Extinction Event www.AssignmentPoint.com An extinction (level
... The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3 ...
... The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3 ...
notes
... – Early: fishes, aquatic vertebrates, ferns – Middle: amphibians – Late: reptiles and mass extinction – Cambrian Period: oceans teemed with many types of animals, including worms, sea stars, and unusual arthropods ...
... – Early: fishes, aquatic vertebrates, ferns – Middle: amphibians – Late: reptiles and mass extinction – Cambrian Period: oceans teemed with many types of animals, including worms, sea stars, and unusual arthropods ...
Geologic Time Webquest - Peoria Public Schools
... End of this period marked by the largest what? What kind of plants are on the scene at this time? Define this type of plant Carboniferous What evolutionary innovation occurred here? Why is this important? What do we find large deposits of during this time period? Devonian, What three types of plants ...
... End of this period marked by the largest what? What kind of plants are on the scene at this time? Define this type of plant Carboniferous What evolutionary innovation occurred here? Why is this important? What do we find large deposits of during this time period? Devonian, What three types of plants ...
Geologic Time Scale Study Guide
... Put the following eras in order from earliest to current: Precambrian, Cenozoic, Paleozoic, Mesozoic. Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic Put the following periods in order from earliest to current: Cretaceous, Ordovician, Carboniferou ...
... Put the following eras in order from earliest to current: Precambrian, Cenozoic, Paleozoic, Mesozoic. Precambrian, Paleozoic, Mesozoic, Cenozoic Put the following periods in order from earliest to current: Cretaceous, Ordovician, Carboniferou ...
Evolution of Life and Mass Extinctions
... apelike animals This is only about 1/10 of 1% of Earth’s age Humans are a very recent life-form ...
... apelike animals This is only about 1/10 of 1% of Earth’s age Humans are a very recent life-form ...
Geologic Time - saintleoky.com
... animal species. The causes of both these events are still not fully understood ...
... animal species. The causes of both these events are still not fully understood ...
Patterns of evolution
... Scientist believe that there are more fossils to be found around the time of mass extinctions than any other time. ...
... Scientist believe that there are more fossils to be found around the time of mass extinctions than any other time. ...
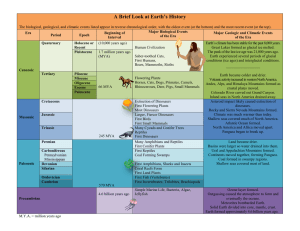
A Brief Look at Earth`s History
... Climate was much warmer than today. Shallow seas covered much of North America. Atlantic Ocean formed. North America and Africa moved apart. Pangaea began to break up. Land became drier. Basins were larger so water drained into them. Ural and Appalachian Mountains formed. Continents moved together, ...
... Climate was much warmer than today. Shallow seas covered much of North America. Atlantic Ocean formed. North America and Africa moved apart. Pangaea began to break up. Land became drier. Basins were larger so water drained into them. Ural and Appalachian Mountains formed. Continents moved together, ...
GEOLOGIC TIME
... longest geologic era, lasted about 4 billion years • No fossil record – WHY? a. Most rocks were non-sedimentary because the earth was still cooling b. Small organisms with no hard shells ...
... longest geologic era, lasted about 4 billion years • No fossil record – WHY? a. Most rocks were non-sedimentary because the earth was still cooling b. Small organisms with no hard shells ...