Hepatitis B
... 1. May be recovering from acute HBV infection. 2. May be distantly immune and test not sensitive enough to detect very low level of anti-HBs in serum. ...
... 1. May be recovering from acute HBV infection. 2. May be distantly immune and test not sensitive enough to detect very low level of anti-HBs in serum. ...
Hepatitis C
... patients can be cleared of the virus by a course of anti-viral medicines. Although early medical intervention is helpful, people with HCV infection can experience mild symptoms, and consequently do not seek treatment.[1] An estimated 150-200 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis C. He ...
... patients can be cleared of the virus by a course of anti-viral medicines. Although early medical intervention is helpful, people with HCV infection can experience mild symptoms, and consequently do not seek treatment.[1] An estimated 150-200 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis C. He ...
street HCV
... clean (dirty sources: gift- stolen or from rubbish) Expired Little (not sufficient to satisfy hunger) 83% of street children are malnourished since birth and anemia ...
... clean (dirty sources: gift- stolen or from rubbish) Expired Little (not sufficient to satisfy hunger) 83% of street children are malnourished since birth and anemia ...
BBP Ppt - South Kitsap School District
... A dirty needle/sharp: 3 in 1000 (0.3%) Mucous membrane splash: 1 in 1000 (0.1%) ...
... A dirty needle/sharp: 3 in 1000 (0.3%) Mucous membrane splash: 1 in 1000 (0.1%) ...
Chapter 12
... • Autoimmune Disorders: immune system attacks healthy cells as if they were antigens Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis ...
... • Autoimmune Disorders: immune system attacks healthy cells as if they were antigens Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis ...
Introduction to Statistical Methods
... Elimination of infection..? Elimination: “Reduction to zero of the incidence of infection caused by a specific agent in a defined geographical area as a result of deliberate efforts; continued measures to prevent re-establishment of transmission are required.” • In theory if the right tools were av ...
... Elimination of infection..? Elimination: “Reduction to zero of the incidence of infection caused by a specific agent in a defined geographical area as a result of deliberate efforts; continued measures to prevent re-establishment of transmission are required.” • In theory if the right tools were av ...
Biology 261 Name __On_Scantron_Sheet
... antigenic variation of the envelope spike proteins coupled with genetic exchange of RNA segments. host immune responses that destroy cells infected with the virus. onset of neurological symptoms in the late stages of infection. the effects of aspirin and aspirin-like compounds. ...
... antigenic variation of the envelope spike proteins coupled with genetic exchange of RNA segments. host immune responses that destroy cells infected with the virus. onset of neurological symptoms in the late stages of infection. the effects of aspirin and aspirin-like compounds. ...
Sample Exam 3 Key
... antigenic variation of the envelope spike proteins coupled with genetic exchange of RNA segments. host immune responses that destroy cells infected with the virus. onset of neurological symptoms in the late stages of infection. the effects of aspirin and aspirin-like compounds. ...
... antigenic variation of the envelope spike proteins coupled with genetic exchange of RNA segments. host immune responses that destroy cells infected with the virus. onset of neurological symptoms in the late stages of infection. the effects of aspirin and aspirin-like compounds. ...
Chicken Pox - Kelsey Trail Health Region
... Chicken Pox is caused by a virus. The chicken pox virus lives in the nose and throat and in blisters on the skin of an infected person. It is spread by direct contact with infected fluids from these areas. The virus can be spread for about 1 - 2 days before a rash appears and up until the blisters a ...
... Chicken Pox is caused by a virus. The chicken pox virus lives in the nose and throat and in blisters on the skin of an infected person. It is spread by direct contact with infected fluids from these areas. The virus can be spread for about 1 - 2 days before a rash appears and up until the blisters a ...
Communicable Diseases Manual
... PERINATAL) 1. Agent: Hepatitis B virus (HBV), several subtypes. ...
... PERINATAL) 1. Agent: Hepatitis B virus (HBV), several subtypes. ...
Bloodborne Pathogens WISHA
... HCV - Hepatitis C Symptoms may or may not be present Infection may lead to carrier state Carrier state can develop with or without symptoms Carrier state can lead to chronic liver disease, cirrhosis (10 year latency), or cancer (alcohol is strong co-factor) Leading cause of liver transpla ...
... HCV - Hepatitis C Symptoms may or may not be present Infection may lead to carrier state Carrier state can develop with or without symptoms Carrier state can lead to chronic liver disease, cirrhosis (10 year latency), or cancer (alcohol is strong co-factor) Leading cause of liver transpla ...
Neuromythology and the Viral Etiologies of Multiple Sclerosis
... Epidemiology of MS: environmental exposure in childhood in genetically susceptible individuals Viral infection may be a co-factor interacting with the immune system immune stimulation from viral antigens and viral infection may be associated with persistent or reactivated viral infection ...
... Epidemiology of MS: environmental exposure in childhood in genetically susceptible individuals Viral infection may be a co-factor interacting with the immune system immune stimulation from viral antigens and viral infection may be associated with persistent or reactivated viral infection ...
Virus and Immunity Webquest
... The remainder of the animation is detailed. Watch it and see if you can get the meaning. What happens on the ribosomes of the cell’s ER (endoplasmic reticulum)? ...
... The remainder of the animation is detailed. Watch it and see if you can get the meaning. What happens on the ribosomes of the cell’s ER (endoplasmic reticulum)? ...
Testing Algorithm for the Screening and Diagnosis of Hepatitis C
... Request HCVQU in 1 to 2 months if abnormal liver enzyme levels persist without alternative diagnosis ...
... Request HCVQU in 1 to 2 months if abnormal liver enzyme levels persist without alternative diagnosis ...
SURCE: WHO: first hepatitis B treatment guidelines
... Treatment is recommended for: o adults with CHB who do not have clinical evidence of cirrhosis (or based on APRI score ≤2 in adults): but are aged more than 30 years (in particular), and have persistently abnormal ALT levels and have evidence of high-level HBV replication (HBV DNA >20 000 IU/m ...
... Treatment is recommended for: o adults with CHB who do not have clinical evidence of cirrhosis (or based on APRI score ≤2 in adults): but are aged more than 30 years (in particular), and have persistently abnormal ALT levels and have evidence of high-level HBV replication (HBV DNA >20 000 IU/m ...
aids_and_the_eye.
... Major advances have occurred in the past decade and a half in both the diagnosis and treatment of patients with HIV infection. The HIV epidemic is still with us, however, and will remain so for the indeterminent future. The most effective strategy for avoiding HIV infection remains celibacy and avoi ...
... Major advances have occurred in the past decade and a half in both the diagnosis and treatment of patients with HIV infection. The HIV epidemic is still with us, however, and will remain so for the indeterminent future. The most effective strategy for avoiding HIV infection remains celibacy and avoi ...
Bacteria Wanted Poster Research Project
... How is it transmitted (Air water droplets, contact ingestion, blood. etc.) 4. Victims Who is most at risk – who should be on the “look out” for the culprit 5. Crime Injury to victim (symptoms) (ex Fever, swelling, pain, loss of consciousness, etc. ) Damage to the body (ex. Tissue damage, los ...
... How is it transmitted (Air water droplets, contact ingestion, blood. etc.) 4. Victims Who is most at risk – who should be on the “look out” for the culprit 5. Crime Injury to victim (symptoms) (ex Fever, swelling, pain, loss of consciousness, etc. ) Damage to the body (ex. Tissue damage, los ...
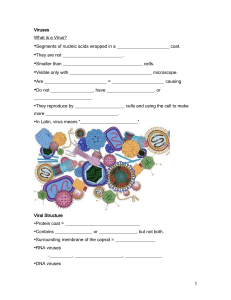
Viruses
... •Virus attaches to ______________ cell and injects its ________ into bacterium and ____________________ with the bacteria’s DNA ...
... •Virus attaches to ______________ cell and injects its ________ into bacterium and ____________________ with the bacteria’s DNA ...
Viral Hepatitis
... •75%-85% of individuals who get Hepatitis C will subsequently develop a chronic infection •Approximately 3.2 million people in the US have a chronic Hepatitis C infection •Of every 100 people that become infected with HCV •75-85 will develop a chronic infection •60-70 will develop chronic liver dise ...
... •75%-85% of individuals who get Hepatitis C will subsequently develop a chronic infection •Approximately 3.2 million people in the US have a chronic Hepatitis C infection •Of every 100 people that become infected with HCV •75-85 will develop a chronic infection •60-70 will develop chronic liver dise ...
slides - Insight Cruises
... AIDS (Acquired immune deficiency syndrome) Common cold Ebola hemorrhagic fever Hepatitis A Herpes simplex Human papillomavirus infection Mononucleosis (Mono) Influenza (flu) Measles (Rubeola) Mumps Poliomyelitis Rabies Rubella Smallpox (Variola) ...
... AIDS (Acquired immune deficiency syndrome) Common cold Ebola hemorrhagic fever Hepatitis A Herpes simplex Human papillomavirus infection Mononucleosis (Mono) Influenza (flu) Measles (Rubeola) Mumps Poliomyelitis Rabies Rubella Smallpox (Variola) ...
Chapter 26: Infectious Diseases
... • Government agencies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and state and county public health departments bear the responsibility for protection of the public health, prevention of epidemics, and management of outbrea ...
... • Government agencies such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and state and county public health departments bear the responsibility for protection of the public health, prevention of epidemics, and management of outbrea ...
Recitation 18 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... Retinoblastoma: This is a cancer of the retina. In Familial retinoblastoma, multiple tumors in the retinas of both eyes occur in the first weeks of infancy when the fetus inherits from one of its parents a chromosome that has its RB locus deleted or otherwise mutated. So in this form of the disease, ...
... Retinoblastoma: This is a cancer of the retina. In Familial retinoblastoma, multiple tumors in the retinas of both eyes occur in the first weeks of infancy when the fetus inherits from one of its parents a chromosome that has its RB locus deleted or otherwise mutated. So in this form of the disease, ...
Infection and it`s mode of transmission:
... It is defined as the person, animal, object or substance from which an infectious agent passes or is disseminated to the host RESERVOIR: ► It is defined as “any person, animal, arthropod, plant, soil, or substance “(or combination of these in which an infectious agent lives and multiplies, on which ...
... It is defined as the person, animal, object or substance from which an infectious agent passes or is disseminated to the host RESERVOIR: ► It is defined as “any person, animal, arthropod, plant, soil, or substance “(or combination of these in which an infectious agent lives and multiplies, on which ...
Infectious bursal disease virus monoclonal antibody, clone
... Immunogen: Native purified very virulent IBD virus (field strain) derived from infected chicken bursas. Host: Mouse Reactivity: Chicken Applications: ELISA, IHC, S-ELISA, WB (See our web site product page for detailed applications information) Protocols: See our web site at http://www.abnova.com/sup ...
... Immunogen: Native purified very virulent IBD virus (field strain) derived from infected chicken bursas. Host: Mouse Reactivity: Chicken Applications: ELISA, IHC, S-ELISA, WB (See our web site product page for detailed applications information) Protocols: See our web site at http://www.abnova.com/sup ...
Viral Hepatitis Fact Sheet
... (HBsAg) has been found in most body secretions. Transmission usually occurs from inoculation or mucosal contact with blood or sexual secretions from a person with active infection (HBsAg positive). Known modes of infection include blood transfusion, sharing of needles and syringes, sexual contact an ...
... (HBsAg) has been found in most body secretions. Transmission usually occurs from inoculation or mucosal contact with blood or sexual secretions from a person with active infection (HBsAg positive). Known modes of infection include blood transfusion, sharing of needles and syringes, sexual contact an ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.