to assign a definite position for a particle in a system. All that can be given is the probability of finding the particle at a particular location. This is why, for example, we describe the electrons in an atom as a “cloud” of charge surrounding the ...
n 1
... Calculate the value of Ar for naturally occurring copper if the distribution of isotopes is 69.2% 63Cu and 30.8% 65Cu; accurate masses are 62.93 and ...
... Calculate the value of Ar for naturally occurring copper if the distribution of isotopes is 69.2% 63Cu and 30.8% 65Cu; accurate masses are 62.93 and ...
4 slides per page() - Wayne State University Physics and
... Atomic Transitions – Energy Levels An atom may have many possible energy levels At ordinary temperatures, most of the atoms in a sample are in the ground state Only photons with energies corresponding to differences between energy levels can be absorbed ...
... Atomic Transitions – Energy Levels An atom may have many possible energy levels At ordinary temperatures, most of the atoms in a sample are in the ground state Only photons with energies corresponding to differences between energy levels can be absorbed ...
Sections 6.3-6.5
... • Electrons move in certain, specific, circular orbitals • Smaller orbit = lower energy level • Assigned the allowable electron orbitals the principle quantum number, n. • 1st orbit= lowest energy: n=1 • 2nd orbit= 2nd lowest energy: n=2 ...
... • Electrons move in certain, specific, circular orbitals • Smaller orbit = lower energy level • Assigned the allowable electron orbitals the principle quantum number, n. • 1st orbit= lowest energy: n=1 • 2nd orbit= 2nd lowest energy: n=2 ...
Chapter 24 Electromagnetic Waves
... Now suppose that the AC source on the far left is off. We now turn it on. The electric and magnetic field lines in the space between the copper links do not appear at the same instant we turn on the AC source. First the leftmost oscillating magnetic field appears, then the leftmost oscillating elect ...
... Now suppose that the AC source on the far left is off. We now turn it on. The electric and magnetic field lines in the space between the copper links do not appear at the same instant we turn on the AC source. First the leftmost oscillating magnetic field appears, then the leftmost oscillating elect ...
The Atom and Its Properties
... Albert Einstein (18791955) proposed that while a beam of light had wavelike characteristics, it also can be thought of as a stream of tiny particles (or bundles of energy) called photons • Each photon carries a quantum of energy ...
... Albert Einstein (18791955) proposed that while a beam of light had wavelike characteristics, it also can be thought of as a stream of tiny particles (or bundles of energy) called photons • Each photon carries a quantum of energy ...
May 2003
... Now consider the case of a ‘chirped’ frequency such that φ̇(t) = −αt for −T < t < T . Hrot (t) now varies with time, but if its matrix elements vary slowly (i.e. if α is small), and there is no level crossing, the adiabatic theorem should apply. This means that the system remains in the ‘same’ eigen ...
... Now consider the case of a ‘chirped’ frequency such that φ̇(t) = −αt for −T < t < T . Hrot (t) now varies with time, but if its matrix elements vary slowly (i.e. if α is small), and there is no level crossing, the adiabatic theorem should apply. This means that the system remains in the ‘same’ eigen ...