Applications of Coherence by Identity
... We have shown that information can be extracted about an object without detecting the photons that interacted with it. ...
... We have shown that information can be extracted about an object without detecting the photons that interacted with it. ...
Chapter 2 – Atoms and Elements - U of L Class Index
... The Bohr model of the atom pictures an electron as a particle circling the nucleus of an atom in a fixed orbital similar to the way that planets circle the sun (except that planets cannot ‘jump’ from one orbital to another – which is probably a good thing!). The main flaw in the Bohr model of the a ...
... The Bohr model of the atom pictures an electron as a particle circling the nucleus of an atom in a fixed orbital similar to the way that planets circle the sun (except that planets cannot ‘jump’ from one orbital to another – which is probably a good thing!). The main flaw in the Bohr model of the a ...
PPT
... ACT/Preflight 24.3 Electron A falls from energy level n=2 to energy level n=1 (ground state), causing a photon to be emitted. Electron B falls from energy level n=3 to energy level n=1 (ground state), causing a photon to be emitted. ...
... ACT/Preflight 24.3 Electron A falls from energy level n=2 to energy level n=1 (ground state), causing a photon to be emitted. Electron B falls from energy level n=3 to energy level n=1 (ground state), causing a photon to be emitted. ...
Comment on" On the realisation of quantum Fisher information"
... Here, M(a, b, x) and U(a, b, x) are Kummer, or confluent hypergeometric, functions (we follow the notation adopted in Ref. [8]), and c1 and c2 are normalization constants. Physically, this mathematical solution vanishes at the origin and, since the second item in the square brackets of the right-han ...
... Here, M(a, b, x) and U(a, b, x) are Kummer, or confluent hypergeometric, functions (we follow the notation adopted in Ref. [8]), and c1 and c2 are normalization constants. Physically, this mathematical solution vanishes at the origin and, since the second item in the square brackets of the right-han ...
Large Quantum Superpositions and Interference of Massive
... continuous spontaneous localization model (CSL). This theory is derived by adding a nonlinear stochastic term to the Schrödinger equation. The model recovers all the phenomenology of quantum mechanics for elementary particles but predicts a fast localization (collapse) of the wave function for larg ...
... continuous spontaneous localization model (CSL). This theory is derived by adding a nonlinear stochastic term to the Schrödinger equation. The model recovers all the phenomenology of quantum mechanics for elementary particles but predicts a fast localization (collapse) of the wave function for larg ...
Ch-27
... (II) A certain type of film is sensitive only to light whose wavelength is less than 630 nm. What is the energy (eV and kcal/mol) needed for the chemical reaction to occur which causes the film to change? ...
... (II) A certain type of film is sensitive only to light whose wavelength is less than 630 nm. What is the energy (eV and kcal/mol) needed for the chemical reaction to occur which causes the film to change? ...
Chapter 2 - Las Positas College
... Q29.23. Reason: The electron gives up some of its energy to the atom. At atom in its ground state cannot emit a photon, so the atom is first boosted to an excited state (one of the orbital electrons jumps to a higher state) and then it can emit a photon as it drops to a lower state. If the excited e ...
... Q29.23. Reason: The electron gives up some of its energy to the atom. At atom in its ground state cannot emit a photon, so the atom is first boosted to an excited state (one of the orbital electrons jumps to a higher state) and then it can emit a photon as it drops to a lower state. If the excited e ...
Learning station III: What oscillates with light?
... hair to a (nylon) comb without making contact. Here we’re dealing with an electric force. This is also a force that works from a distance through a field . Your hair doesn’t need to make contact with the comb. Between the hairs, there is an electric repulsive force that also works without making con ...
... hair to a (nylon) comb without making contact. Here we’re dealing with an electric force. This is also a force that works from a distance through a field . Your hair doesn’t need to make contact with the comb. Between the hairs, there is an electric repulsive force that also works without making con ...
Name - Quia
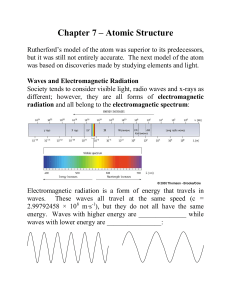
... Explain the mathematical relationship among the speed, wavelength & frequency of electromagnetic radiation Discuss the dual wave-particle nature of light Discuss the significance of the photoelectric effect & line-emission spectrum Describe the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom Discuss the developmen ...
... Explain the mathematical relationship among the speed, wavelength & frequency of electromagnetic radiation Discuss the dual wave-particle nature of light Discuss the significance of the photoelectric effect & line-emission spectrum Describe the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom Discuss the developmen ...
September 6th, 2007
... When the basis consist on one atom, there are three independent vibration modes, 1 longitudinal (the atoms in the plane oscillate in a direction perpendicular to the plane) and 2 transversal where the atoms oscillates parallel to the plane (the two modes come from the two dimensions of the plane). W ...
... When the basis consist on one atom, there are three independent vibration modes, 1 longitudinal (the atoms in the plane oscillate in a direction perpendicular to the plane) and 2 transversal where the atoms oscillates parallel to the plane (the two modes come from the two dimensions of the plane). W ...
7.4 The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
... – Assumes the quantization without explanation – Does not take into account Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle – Limited success only for the H atom ...
... – Assumes the quantization without explanation – Does not take into account Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle – Limited success only for the H atom ...
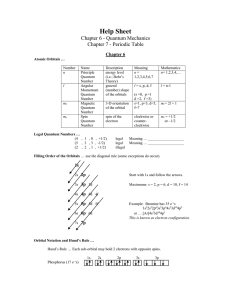
Help Sheet
... General rule: Any element with an odd-electron number must be paramagnetic. Shielding … describes why some orbitals are at higher or lower energy levels than others. Example: A 2s electron spends more of its time (on average) around the nucleus than a 2p electron due to the size of the orbitals. The ...
... General rule: Any element with an odd-electron number must be paramagnetic. Shielding … describes why some orbitals are at higher or lower energy levels than others. Example: A 2s electron spends more of its time (on average) around the nucleus than a 2p electron due to the size of the orbitals. The ...
Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Georgia —
... PROBLEM 4 (six parts) In an atom optical interferometer shown below, a highly collimated beam of atoms interacts with three regions of standing-wave laser fields (the intensity of the standing wave modulates the atomic wavefunctions), are created by lasers of wavelength 590 nm. (a) If the atoms are ...
... PROBLEM 4 (six parts) In an atom optical interferometer shown below, a highly collimated beam of atoms interacts with three regions of standing-wave laser fields (the intensity of the standing wave modulates the atomic wavefunctions), are created by lasers of wavelength 590 nm. (a) If the atoms are ...
Lecture - ChemWeb (UCC)
... Quantum Mechanical Molecular Energy of the Nuclei. The motion of nuclei in molecules does not obey classical mechanics. The energies of translational, rotational and vibrations motion of nuclei obey Quantum Mechanics. In all three cases quantum mechanics finds the energy to be quantized. Only certa ...
... Quantum Mechanical Molecular Energy of the Nuclei. The motion of nuclei in molecules does not obey classical mechanics. The energies of translational, rotational and vibrations motion of nuclei obey Quantum Mechanics. In all three cases quantum mechanics finds the energy to be quantized. Only certa ...
The Schrodinger Equation
... Some Handy Equations Before We Move On • KNOW THESE! • E = hn one quantum of energy • *This is the most important equation for the course. ...
... Some Handy Equations Before We Move On • KNOW THESE! • E = hn one quantum of energy • *This is the most important equation for the course. ...
Sections 4 - Columbia Physics
... 4. A hypothetical particle has negative squared mass such that we can write m = iµ where µ is a real quantity with units of mass. In all other respects, the particle satisfies the rules of special relativity, though sometimes in surprising ways. In answering the questions below you are encouraged t ...
... 4. A hypothetical particle has negative squared mass such that we can write m = iµ where µ is a real quantity with units of mass. In all other respects, the particle satisfies the rules of special relativity, though sometimes in surprising ways. In answering the questions below you are encouraged t ...
PHYSICS OF THE ZERO-POINT FIELD: IMPLICATIONS FOR
... a unique attractive quantum force (the Casimir force) between dielectric or conducting plates can be shown to exist on the basis that absorption and reemission of the ZPF radiation by the plates results in interference and cancellation of certain electromagnetic modes between the plates. The result ...
... a unique attractive quantum force (the Casimir force) between dielectric or conducting plates can be shown to exist on the basis that absorption and reemission of the ZPF radiation by the plates results in interference and cancellation of certain electromagnetic modes between the plates. The result ...
|ket> and notation
... This is another object you will have to get used to. Insertion of this gives ...
... This is another object you will have to get used to. Insertion of this gives ...