Acute childhood exanthems
... droplets and contact with skin lesions. It predominates in preschool age children and outbreaks in nurseries are common.24 Incidence peaks in summer and autumn in temperate climates. There is a prodrome lasting 1e2 days before the rash appears of low-grade fever, anorexia and a sore mouth. Lesions i ...
... droplets and contact with skin lesions. It predominates in preschool age children and outbreaks in nurseries are common.24 Incidence peaks in summer and autumn in temperate climates. There is a prodrome lasting 1e2 days before the rash appears of low-grade fever, anorexia and a sore mouth. Lesions i ...
Student Health Information Infectious Mononucleosis
... Mono, or Infectious Mononucleosis, is an illness caused by the Epstein-Barr Virus. It varies in severity from a mild illness with barely noticeable symptoms to a more serious one, which rarely requires hospital admission. It spreads mainly through intimate contact and exchange of saliva (kissing, sh ...
... Mono, or Infectious Mononucleosis, is an illness caused by the Epstein-Barr Virus. It varies in severity from a mild illness with barely noticeable symptoms to a more serious one, which rarely requires hospital admission. It spreads mainly through intimate contact and exchange of saliva (kissing, sh ...
Herpes genitalis & Syphilis
... reddening of the skin with small, fluid-filled blisters and ulcers initial episodes may be more severe – inguinal lymphadenopathy, fever, malaise, headache PCR Tzank test ...
... reddening of the skin with small, fluid-filled blisters and ulcers initial episodes may be more severe – inguinal lymphadenopathy, fever, malaise, headache PCR Tzank test ...
Attached is some general information about
... few or no symptoms, but HIV is detectable through the presence of antibodies in the blood. This period usually lasts from three to eight years after the initial infection. • As the virus begins to destroy the immune system, symptoms such as weight loss, fever, diarrhea and lymph gland enlargement ma ...
... few or no symptoms, but HIV is detectable through the presence of antibodies in the blood. This period usually lasts from three to eight years after the initial infection. • As the virus begins to destroy the immune system, symptoms such as weight loss, fever, diarrhea and lymph gland enlargement ma ...
Immunology & Disease
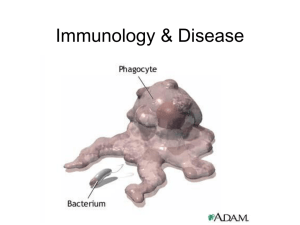
... • Ex. Immunity developed following the vaccination of the chicken pox virus • (most vaccines are either heat killed viruses or synthetic antigen replicates) ...
... • Ex. Immunity developed following the vaccination of the chicken pox virus • (most vaccines are either heat killed viruses or synthetic antigen replicates) ...
Michael McGarvey Hepatitis C virus infection Hepatitis C virus (HCV
... Hepatitis C virus (HCV) causes major changes to infected liver cells to facilitate the production of new virus particles. We are interested in understanding the how HCV can alter key metabolic pathways involved in lipid metabolism and how it can disrupt the normal innate host immune defences and the ...
... Hepatitis C virus (HCV) causes major changes to infected liver cells to facilitate the production of new virus particles. We are interested in understanding the how HCV can alter key metabolic pathways involved in lipid metabolism and how it can disrupt the normal innate host immune defences and the ...
Estimating minimum host population size for Varicella zoster virus
... alphaherpesvirinae subfamily. VZV causes chickenpox at primary infection and establish lifelong latency in sensory and trigeminal ganglia. Later in life, the virus may reactivate to cause herpes zoster. All herpesviruses have been thought to evolve with a relatively constant evolutionary clock. Phyl ...
... alphaherpesvirinae subfamily. VZV causes chickenpox at primary infection and establish lifelong latency in sensory and trigeminal ganglia. Later in life, the virus may reactivate to cause herpes zoster. All herpesviruses have been thought to evolve with a relatively constant evolutionary clock. Phyl ...
Slapped face syndrome
... At first a bright-red rash appears on the face but leaves a pale area around the lips. After a day or so it appears on the arms and legs and also possibly on the trunk. The rash lasts only for 2-3 days but may reappear on and off for several weeks. It is not unusual for the cheeks to become red agai ...
... At first a bright-red rash appears on the face but leaves a pale area around the lips. After a day or so it appears on the arms and legs and also possibly on the trunk. The rash lasts only for 2-3 days but may reappear on and off for several weeks. It is not unusual for the cheeks to become red agai ...
Infectious Disease Terms - Lewiston Altura High School
... Meningitis: an inflammation of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms might include: headache, fever, stiff neck, sensitivity to light, nausea Sinus Infection: Feeling of pressure in the head, swollen and tender sinuses and spread by contact with the mucous. Salmonella: a bacteri ...
... Meningitis: an inflammation of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms might include: headache, fever, stiff neck, sensitivity to light, nausea Sinus Infection: Feeling of pressure in the head, swollen and tender sinuses and spread by contact with the mucous. Salmonella: a bacteri ...
To Click here
... There is no specific treatment for the disease but administering antibiotics for 3-5 days may aid in fighting off any secondary bacterial infections. For brooding chicks, it’s helpful to raise the room temperatures to 500F until the Symptoms go away. An effective insecurity program is the best metho ...
... There is no specific treatment for the disease but administering antibiotics for 3-5 days may aid in fighting off any secondary bacterial infections. For brooding chicks, it’s helpful to raise the room temperatures to 500F until the Symptoms go away. An effective insecurity program is the best metho ...
1. Precaution Lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) is a rodent
... Of special note, tumors may acquire LCMV as an adventitious virus without obvious effects on the tumor. Virus may survive freezing and storage in liquid nitrogen for long periods. When infected tumor ce ...
... Of special note, tumors may acquire LCMV as an adventitious virus without obvious effects on the tumor. Virus may survive freezing and storage in liquid nitrogen for long periods. When infected tumor ce ...
Smallpox Overheads
... VIRUS CHARACTERISTICS DNA ds POXIVIRIDAE TWO VIRUS VARIANTS: VARIOLA major IS THE MORE VIRULENT FORM WITH A TYPICAL MORTALITY OF 20 to 40%. VARIOLA minor KILLS ABOUT 1% OF VICTIMS. ...
... VIRUS CHARACTERISTICS DNA ds POXIVIRIDAE TWO VIRUS VARIANTS: VARIOLA major IS THE MORE VIRULENT FORM WITH A TYPICAL MORTALITY OF 20 to 40%. VARIOLA minor KILLS ABOUT 1% OF VICTIMS. ...
Factsheet on Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
... What is the incubation period? The incubation period (this is from exposure to a case to development of the first signs and symptoms of the disease) is three to five days. It is communicable immediately before and during the acute stage of the illness, and perhaps longer as the virus may be present ...
... What is the incubation period? The incubation period (this is from exposure to a case to development of the first signs and symptoms of the disease) is three to five days. It is communicable immediately before and during the acute stage of the illness, and perhaps longer as the virus may be present ...
College of Medicine Microbiology
... The virus infects epithelial cells of URT and then spreads through blood to salivary glands , primarily parotid glands , testes, ovaries, pancreas, kidney, and in some cases to CNS(meninges). Alternatively the virus may ascend from buccal mucosa up Stensen duct to parotid glands. C/F: Ip :18-2 ...
... The virus infects epithelial cells of URT and then spreads through blood to salivary glands , primarily parotid glands , testes, ovaries, pancreas, kidney, and in some cases to CNS(meninges). Alternatively the virus may ascend from buccal mucosa up Stensen duct to parotid glands. C/F: Ip :18-2 ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.