2012 December Vol. 49 No 584
... the light pollution which most of us suffered today wherever we are in the world. However against this simplistic comparison with today’s astronomers, those in the past did not necessarily have the same quality optics even if of similar aperture. Also various aspects of the weather such as haze and ...
... the light pollution which most of us suffered today wherever we are in the world. However against this simplistic comparison with today’s astronomers, those in the past did not necessarily have the same quality optics even if of similar aperture. Also various aspects of the weather such as haze and ...
introduction to geodetic astronomy
... in the same natural system; therefore, to use this information for computations in a geodetic system, the relationships must be known. The astro-geodetic (relative) deflection of the vertical (a) at a point is the angle between the astronomic normal at that point and the normal to the reference elli ...
... in the same natural system; therefore, to use this information for computations in a geodetic system, the relationships must be known. The astro-geodetic (relative) deflection of the vertical (a) at a point is the angle between the astronomic normal at that point and the normal to the reference elli ...
SOFA Astrometry Tools
... The positions of astronomical targets need to be expressed in different ways for different purposes. In the case of stars, and a terrestrial observer, three distinct needs have to be satisfied: • A star catalog must describe the position in a way that is valid over a long period of time. The usual met ...
... The positions of astronomical targets need to be expressed in different ways for different purposes. In the case of stars, and a terrestrial observer, three distinct needs have to be satisfied: • A star catalog must describe the position in a way that is valid over a long period of time. The usual met ...
GEK 1506 Heavenly Mathematics: Cultural Astronomy
... time shown on the clock at the central meridian of a given time zone, and the Earth's rate of rotation is assumed to be constant. The civil time (shown on the clock) is based on the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) and is the region’s legally-accepted time scale based on the standard time for that particul ...
... time shown on the clock at the central meridian of a given time zone, and the Earth's rate of rotation is assumed to be constant. The civil time (shown on the clock) is based on the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) and is the region’s legally-accepted time scale based on the standard time for that particul ...
EXPOSITION OF TIME
... It takes into account the requirements of consultants in the field of museum-pedagogy referring to educational topics and interconnection to the system of education (RVP ZV). Institutions and organisation concerned with the protection of the environment (MŽP) were invited to join the exhibition and ...
... It takes into account the requirements of consultants in the field of museum-pedagogy referring to educational topics and interconnection to the system of education (RVP ZV). Institutions and organisation concerned with the protection of the environment (MŽP) were invited to join the exhibition and ...
A new method to determine the mean density of massive Solar
... distances to the Sun (Fig. 2); therefore their mean density trend is subtle. We allocate the asteroids into two groups, according to the values of the mean density. The first group includes a few asteroids with their mean densities higher than 4 g/cm 3. The mean densities of these asteroids show the ...
... distances to the Sun (Fig. 2); therefore their mean density trend is subtle. We allocate the asteroids into two groups, according to the values of the mean density. The first group includes a few asteroids with their mean densities higher than 4 g/cm 3. The mean densities of these asteroids show the ...
(a) Mean solar time
... (α,δ) to the mean equator and equinox for the time of observation, instead of the true equator and equinox. The mean position still has the effects of precession and proper motion included. This is the position actually used in star catalogues. Mean positions are quoted for a given epoch, e.g. (α,δ) ...
... (α,δ) to the mean equator and equinox for the time of observation, instead of the true equator and equinox. The mean position still has the effects of precession and proper motion included. This is the position actually used in star catalogues. Mean positions are quoted for a given epoch, e.g. (α,δ) ...
the orbits of neptune`s outer satellites
... movement that was not uniform and consistent like the Neptune satellites over a 24 hr period. Because of the superior seeing on consecutive nights in October, these images were the primary ones used in our attempt to discover possible new satellites. By placing artificial objects matched to the poin ...
... movement that was not uniform and consistent like the Neptune satellites over a 24 hr period. Because of the superior seeing on consecutive nights in October, these images were the primary ones used in our attempt to discover possible new satellites. By placing artificial objects matched to the poin ...
Using the Heavens to Know Time to Using Time to Know the Heavens
... dictionary provides a definition of a clock as ‘a device other than a watch for indicating or measuring time commonly by means of hands moving on a dial’ or broadly as ‘any periodic system by which time is measured’. To many in the present age, they would probably come in the form of a device with m ...
... dictionary provides a definition of a clock as ‘a device other than a watch for indicating or measuring time commonly by means of hands moving on a dial’ or broadly as ‘any periodic system by which time is measured’. To many in the present age, they would probably come in the form of a device with m ...
Calculations of tithis
... Lunation is the time taken by the Moon to complete one revolution around the Earth. The 360o angular path of the Moon in the sky is divided into 10,000 parts and 1 part, the finest possible resolution amounts 2.16 arc min (2.16 ). The time between two conjunctions is a synodic lunar month. The small ...
... Lunation is the time taken by the Moon to complete one revolution around the Earth. The 360o angular path of the Moon in the sky is divided into 10,000 parts and 1 part, the finest possible resolution amounts 2.16 arc min (2.16 ). The time between two conjunctions is a synodic lunar month. The small ...
Moon-Earth-Sun: The oldest three-body problem
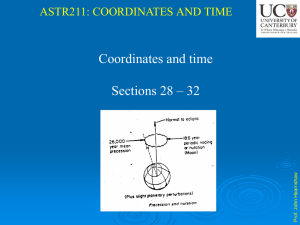
... The three principal coordinate systems in the sky are described in Sec. II; they are based on the local horizon, on the equator, and on the ecliptic. The relations between these coordinate systems are fundamental for understanding the process of observing and interpreting the results of the observat ...
... The three principal coordinate systems in the sky are described in Sec. II; they are based on the local horizon, on the equator, and on the ecliptic. The relations between these coordinate systems are fundamental for understanding the process of observing and interpreting the results of the observat ...
Basic Solar Positional Astronomy
... Before atomic clocks, the problem with GMT was that it was based on an imaginary mean Sun. Thus it was not measurable, especially by navigators trying to calculate longitude. They require an entirely uniform, definable and measurable time scale that accords with the axis of spin of the Earth and whi ...
... Before atomic clocks, the problem with GMT was that it was based on an imaginary mean Sun. Thus it was not measurable, especially by navigators trying to calculate longitude. They require an entirely uniform, definable and measurable time scale that accords with the axis of spin of the Earth and whi ...
Determination of accurate stellar radial
... ELODIE (Baranne et al. 1996) is an échelle spectrometer physically located in a coudé room at the 1.93 m telescope at Observatoire de Haute-Provence (OHP). For this programme, the spectrometer was fed via one optical fibre from the Cassegrain focus. The instrument FWHM is '7.2 km s−1 , correspondi ...
... ELODIE (Baranne et al. 1996) is an échelle spectrometer physically located in a coudé room at the 1.93 m telescope at Observatoire de Haute-Provence (OHP). For this programme, the spectrometer was fed via one optical fibre from the Cassegrain focus. The instrument FWHM is '7.2 km s−1 , correspondi ...
Differential rotation of the Sun
... Internal rotation in the Sun, showing differential rotation in the outer convective region and almost uniform rotation in the central radiative region. See also: Solar rotation On the Sun, the study of oscillations revealed that rotation is roughly constant within the whole radiative interior and v ...
... Internal rotation in the Sun, showing differential rotation in the outer convective region and almost uniform rotation in the central radiative region. See also: Solar rotation On the Sun, the study of oscillations revealed that rotation is roughly constant within the whole radiative interior and v ...
a PDF version of the Uniglobe Manual.
... Azimuth. The horizontal angle between a reference direction and another direction of interest. It is measured from 0° at the reference direction clockwise or counter clockwise through 360. ...
... Azimuth. The horizontal angle between a reference direction and another direction of interest. It is measured from 0° at the reference direction clockwise or counter clockwise through 360. ...
CELESTIAL COORDINATES
... From a latitude of 40°, an object with a declination of +40° will, at some point in time during the day or night, pass directly overhead through the zenith. In general Declination at zenith = Latitude of observer The 24 Ephemeris Stars in the SBO Catalog of Astronomical Objects have Object Numbers r ...
... From a latitude of 40°, an object with a declination of +40° will, at some point in time during the day or night, pass directly overhead through the zenith. In general Declination at zenith = Latitude of observer The 24 Ephemeris Stars in the SBO Catalog of Astronomical Objects have Object Numbers r ...
Task - Illustrative Mathematics
... in the sky? Size and distance must play a role but are there other factors? Are there other stars that are closer to the earth than Canopus but not as bright? The light we see today in the sky from Canopus was emitted in the very early 1700's!!! If some important changes took place to the star Canop ...
... in the sky? Size and distance must play a role but are there other factors? Are there other stars that are closer to the earth than Canopus but not as bright? The light we see today in the sky from Canopus was emitted in the very early 1700's!!! If some important changes took place to the star Canop ...
Solar Radius Variations Measured in Central Eclipses
... one, modifying the time of bead’s dis/appearance and the position of the shadow. Also a shift in lunar latitude is possible. In order to distinguish the contributions of lunar longitude, latitude, solar longitude, lunar parallax and UTC synchronization the residuals hi=Si-Mi SolarLunar limbs from ep ...
... one, modifying the time of bead’s dis/appearance and the position of the shadow. Also a shift in lunar latitude is possible. In order to distinguish the contributions of lunar longitude, latitude, solar longitude, lunar parallax and UTC synchronization the residuals hi=Si-Mi SolarLunar limbs from ep ...
Telescopic Drawings or Photographs of Celestial
... • Two tasks that make up 25% of GCSE marks • An unaided observation and an aided observation chosen from the approved list • Unaided and aided observations can’t be from same row of approved list • If more than one task completed the best mark counts • Each task marked using the same markscheme givi ...
... • Two tasks that make up 25% of GCSE marks • An unaided observation and an aided observation chosen from the approved list • Unaided and aided observations can’t be from same row of approved list • If more than one task completed the best mark counts • Each task marked using the same markscheme givi ...
preprint, pdf version - LESIA
... the Earth radius in the predicted shadow paths. In addition, these earlier predictions were degraded by the poorer precision of the older Pluto ephemerides. To overcome the problems faced by these first prediction efforts, we used more modern facilities, namely the most up-to-date CCD detectors, refe ...
... the Earth radius in the predicted shadow paths. In addition, these earlier predictions were degraded by the poorer precision of the older Pluto ephemerides. To overcome the problems faced by these first prediction efforts, we used more modern facilities, namely the most up-to-date CCD detectors, refe ...
SU3150-Astronomy - Michigan Technological University
... they too are not suitable as universal coordinates To an observer in the northern hemisphere (of earth), all stars having north declinations are visible but only some south stars are visible depending on the location of the observer The scenario is reversed for observers on the southern hemisphere ...
... they too are not suitable as universal coordinates To an observer in the northern hemisphere (of earth), all stars having north declinations are visible but only some south stars are visible depending on the location of the observer The scenario is reversed for observers on the southern hemisphere ...
Section 1.2 Astrometric Data
... • positions and proper motions are given for the catalogue epoch, T0 = J1991.25(TT), which is close to the central epoch of observations (the distinction between the epoch which specifies the equinox and equator of a coordinate system, typically B1950 or J2000, and the epoch at which the star passed ...
... • positions and proper motions are given for the catalogue epoch, T0 = J1991.25(TT), which is close to the central epoch of observations (the distinction between the epoch which specifies the equinox and equator of a coordinate system, typically B1950 or J2000, and the epoch at which the star passed ...
NJIT Physics 320: Astronomy and Astrophysics
... Statistics of sunspot number by Swiss astronomer Rudolf Wolf (1816-1893) Relative sunspot number: r = k (f + 10 g), where g is the number of sunspots groups visible on the solar disk, f is the number of individual sunspots (including those distinguishable within groups), and k is a correction factor ...
... Statistics of sunspot number by Swiss astronomer Rudolf Wolf (1816-1893) Relative sunspot number: r = k (f + 10 g), where g is the number of sunspots groups visible on the solar disk, f is the number of individual sunspots (including those distinguishable within groups), and k is a correction factor ...
VARIOUS MEASUREMENTS OF TIME
... Since the earth rotates on its axis from west to east, all heavenly bodies (i.e. the sun and the fixed stars) appear to revolve from east to west (i.e. in clock-wise direction) around the earth. Such motion of the heavenly bodies is known as apparent motion. We may consider the earth to turn on it a ...
... Since the earth rotates on its axis from west to east, all heavenly bodies (i.e. the sun and the fixed stars) appear to revolve from east to west (i.e. in clock-wise direction) around the earth. Such motion of the heavenly bodies is known as apparent motion. We may consider the earth to turn on it a ...
On the definition and use of the ecliptic in
... 1) The adoption of the ICRS and ICRF (IAU 1997 Resolution B2) International Celestial Reference System (ICRS)*: the idealized barycentric coordinate system to which celestial positions are referred. It is kinematically non-rotating with respect to the ensemble of distant extragalactic objects. It h ...
... 1) The adoption of the ICRS and ICRF (IAU 1997 Resolution B2) International Celestial Reference System (ICRS)*: the idealized barycentric coordinate system to which celestial positions are referred. It is kinematically non-rotating with respect to the ensemble of distant extragalactic objects. It h ...