Name - MrKanesSciencePage
... virus for the first time. A virus is a particle made of nucleic acid, protein, and, in some cases, lipids. A typical virus is composed of a core of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid. Viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages. They enter living cells and, once insid ...
... virus for the first time. A virus is a particle made of nucleic acid, protein, and, in some cases, lipids. A typical virus is composed of a core of DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid. Viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages. They enter living cells and, once insid ...
Virus Notes
... simplex virus modified so that it selectively replicates in virus cells, killing them in the process. A mixture of six bacteria-killing viruses, called bacteriophages, can be safely sprayed on meat and poultry to combat common microbes that kill hundreds of people a year ...
... simplex virus modified so that it selectively replicates in virus cells, killing them in the process. A mixture of six bacteria-killing viruses, called bacteriophages, can be safely sprayed on meat and poultry to combat common microbes that kill hundreds of people a year ...
Text S3: Probability of extinction Our results show that long
... inoculation) prophylaxis is very effective (virological and symptom efficacy > 99.9% (see Figure S2). The virological efficacy is not quite perfect however, because of a small fraction of patients who shed resistant virus (proportion of subject shedding resistant virus and proportion of virus shed t ...
... inoculation) prophylaxis is very effective (virological and symptom efficacy > 99.9% (see Figure S2). The virological efficacy is not quite perfect however, because of a small fraction of patients who shed resistant virus (proportion of subject shedding resistant virus and proportion of virus shed t ...
AH1N1_Resource_MOH
... Use of anti-virals can make illness milder and recovery faster They may also prevent serious flu complications For treatment, antiviral drugs work best if started soon after getting sick (within 2 days of symptoms) ...
... Use of anti-virals can make illness milder and recovery faster They may also prevent serious flu complications For treatment, antiviral drugs work best if started soon after getting sick (within 2 days of symptoms) ...
Document
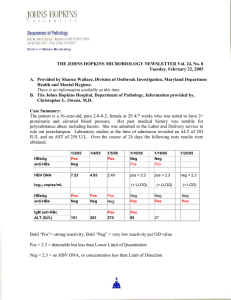
... ¶ Adequate response is anti-HBs 10mIU/mL; inadequate response is anti-HBs<10mIU/mL #The person should be evaluated for antibody response after the vaccine booster dose. For persons who received HBIG, anti-HBs testing should be done when passively acquired antibody from HBIG is no longer detectable ...
... ¶ Adequate response is anti-HBs 10mIU/mL; inadequate response is anti-HBs<10mIU/mL #The person should be evaluated for antibody response after the vaccine booster dose. For persons who received HBIG, anti-HBs testing should be done when passively acquired antibody from HBIG is no longer detectable ...
Diseases Worksheet - Hickman Science Department
... 13. Name three ways to get hepatitis B. 14. If your little sister gets chickenpox when will it be OK to let her go back to school? 15. Which of the following diseases has killed the most people? Measles, German measles, Smallpox, Chickenpox 16. When was the first case of AIDS reported in the United ...
... 13. Name three ways to get hepatitis B. 14. If your little sister gets chickenpox when will it be OK to let her go back to school? 15. Which of the following diseases has killed the most people? Measles, German measles, Smallpox, Chickenpox 16. When was the first case of AIDS reported in the United ...
HBV DNA - Scioto County Medical Society
... HAV IgM positive Occasionally relapsing course Chronic liver disease doesn’t occur ...
... HAV IgM positive Occasionally relapsing course Chronic liver disease doesn’t occur ...
8.L.1.1 Warm-Up Questions
... To promote viral contamination To reduce the number of virus strands To increase cell production on one’s hands To decrease the bacteria found on one’s hands ...
... To promote viral contamination To reduce the number of virus strands To increase cell production on one’s hands To decrease the bacteria found on one’s hands ...
Vaccinations - Griffith Animal Hospital PC
... Feline Rhenotracheitis (FVR) - an upper respiratory or pulmonary infection of cats caused by feline herpesvirus 1 and causes one-half of the respiratory diseases in cats. Claicivirus (C) - a virus of the family Caliciviridae that causes disease in cats. It is one of the two important viral causes of ...
... Feline Rhenotracheitis (FVR) - an upper respiratory or pulmonary infection of cats caused by feline herpesvirus 1 and causes one-half of the respiratory diseases in cats. Claicivirus (C) - a virus of the family Caliciviridae that causes disease in cats. It is one of the two important viral causes of ...
Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD) or Gumboro Disease
... Delaware, USA. Variant IBDV strains were first reported in the USA in 1986/87, while Hyper or very virulent IBDV strains were first reported in Belgium and The Netherlands in 1987. The economic impact of an Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV) infection is twofold: 1. Direct mortality that can rea ...
... Delaware, USA. Variant IBDV strains were first reported in the USA in 1986/87, while Hyper or very virulent IBDV strains were first reported in Belgium and The Netherlands in 1987. The economic impact of an Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV) infection is twofold: 1. Direct mortality that can rea ...
WHAT THE HECK IS A VIRUS
... Noticed milk maids DID NOT get smallpox Developed smallpox vaccine by exposing patients to cowpox Allows patients to develop antibodies to small pox virus ...
... Noticed milk maids DID NOT get smallpox Developed smallpox vaccine by exposing patients to cowpox Allows patients to develop antibodies to small pox virus ...
Volume 24 - No 8: Hepatitis B
... proteins on which serologic assay are based. Clinical Significance: HBV can cause acute hepatitis with resolution, chronic hepatitis, which may evolve to cirrhosis, or fulminant hepatitis with massive liver necrosis. Only about 5-10% of adults who are acutely HBV infected will develop chronic hepati ...
... proteins on which serologic assay are based. Clinical Significance: HBV can cause acute hepatitis with resolution, chronic hepatitis, which may evolve to cirrhosis, or fulminant hepatitis with massive liver necrosis. Only about 5-10% of adults who are acutely HBV infected will develop chronic hepati ...
Infectious Diseases - Laing Middle School
... Cold – An illness caused by a virus that affects the respiratory system. The symptoms of a cold include sore throat and runny nose. Influenza/Flu – A viral infection affecting the respiratory system. The symptoms include: fever, muscle aches, and a cough. This usually last longer than a cold. Athlet ...
... Cold – An illness caused by a virus that affects the respiratory system. The symptoms of a cold include sore throat and runny nose. Influenza/Flu – A viral infection affecting the respiratory system. The symptoms include: fever, muscle aches, and a cough. This usually last longer than a cold. Athlet ...
Infectious Disease Process
... Three shots in upper arm over a 6-month period (0, 1, 4-6 months) Low incidence of side effects, people should not get the vaccine if they have had a life threatening allergic reaction to baker’s yeast or to a previous dose of hepatitis vaccine Routine booster doses are NOT recommended for any ...
... Three shots in upper arm over a 6-month period (0, 1, 4-6 months) Low incidence of side effects, people should not get the vaccine if they have had a life threatening allergic reaction to baker’s yeast or to a previous dose of hepatitis vaccine Routine booster doses are NOT recommended for any ...
The Chain of Infection
... -the person that the pathogen enters A susceptible person is someone at higher risk for developing an infection ...
... -the person that the pathogen enters A susceptible person is someone at higher risk for developing an infection ...
Immunology_IX__immunity_against_infections
... • Recognition of target cells in antigen nonspeciphic. • Virus infected and tumor cells are killed. • Target cells are characterised namely by decreased HLA-I expression. • Cytotoxic mechanisms are similar to Tc cells: perforin and induction of apoptosis. ...
... • Recognition of target cells in antigen nonspeciphic. • Virus infected and tumor cells are killed. • Target cells are characterised namely by decreased HLA-I expression. • Cytotoxic mechanisms are similar to Tc cells: perforin and induction of apoptosis. ...
Nosocomial Infections and Infection Control
... Because more than two-thirds of all cases have no symptoms, carriers are often not aware of their HBV status. Newer antiviral medications may allow many patients to enjoy prolonged viral-suppression ...
... Because more than two-thirds of all cases have no symptoms, carriers are often not aware of their HBV status. Newer antiviral medications may allow many patients to enjoy prolonged viral-suppression ...
Viral Hepatitides in Childhood Marcela Galoppoa, Carol Lezama E
... Health, in 2011, two multicentric studies were conducted, making it possible to conclude that the administration of a second dose would not be necessary in the national schedule. However, this strategy must be followed up over time with biannual serological studies and exhaustive epidemiological sur ...
... Health, in 2011, two multicentric studies were conducted, making it possible to conclude that the administration of a second dose would not be necessary in the national schedule. However, this strategy must be followed up over time with biannual serological studies and exhaustive epidemiological sur ...
Chapter 13 - Faculty Web Sites
... 7) A system that consists of a group of 20 proteins whose activities enhance the body's other defense mechanisms is called ______________. 8) Which of the following would stimulate an antibody-mediated response? 1. Cancerous cells 2. Wrong blood cells from a transfusion 3. Virally infected cells ...
... 7) A system that consists of a group of 20 proteins whose activities enhance the body's other defense mechanisms is called ______________. 8) Which of the following would stimulate an antibody-mediated response? 1. Cancerous cells 2. Wrong blood cells from a transfusion 3. Virally infected cells ...
Period of infectivity The patient is infectious from one day before to 3
... A person can be infectious from 5 days before onset of rash until the vesicles are crusted (usually 5 days). The virus can lay dormant and reactivate in later life. Herpes-Zoster (shingles) is caused by reactivation of the chickenpox virus. Virus from lesions can be transmitted to susceptible indivi ...
... A person can be infectious from 5 days before onset of rash until the vesicles are crusted (usually 5 days). The virus can lay dormant and reactivate in later life. Herpes-Zoster (shingles) is caused by reactivation of the chickenpox virus. Virus from lesions can be transmitted to susceptible indivi ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.