What are Antibiotics?
... A communicable disease is disease that can be passed from one person to another. These diseases are often caused by germs, such as bacteria or viruses. ...
... A communicable disease is disease that can be passed from one person to another. These diseases are often caused by germs, such as bacteria or viruses. ...
Precautions for CPR article for Judy B
... travel long distances from their source (3 to 6 feet) and do not remain suspended in the air. Droplet precautions do not require that the source be cared for in a room with negative air ...
... travel long distances from their source (3 to 6 feet) and do not remain suspended in the air. Droplet precautions do not require that the source be cared for in a room with negative air ...
13. Why Do We Fall Ill 13.1 HEALTH AND ITS FAILURE
... infectious disease.They spread in the community by microbes. (b) Non-infectious causes : They do not spread in the community. Instead these are mostly internal non-infectious e.g., high blood pressure. 6. Ravi suffered from tuberculosis, while Rehman suffered from typhoid. Which disease (CBSE, SA-2, ...
... infectious disease.They spread in the community by microbes. (b) Non-infectious causes : They do not spread in the community. Instead these are mostly internal non-infectious e.g., high blood pressure. 6. Ravi suffered from tuberculosis, while Rehman suffered from typhoid. Which disease (CBSE, SA-2, ...
Full Paper
... association with intact skin exposure to HIV is too low to be detected in these studies[18]. HIV infection risk factors.The average of transmission derived from prospective studies is helpful in evaluating populations of exposed persons but does not necessarily reflect the risk associated with speci ...
... association with intact skin exposure to HIV is too low to be detected in these studies[18]. HIV infection risk factors.The average of transmission derived from prospective studies is helpful in evaluating populations of exposed persons but does not necessarily reflect the risk associated with speci ...
Announcements_files/Keeling and Rohani Chapter 2
... (1927) and is referred to as the “threshold phenomenon” because initially the proportion of susceptibles in the population must exceed this critical threshold for an infection to invade (see also Ransom 1880, 1881; Hamer 1897). Alternatively, we can interpret this result as requiring γ/β, the relati ...
... (1927) and is referred to as the “threshold phenomenon” because initially the proportion of susceptibles in the population must exceed this critical threshold for an infection to invade (see also Ransom 1880, 1881; Hamer 1897). Alternatively, we can interpret this result as requiring γ/β, the relati ...
Rotavirus - International Scientific Forum on Home Hygiene
... in life this occurs, and the lower the dose, the milder the infection. Once someone has had a rotavirus infection they usually become immune to the virus, therefore infections in adults are uncommon. Rotavirus gastroenteritis is a self-limiting, mild to severe disease characterised by vomiting, wate ...
... in life this occurs, and the lower the dose, the milder the infection. Once someone has had a rotavirus infection they usually become immune to the virus, therefore infections in adults are uncommon. Rotavirus gastroenteritis is a self-limiting, mild to severe disease characterised by vomiting, wate ...
What is tetanus?
... Symptoms of tetanus typically appear 10 days after infection by the bacteria, and include irritability, headache, fever, and spasms of the jaw muscles. These are followed by intense, painful muscle contractions in the neck, arms, legs, and stomach. Muscle spasms occur frequently and last for several ...
... Symptoms of tetanus typically appear 10 days after infection by the bacteria, and include irritability, headache, fever, and spasms of the jaw muscles. These are followed by intense, painful muscle contractions in the neck, arms, legs, and stomach. Muscle spasms occur frequently and last for several ...
Jemds.com
... (rabid) animal to humans. In India, rabies is transmitted to humans, mainly by dogs. Other wild animals that are known to transmit rabies include bats, raccoons, skunks and foxes. According to the World Health Organisation data, the incidence of deaths due to rabies is much higher in India than othe ...
... (rabid) animal to humans. In India, rabies is transmitted to humans, mainly by dogs. Other wild animals that are known to transmit rabies include bats, raccoons, skunks and foxes. According to the World Health Organisation data, the incidence of deaths due to rabies is much higher in India than othe ...
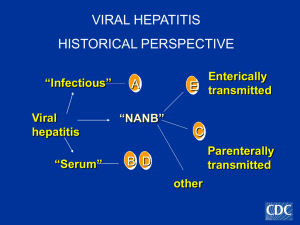
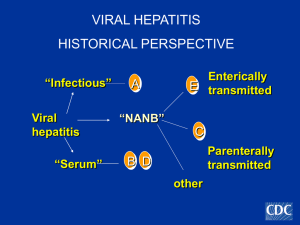
Feco-orally transmitted viral hepatitis in a tertiary care hospital in
... the peak age of seroprevalence is shifting from 1st decade of life to 2nd and 3rd decades.13,19 HAV infection is a vaccine preventable disease but in India, vaccination against HAV is still not included in the universal immunization program and also there are no recommended HEV vaccination strategie ...
... the peak age of seroprevalence is shifting from 1st decade of life to 2nd and 3rd decades.13,19 HAV infection is a vaccine preventable disease but in India, vaccination against HAV is still not included in the universal immunization program and also there are no recommended HEV vaccination strategie ...
Strep Throat - Pediatric Associates of NYC, PC
... How You Get Strep Throat Strep throat is an infection in the throat and tonsils caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria (called "group A strep"). Group A strep bacteria can live in a person's nose and throat. The bacteria are spread through contact with droplets from an infected person's sneeze or ...
... How You Get Strep Throat Strep throat is an infection in the throat and tonsils caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria (called "group A strep"). Group A strep bacteria can live in a person's nose and throat. The bacteria are spread through contact with droplets from an infected person's sneeze or ...
Mumps - Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines
... Mumps is an acute infectious disease caused by the mumps virus. Subclinical infection is common. The prodromal period tends to be rather nonspecific and may include a low grade fever, anorexia, malaise, and headache. Parotitis (unilateral or bilateral) is the most common manifestation occurring in 3 ...
... Mumps is an acute infectious disease caused by the mumps virus. Subclinical infection is common. The prodromal period tends to be rather nonspecific and may include a low grade fever, anorexia, malaise, and headache. Parotitis (unilateral or bilateral) is the most common manifestation occurring in 3 ...
Alere™ HIV Combo Test Receives WHO
... Broadened Access to a New 4th-generation Test in Resource-limited Countries Increases Opportunities to Meet Ambitious New Goals for Screening and Linkage to Care WALTHAM, Mass., July 13, 2016 – Alere (NYSE: ALR), a global leader in rapid diagnostics, today announced that its Alere™ HIV Combo, a rapi ...
... Broadened Access to a New 4th-generation Test in Resource-limited Countries Increases Opportunities to Meet Ambitious New Goals for Screening and Linkage to Care WALTHAM, Mass., July 13, 2016 – Alere (NYSE: ALR), a global leader in rapid diagnostics, today announced that its Alere™ HIV Combo, a rapi ...
The Role of the Microbiology Laboratory in Surveillance and Control
... Fourth, during nosocomial epidemics laboratory personnel may conduct culture surveys of patients, hospital personnel, and the environment. Large numbers of cultures may have to be obtained, processed, and evaluated over a short period. Data gathered by microbiology personnel in such surveys may be c ...
... Fourth, during nosocomial epidemics laboratory personnel may conduct culture surveys of patients, hospital personnel, and the environment. Large numbers of cultures may have to be obtained, processed, and evaluated over a short period. Data gathered by microbiology personnel in such surveys may be c ...
INFECTIOUS DISEASES POLICY
... Exclude until there has not been a loose bowel motion for 24 hours. Exclusion of Contacts - Not excluded. Exclusion is NOT necessary. Exclusion of Contacts - Not excluded. Exclude until all blisters have dried. Exclusion of Contacts - Not excluded Exclude until the person has received appropriate an ...
... Exclude until there has not been a loose bowel motion for 24 hours. Exclusion of Contacts - Not excluded. Exclusion is NOT necessary. Exclusion of Contacts - Not excluded. Exclude until all blisters have dried. Exclusion of Contacts - Not excluded Exclude until the person has received appropriate an ...
Home Care Manual - 2008
... Although colds and other viruses may cause similar symptoms, influenza weakens a person much more than other viruses and can lead to complications. The COMMON COLD is caused by over 200 different viruses. A cold will develop gradually, and is spread through hand-to-hand contact and by sneezes and co ...
... Although colds and other viruses may cause similar symptoms, influenza weakens a person much more than other viruses and can lead to complications. The COMMON COLD is caused by over 200 different viruses. A cold will develop gradually, and is spread through hand-to-hand contact and by sneezes and co ...
DRAFT Data sheets on Quarantine Pests
... develops from one or several secondary germ tubes and, dependent on temperature and light conditions, conidiophores and conidia are generated. When sporulation starts, powdery mildew infection gets visible to the naked eye. 15-23°C are favourable to sporulation. The fungus produces large numbers of ...
... develops from one or several secondary germ tubes and, dependent on temperature and light conditions, conidiophores and conidia are generated. When sporulation starts, powdery mildew infection gets visible to the naked eye. 15-23°C are favourable to sporulation. The fungus produces large numbers of ...
Full Text - Oxford Academic
... Figure 1. Purulent skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs). Mild infection: for purulent SSTI, incision and drainage is indicated. Moderate infection: patients with purulent infection with systemic signs of infection. Severe infection: patients who have failed incision and drainage plus oral antibi ...
... Figure 1. Purulent skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs). Mild infection: for purulent SSTI, incision and drainage is indicated. Moderate infection: patients with purulent infection with systemic signs of infection. Severe infection: patients who have failed incision and drainage plus oral antibi ...
Chicken embros
... laboratory and field tests of this vaccine. In addition, on the basis of the epidemiology information of H5N1 influenza virus, the clade 2.3.2.1 viruses are the dominative strains in the wild birds and poultry in southeast Asia, we developed new H5N1 inactivated vaccine and recombinant NDV vaccine a ...
... laboratory and field tests of this vaccine. In addition, on the basis of the epidemiology information of H5N1 influenza virus, the clade 2.3.2.1 viruses are the dominative strains in the wild birds and poultry in southeast Asia, we developed new H5N1 inactivated vaccine and recombinant NDV vaccine a ...
Document
... 2. (Cont.) In regards to planning a contact evaluation for this case, lowest priority for assessment would be: A. Assessment of the clinical factors that influence infectious risk, such as the presence and duration of cough symptoms B. Gathering information regarding age, health status (especially r ...
... 2. (Cont.) In regards to planning a contact evaluation for this case, lowest priority for assessment would be: A. Assessment of the clinical factors that influence infectious risk, such as the presence and duration of cough symptoms B. Gathering information regarding age, health status (especially r ...
Treatment of Complicated and Uncomplicated Preauricular Pits
... injected with methylene blue to ensure identification of all branches distal to the cutaneous pit.12,4-5 Some authors, including our group, advocate for the excision of a small cartilaginous cuff at the end of the sinus tract, as the sinus is intimately associated with the perichondrium of the auric ...
... injected with methylene blue to ensure identification of all branches distal to the cutaneous pit.12,4-5 Some authors, including our group, advocate for the excision of a small cartilaginous cuff at the end of the sinus tract, as the sinus is intimately associated with the perichondrium of the auric ...
VHF Review - Case Western Reserve University
... important, but also by exposure to infected animals or their carcasses, contact with blood and bodily secretions of infected persons, and by aerosol. The agent of CCHF is a Nairovirus. Although descriptions of this illness can be traced to antiquity, this disease was first recognized in 1944–1945 wh ...
... important, but also by exposure to infected animals or their carcasses, contact with blood and bodily secretions of infected persons, and by aerosol. The agent of CCHF is a Nairovirus. Although descriptions of this illness can be traced to antiquity, this disease was first recognized in 1944–1945 wh ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.