Unit 3 Chapter
... changes in evolution take place quickly or if they are slow and steady. The best scientific evidence now points to Punctuated Equilibrium. Which involves a slow natural process then some kind of change happens to the environment and there is a series of very rapid changes or Bursts of Evolution. Pre ...
... changes in evolution take place quickly or if they are slow and steady. The best scientific evidence now points to Punctuated Equilibrium. Which involves a slow natural process then some kind of change happens to the environment and there is a series of very rapid changes or Bursts of Evolution. Pre ...
Frozen in Time. Prehistoric life in Antarctica.
... recommendation of the book for a reader interested in our planet and life on earth. First three chapters ("The cold, barren land we call Antarctica", "A continent discovered" and "The fossil pioneers") introduce us to the basic geographical and geological characteristics of Antarctica and their grad ...
... recommendation of the book for a reader interested in our planet and life on earth. First three chapters ("The cold, barren land we call Antarctica", "A continent discovered" and "The fossil pioneers") introduce us to the basic geographical and geological characteristics of Antarctica and their grad ...
Chapter Outline - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... i. It is called the “Age of the Amphibians” because amphibians diversified at this time. ii. Early vascular plants and amphibians were larger and more abundant during the Carboniferous Period; a climate change to colder and drier began the process that produced coal. E. The Mesozoic Era 1. Although ...
... i. It is called the “Age of the Amphibians” because amphibians diversified at this time. ii. Early vascular plants and amphibians were larger and more abundant during the Carboniferous Period; a climate change to colder and drier began the process that produced coal. E. The Mesozoic Era 1. Although ...
document
... some invertebrates lived on land (cockroaches/dragonflies) continents colliding forming mountain ranges Late Paleozoic consists of Carboniferous and Permian periods Age of Amphibians (reptiles evolved from amphibians) continental collisions led to formation of Pangaea largest mass extincti ...
... some invertebrates lived on land (cockroaches/dragonflies) continents colliding forming mountain ranges Late Paleozoic consists of Carboniferous and Permian periods Age of Amphibians (reptiles evolved from amphibians) continental collisions led to formation of Pangaea largest mass extincti ...
Earth: An Ever changing planet
... Pangea covers ¼ Earth’s surface Warm and dry climate On land: 1st small dinosaurs Plants: Ferns, ginkgoes, & conifers In ocean: 1st reptiles Dec. 10- Dec. 14 ...
... Pangea covers ¼ Earth’s surface Warm and dry climate On land: 1st small dinosaurs Plants: Ferns, ginkgoes, & conifers In ocean: 1st reptiles Dec. 10- Dec. 14 ...
Earth: An Ever changing planet
... Pangea covers ¼ Earth’s surface Warm and dry climate On land: 1st small dinosaurs Plants: Ferns, ginkgoes, & conifers In ocean: 1st reptiles Dec. 10- Dec. 14 ...
... Pangea covers ¼ Earth’s surface Warm and dry climate On land: 1st small dinosaurs Plants: Ferns, ginkgoes, & conifers In ocean: 1st reptiles Dec. 10- Dec. 14 ...
Earth: An Ever changing planet
... Pangaea covers ¼ Earth’s surface Warm and dry climate On Land: 1st small dinosaurs Plants: Ferns, ginkgoes, & conifers In ocean: 1st reptiles Dec. 10- Dec. 14 ...
... Pangaea covers ¼ Earth’s surface Warm and dry climate On Land: 1st small dinosaurs Plants: Ferns, ginkgoes, & conifers In ocean: 1st reptiles Dec. 10- Dec. 14 ...
5 Time Marches On - Columbus Humanities Middle School
... The fossils in the figure below are dinosaur bones. The dinosaurs that became these fossils lived 150 million years ago. To most people, 150 million years seems like a very long time. However, to geologists, 150 million years is not very long at all. Geologists study the history of the Earth. The Ea ...
... The fossils in the figure below are dinosaur bones. The dinosaurs that became these fossils lived 150 million years ago. To most people, 150 million years seems like a very long time. However, to geologists, 150 million years is not very long at all. Geologists study the history of the Earth. The Ea ...
EARTH AND SPACE SCIENCE
... • The Permian-Triassic mass extinction claimed 90% of marine species and 70% of terrestrial species. • The surviving life forms had a number of niches available to exploit as a result of the loss of so many species. • Adaptive radiation of surviving species into newly vacated niches resulted in an a ...
... • The Permian-Triassic mass extinction claimed 90% of marine species and 70% of terrestrial species. • The surviving life forms had a number of niches available to exploit as a result of the loss of so many species. • Adaptive radiation of surviving species into newly vacated niches resulted in an a ...
Gondwana The Earth is really an ocean planet since less than one
... The Earth is really an ocean planet since less than one third of the Earth’s surface is covered by land and over two thirds covered by water. The land mass consists of continents and islands which are grouped together into seven regions - North America, South America, Asia, Africa, Antarctica, Europ ...
... The Earth is really an ocean planet since less than one third of the Earth’s surface is covered by land and over two thirds covered by water. The land mass consists of continents and islands which are grouped together into seven regions - North America, South America, Asia, Africa, Antarctica, Europ ...
Geologic Time: Group 1: You have been assigned the entire
... Deposition of Shawangunk Quartzite (rock climbing cliffs in New Paltz) Earliest fossil amphibians (i.e first animals on land!) Acadian Mountains (second period of high grade metamorphism in Central Parkformation of small granite bodies); deposition of sediments that form the Catskills Early trees, f ...
... Deposition of Shawangunk Quartzite (rock climbing cliffs in New Paltz) Earliest fossil amphibians (i.e first animals on land!) Acadian Mountains (second period of high grade metamorphism in Central Parkformation of small granite bodies); deposition of sediments that form the Catskills Early trees, f ...
Geological Timescale Tables
... Deposition of Shawangunk Quartzite (rock climbing cliffs in New Paltz) Earliest fossil amphibians (i.e first animals on land!) Acadian Mountains (second period of high grade metamorphism in Central Parkformation of small granite bodies); deposition of sediments that form the Catskills Early trees, f ...
... Deposition of Shawangunk Quartzite (rock climbing cliffs in New Paltz) Earliest fossil amphibians (i.e first animals on land!) Acadian Mountains (second period of high grade metamorphism in Central Parkformation of small granite bodies); deposition of sediments that form the Catskills Early trees, f ...
Notes – Early Earth History
... Ordovician period, Silurian period Vertebrates of the Paleozoic Era Vertebrates—animals _____________________ backbones—evolved during the early Paleozoic era. The first of these lived in the _____________________. o Bony fish with bony rays that supported their fins o Bony fish with thick fins supp ...
... Ordovician period, Silurian period Vertebrates of the Paleozoic Era Vertebrates—animals _____________________ backbones—evolved during the early Paleozoic era. The first of these lived in the _____________________. o Bony fish with bony rays that supported their fins o Bony fish with thick fins supp ...
History Channel`s How the Earth was Made Video Questions Name
... 14. What is the average rate of continental drift? ...
... 14. What is the average rate of continental drift? ...
Geo Vocab Puzzle
... earth's crust and many associated phenomena resulting from lithospheric plates that move over the underlying mantle. 6. the remains or impression of a prehistoric organism preserved in petrified form or as a mold or cast in rock. 7. internal skeleton 8. mammal whose members are born incompletely dev ...
... earth's crust and many associated phenomena resulting from lithospheric plates that move over the underlying mantle. 6. the remains or impression of a prehistoric organism preserved in petrified form or as a mold or cast in rock. 7. internal skeleton 8. mammal whose members are born incompletely dev ...
1 billion years ago
... The rocks of the Appalachian Mountains continued to form as a continental mass earth scientists call “Avalonia” collided with eastern North America. ...
... The rocks of the Appalachian Mountains continued to form as a continental mass earth scientists call “Avalonia” collided with eastern North America. ...
Glossary - Queensland Museum
... The continent that existed in the southern hemisphere throughout much of the past 600 million years. It was comprised of Australia, Antarctica, South America, Africa, India and smaller pieces. It was subsequently broken apart by continental drift. An animal that eats only plants. A large group of sm ...
... The continent that existed in the southern hemisphere throughout much of the past 600 million years. It was comprised of Australia, Antarctica, South America, Africa, India and smaller pieces. It was subsequently broken apart by continental drift. An animal that eats only plants. A large group of sm ...
Geologic Time Scale - CVHS Chicklas
... Formation of Pangaea caused deserts to expand in tropics. Sheets of ice covered land closer to South Pole. Organisms could not survive. ...
... Formation of Pangaea caused deserts to expand in tropics. Sheets of ice covered land closer to South Pole. Organisms could not survive. ...
Geologic Time Scale
... Formation of Pangaea caused deserts to expand in tropics. Sheets of ice covered land closer to South Pole. Organisms could not survive. ...
... Formation of Pangaea caused deserts to expand in tropics. Sheets of ice covered land closer to South Pole. Organisms could not survive. ...
Notebook #4 Catastrophic Events Affect Diversity GT
... * During the Mesozoic era, many climate changes occurred due to plate tectonics and the movement of landmasses. Plants and animals that survived through this time had structures and systems that allowed for greater adaptations, such as seed coverings for plant seeds and protective body coverings or ...
... * During the Mesozoic era, many climate changes occurred due to plate tectonics and the movement of landmasses. Plants and animals that survived through this time had structures and systems that allowed for greater adaptations, such as seed coverings for plant seeds and protective body coverings or ...
chapter 21
... Sharks and ray finned fish Lobe finned fish like lungfish Ferns and seed bearing plants on land Amphibians in coal swamps Reptiles evolved amniotic egg which allowed them to live farther from water • Mass extinction due to loss of seas ...
... Sharks and ray finned fish Lobe finned fish like lungfish Ferns and seed bearing plants on land Amphibians in coal swamps Reptiles evolved amniotic egg which allowed them to live farther from water • Mass extinction due to loss of seas ...
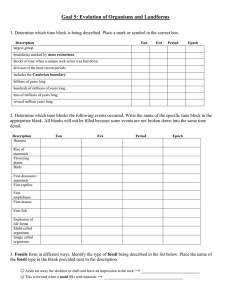
Goal 5: Evolution of Organisms and Landforms
... ☺ Object buried in mud has its molecules replaced by minerals → _____________________________ ☺ Whole organisms locked in tar pits, asphalt, amber, etc. → ______________________________ ☺ Mummification, frozen in ice → _____________________________ 4. Most fossils form in ________________________ ro ...
... ☺ Object buried in mud has its molecules replaced by minerals → _____________________________ ☺ Whole organisms locked in tar pits, asphalt, amber, etc. → ______________________________ ☺ Mummification, frozen in ice → _____________________________ 4. Most fossils form in ________________________ ro ...