Molecular Characterization of Thymidine Kinase and Glycoprotein G
... threonine at position 252 with ILTV strains either of high virulence, such as strain 632 from the United States (Keeler et al., 1991), or Korean low-virulence field isolates (Han and Kim, 2001). The discrimination of vaccine and field ILT viruses based on sequencing of UL47 and gG genes could serve ...
... threonine at position 252 with ILTV strains either of high virulence, such as strain 632 from the United States (Keeler et al., 1991), or Korean low-virulence field isolates (Han and Kim, 2001). The discrimination of vaccine and field ILT viruses based on sequencing of UL47 and gG genes could serve ...
Lecture 19
... General Features of Viral Reproductive Cycles • Viruses insert their genomes into a host cell • The cell manufactures viral proteins • The virus uses host enzymes, ribosomes, tRNAs, amino acids, ATP, and other molecules • Viral nucleic acids and proteins spontaneously selfassemble into new viruses ...
... General Features of Viral Reproductive Cycles • Viruses insert their genomes into a host cell • The cell manufactures viral proteins • The virus uses host enzymes, ribosomes, tRNAs, amino acids, ATP, and other molecules • Viral nucleic acids and proteins spontaneously selfassemble into new viruses ...
Lymphocystis disease in cultured false clown anemonefish
... cells contained thick smooth hyaline capsules (HC) and basophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies (IB) (Fig. 1.B). Magnification of lymphocystis cell (LC) at the operculum, showing an irregular nucleus (N), marginated chromatin, unevenly stained cytoplasm, inclusion body at the cell periphery, and ...
... cells contained thick smooth hyaline capsules (HC) and basophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies (IB) (Fig. 1.B). Magnification of lymphocystis cell (LC) at the operculum, showing an irregular nucleus (N), marginated chromatin, unevenly stained cytoplasm, inclusion body at the cell periphery, and ...
Medical Textiles & Regulations by Mr. Kulveen Singh Bali, 3M
... manufacture, testing, storage and use along with their development based on clinical trials The need for regulating ‘Medical Devices’ was necessitated by the increasing use of ‘engineered’ products with non pharmacological action. World over, Medical Devices are being increasingly regulated sepa ...
... manufacture, testing, storage and use along with their development based on clinical trials The need for regulating ‘Medical Devices’ was necessitated by the increasing use of ‘engineered’ products with non pharmacological action. World over, Medical Devices are being increasingly regulated sepa ...
Aspects of process development for virus vector production to
... The use of viral vectors as gene delivery and vaccine vehicles has developed rapidly during the last two decades owing to several viral properties. Viruses can infect cells efficiently, often have a broad tissue tropism and can achieve very high levels of either stable or transient transgene express ...
... The use of viral vectors as gene delivery and vaccine vehicles has developed rapidly during the last two decades owing to several viral properties. Viruses can infect cells efficiently, often have a broad tissue tropism and can achieve very high levels of either stable or transient transgene express ...
and HA 2 - Elsevier
... Also removes sialic acid from HA so that progeny influenza virions cannot aggregate. Separates virus particles from inhibitory mucopolysaccharides in the respiratory tract allowing efficient infection. ...
... Also removes sialic acid from HA so that progeny influenza virions cannot aggregate. Separates virus particles from inhibitory mucopolysaccharides in the respiratory tract allowing efficient infection. ...
the full sized image - ScholarSphere
... further complication such as a rupture. Although the symptoms are straight-forward, an infected individual may not know they have mononucleosis for weeks due to the long incubation period of four to eight weeks (Stoppler, 2014). In order to diagnose mononucleosis, blood tests are required, specifica ...
... further complication such as a rupture. Although the symptoms are straight-forward, an infected individual may not know they have mononucleosis for weeks due to the long incubation period of four to eight weeks (Stoppler, 2014). In order to diagnose mononucleosis, blood tests are required, specifica ...
Zoonosis in xenotransplantation Clive Patience*, Yasuhiro
... virus and avian leukosis virus [21°]. Horizontal transmission results in a transient viraemia, followed by immunity and only rare incidence of leukaemia; however, if the virus is transmitted congenitally or to newborn animals, they become viraemic and are often tolerant to viral antigens. Although t ...
... virus and avian leukosis virus [21°]. Horizontal transmission results in a transient viraemia, followed by immunity and only rare incidence of leukaemia; however, if the virus is transmitted congenitally or to newborn animals, they become viraemic and are often tolerant to viral antigens. Although t ...
Flu, Flu Vaccines, and Why We Need to Do Better
... A feature of all living things is their ability to replicate (make copies of themselves). The cells that make up your body are constantly making copies of themselves to replace the ones that get washed, scratched, or rubbed away. Replication is a carefully controlled process and requires an instruc ...
... A feature of all living things is their ability to replicate (make copies of themselves). The cells that make up your body are constantly making copies of themselves to replace the ones that get washed, scratched, or rubbed away. Replication is a carefully controlled process and requires an instruc ...
VIRUSES AND KOCH`S POSTULATES1 Diseases at
... acceptance is a simple one; the disease produced in the experimental animals is not poliomyelitis. Paralysis is not a characteristic sign of a single disease, and the pathological picture observed in the experimental hosts is quite different from that seen in human beings dead of infantile paralysis ...
... acceptance is a simple one; the disease produced in the experimental animals is not poliomyelitis. Paralysis is not a characteristic sign of a single disease, and the pathological picture observed in the experimental hosts is quite different from that seen in human beings dead of infantile paralysis ...
sexually transmitted infections
... of genitals, perianal /anal canal area or the oral cavity that are called condyloma or anal-genital warts. In general, these lesions do not cause discomfort; sometimes, they may cause itching or bleeding if subject to traumatism. Transmission occurs by contact with infected skin/mucosa. Some types o ...
... of genitals, perianal /anal canal area or the oral cavity that are called condyloma or anal-genital warts. In general, these lesions do not cause discomfort; sometimes, they may cause itching or bleeding if subject to traumatism. Transmission occurs by contact with infected skin/mucosa. Some types o ...
Diagnosis and Treatment of latent Tuberculosis Infection
... cause a false-positive PPD result. The tuberculin skin test should be performed by injecting intradermally 0.1 mL of 5 tuberculin units of PPD into the volar surface of the forearm (Figure 2A). In many countries outside the United States, a tuberculin formulation known as RT-23 at a dose of 2 tuberc ...
... cause a false-positive PPD result. The tuberculin skin test should be performed by injecting intradermally 0.1 mL of 5 tuberculin units of PPD into the volar surface of the forearm (Figure 2A). In many countries outside the United States, a tuberculin formulation known as RT-23 at a dose of 2 tuberc ...
What is MRSA? - Santa Fe Institute
... colonized people will not develop an infection. Colonization may last a few days or months. • Direct physical contact (such as hugging, holding hands, child care or contact sports) with a colonized or infected person can spread MRSA. • Uncovered skin infections are more likely than colonizations to ...
... colonized people will not develop an infection. Colonization may last a few days or months. • Direct physical contact (such as hugging, holding hands, child care or contact sports) with a colonized or infected person can spread MRSA. • Uncovered skin infections are more likely than colonizations to ...
rhinoscleroma - Repositório do Centro Hospitalar de Lisboa Central
... - Antimicrobial therapy must be administered for prolonged periods (3-9 M). - Needed antibiotics with activity against gram-negative ...
... - Antimicrobial therapy must be administered for prolonged periods (3-9 M). - Needed antibiotics with activity against gram-negative ...
Pharyngeal Gonorrhea - San Francisco City Clinic
... after receiving recommended therapy and no history of sexual contact during the post-treatment period) should perform culture and susceptibility testing of relevant clinical specimens and consult a specialist for guidance in clinical management. Those cases with isolates indicating decreased suscept ...
... after receiving recommended therapy and no history of sexual contact during the post-treatment period) should perform culture and susceptibility testing of relevant clinical specimens and consult a specialist for guidance in clinical management. Those cases with isolates indicating decreased suscept ...
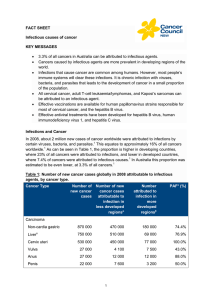
Infectious causes of cancer factsheet
... that skin cancers in people with weakened immune systems contain HPV, however ongoing research is needed to determine the role of HPV in skin cancers.6 The HPV vaccine can prevent more than 70% of infections associated with the development of cervical abnormalities that can progress to cancer.22 Gar ...
... that skin cancers in people with weakened immune systems contain HPV, however ongoing research is needed to determine the role of HPV in skin cancers.6 The HPV vaccine can prevent more than 70% of infections associated with the development of cervical abnormalities that can progress to cancer.22 Gar ...
Communicable-Disease-Reference-Chart
... The following chart contains general recommendations involving uncomplicated cases of commonly encountered communicable diseases. The recommendations are for use by school administration to exclude and re-admit children who are ill or are suspected of being ill. Contacts without symptoms need not be ...
... The following chart contains general recommendations involving uncomplicated cases of commonly encountered communicable diseases. The recommendations are for use by school administration to exclude and re-admit children who are ill or are suspected of being ill. Contacts without symptoms need not be ...
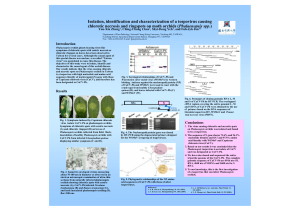
Isolation, identification and characterization of a tospovirus causing
... Phalaenopsis orchids plants bearing virus-like symptoms of chlorotic spots with centric necrosis or chlorotic ringspot on leaves have been observed in Taiwan for several years. Although the causal agent of this special disease was unclear, a so-called “Taiwan virus” was postulated to cause this dise ...
... Phalaenopsis orchids plants bearing virus-like symptoms of chlorotic spots with centric necrosis or chlorotic ringspot on leaves have been observed in Taiwan for several years. Although the causal agent of this special disease was unclear, a so-called “Taiwan virus” was postulated to cause this dise ...
CHARLES H. CALISHER AND BRIAN WJ MAHY
... of many viruses, an overly enthusiastic or conniving bureaucrat might make use of the Federal Register itself 10 to make life for virologists more complicated than it need be. One cannot titrate, aliquot, ship, or be vaccinated against infection with a virus species. Virus species exist only in the ...
... of many viruses, an overly enthusiastic or conniving bureaucrat might make use of the Federal Register itself 10 to make life for virologists more complicated than it need be. One cannot titrate, aliquot, ship, or be vaccinated against infection with a virus species. Virus species exist only in the ...
Immunity - porterhealthscience
... Natural passive acquired immunity – is passed from mother to child across the placenta. Artificially acquired passive immunity – occurs when one receives gamma globulin, an antitoxin, or an immune serum. ...
... Natural passive acquired immunity – is passed from mother to child across the placenta. Artificially acquired passive immunity – occurs when one receives gamma globulin, an antitoxin, or an immune serum. ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.