Document
... • High IFN-/IL-5 ratio=Th1-type (antiviral) response2 • Low IFN-/IL-5 ratio=Th2-type (allergic) response2 1. Rakes GP et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;159:785. 2. Gern JE et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162:2226. ...
... • High IFN-/IL-5 ratio=Th1-type (antiviral) response2 • Low IFN-/IL-5 ratio=Th2-type (allergic) response2 1. Rakes GP et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;159:785. 2. Gern JE et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;162:2226. ...
REVIEW ARTICLE Viral Infections in Domestic Animals as Models
... lend themselves as obvious tools for studies in teratology that have immediate relevance to both animal and human viral infections. Of even greater interest are the disease manifestations encountered later on in postnatal life, notably in persistently viraemic animals lacking evidence of a virus-spe ...
... lend themselves as obvious tools for studies in teratology that have immediate relevance to both animal and human viral infections. Of even greater interest are the disease manifestations encountered later on in postnatal life, notably in persistently viraemic animals lacking evidence of a virus-spe ...
College of Dental Sciences of the Radboud University Nijmegen
... very occasionally. A number of measures are taken in order to prevent them becoming infected during their activities or stay abroad, so they do not constitute an additional infectious risk to patients and staff upon their return. Vaccination and screening can limit this risk to a minimum. 5.4.1 Exch ...
... very occasionally. A number of measures are taken in order to prevent them becoming infected during their activities or stay abroad, so they do not constitute an additional infectious risk to patients and staff upon their return. Vaccination and screening can limit this risk to a minimum. 5.4.1 Exch ...
Anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in patients with chronic heart
... species was named gondii. Although serological evidence indicates a high rate of human exposure to the organism, toxoplasmosis is relatively rare. T. gondii can infect many vertebrates as well as humans, but the definitive host is the house cat and other members of the Felidae (Garcia & Bruckner, 19 ...
... species was named gondii. Although serological evidence indicates a high rate of human exposure to the organism, toxoplasmosis is relatively rare. T. gondii can infect many vertebrates as well as humans, but the definitive host is the house cat and other members of the Felidae (Garcia & Bruckner, 19 ...
The alternate role of direct and environmental - Hal-UPMC
... experimental infections, where bream were highly susceptible to S. destruens infection and represented the most sensitive host. During these experimental challenges to the pathogen, all mortalities occurred within 23 days of the last exposure to the pathogen, suggesting both a short incubation rate ...
... experimental infections, where bream were highly susceptible to S. destruens infection and represented the most sensitive host. During these experimental challenges to the pathogen, all mortalities occurred within 23 days of the last exposure to the pathogen, suggesting both a short incubation rate ...
IS IT A COLD OR THE FLU?
... a fever of over 100.4°F, if your cold lasts longer than 10 days, or if you have severe or unusual symptoms. ...
... a fever of over 100.4°F, if your cold lasts longer than 10 days, or if you have severe or unusual symptoms. ...
INFECTIOUS DISEASES KILL OVER 17 BILLION PEOPLE A YEAR
... Zaire killed 245 people, or about 80% of the 316 cases. Diphtheria epidemics that began in the Russian Federation in 1990, have since spread to a total of 15 countries in Eastern Europe, causing tens of thousands of cases and many hundreds of deaths. WHO estimates that there were about 8,000 diphthe ...
... Zaire killed 245 people, or about 80% of the 316 cases. Diphtheria epidemics that began in the Russian Federation in 1990, have since spread to a total of 15 countries in Eastern Europe, causing tens of thousands of cases and many hundreds of deaths. WHO estimates that there were about 8,000 diphthe ...
VACCINES
... Often the lung is affected. About 2 billion people are infected and there are 3 million deaths/year. Currently tuberculosis is controlled by a vaccine called BCG (Bacillus CalmetteGuerin) which is a strain of M. bovis. M. bovis often responds to diagnostic test for M. tuberculosis. Six extracellular ...
... Often the lung is affected. About 2 billion people are infected and there are 3 million deaths/year. Currently tuberculosis is controlled by a vaccine called BCG (Bacillus CalmetteGuerin) which is a strain of M. bovis. M. bovis often responds to diagnostic test for M. tuberculosis. Six extracellular ...
www.cda-adc.ca - Canadian Dental Association
... is crucial as prophylaxis for HIV, which can reduce risk of infection by 79%, is recommended within 2 hours of exposure.7 There are also time constraints for the administration of hepatitis B immune globulin to those who have inadequate HBV antibody protection.8 Approximately one-third of all dental ...
... is crucial as prophylaxis for HIV, which can reduce risk of infection by 79%, is recommended within 2 hours of exposure.7 There are also time constraints for the administration of hepatitis B immune globulin to those who have inadequate HBV antibody protection.8 Approximately one-third of all dental ...
Isolation of Haemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome Virus from
... intraperitoneally (i.p.) with 0.05 ml of virus (8.5 × 102 f.f.u./rat). Virus isolation. Virus isolation from brain, lung, spleen, kidney and peripheral blood of newborn rats was attempted at 1,3, 5, 8, 11, 15, 20 and 25 weeks after inoculation. Each organ was not homogenized but minced, and put on t ...
... intraperitoneally (i.p.) with 0.05 ml of virus (8.5 × 102 f.f.u./rat). Virus isolation. Virus isolation from brain, lung, spleen, kidney and peripheral blood of newborn rats was attempted at 1,3, 5, 8, 11, 15, 20 and 25 weeks after inoculation. Each organ was not homogenized but minced, and put on t ...
Microbiology - International Federation of Infection Control
... • IFIC’s mission is to facilitate international networking in order to improve the prevention and control of healthcare associated infections worldwide. It is an umbrella organisation of societies and associations of healthcare professionals in infection control and related fields across the globe ...
... • IFIC’s mission is to facilitate international networking in order to improve the prevention and control of healthcare associated infections worldwide. It is an umbrella organisation of societies and associations of healthcare professionals in infection control and related fields across the globe ...
Immunity of Mice to Intranasal Infection after Intraperitoneal
... twice daily, their appetites noted, and records of nasal and respiratory symptoms made by a trained caretaker who was uninformed as to the nature of the study. One or two unvaccinated control animals were infected at the same time. 2 weeks after infection each animal was bled from the heart and the ...
... twice daily, their appetites noted, and records of nasal and respiratory symptoms made by a trained caretaker who was uninformed as to the nature of the study. One or two unvaccinated control animals were infected at the same time. 2 weeks after infection each animal was bled from the heart and the ...
The Fungi of Medical Importance
... Cutaneous candidiasis – occurs in chronically moist areas of skin and burn patients ...
... Cutaneous candidiasis – occurs in chronically moist areas of skin and burn patients ...
Tuberculosis: Commentary on a Reemergent Killer
... Bronx, NY 10461 and C. J. L Murray is an Assistant Professor of the Harvard School of Public Heallh at the Center for Populahon and Development Studies, Cambridge, MA 02138. ...
... Bronx, NY 10461 and C. J. L Murray is an Assistant Professor of the Harvard School of Public Heallh at the Center for Populahon and Development Studies, Cambridge, MA 02138. ...
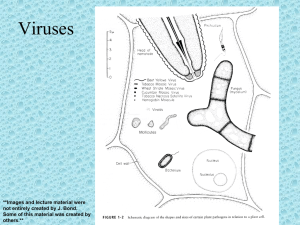
VIRUSES
... Ex: Tobacco Rattle Virus (TRV) - consists of two particles of different lengths. Can infect but unstable because it lacks the gene for protein coat. ...
... Ex: Tobacco Rattle Virus (TRV) - consists of two particles of different lengths. Can infect but unstable because it lacks the gene for protein coat. ...
The pathogenesis of bovine virus diarrhoea virus infections
... and Brownlie, unpublished results). Those capable of rapid growth within the oronasal mucosa m a y account for the limited oculonasal discharge and shallow ulcerations seen in some of the acute infections (2). Systemic spread of infection m a y occur as virus free in serum or as virus associated wit ...
... and Brownlie, unpublished results). Those capable of rapid growth within the oronasal mucosa m a y account for the limited oculonasal discharge and shallow ulcerations seen in some of the acute infections (2). Systemic spread of infection m a y occur as virus free in serum or as virus associated wit ...
BPRC Achievements - Biomedical Primate Research Centre
... information can be used to identify new targets for drug development. Worldwide, around 0.7 million people die annually from malaria. ...
... information can be used to identify new targets for drug development. Worldwide, around 0.7 million people die annually from malaria. ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.