Zoonotic aspects of vector-borne infections
... bird species. There are seven West Nile virus strains, with lineage 1 the most widely distributed in Africa, Europe and the Americas. In 1994, the West Nile virus became more active again in the Old World, with greater pathogenicity for humans and/or horses. In 1996, there was an epidemic in Buchare ...
... bird species. There are seven West Nile virus strains, with lineage 1 the most widely distributed in Africa, Europe and the Americas. In 1994, the West Nile virus became more active again in the Old World, with greater pathogenicity for humans and/or horses. In 1996, there was an epidemic in Buchare ...
Toxoplasma gondii
... drying and freezing. Tissue cysts are less resistant, and are destroyed by proper cooking of food ...
... drying and freezing. Tissue cysts are less resistant, and are destroyed by proper cooking of food ...
Reactivation of Heat Inactivated Reovirus
... University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, Kansas U.S.A. 66103 (Z. Naturforsch. 23 b, 884—885 [1968]; eingegangen am 22. Januar 1968) ...
... University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, Kansas U.S.A. 66103 (Z. Naturforsch. 23 b, 884—885 [1968]; eingegangen am 22. Januar 1968) ...
Control of coronavirus infection through
... immune responses.1 Signaling through the type I IFN receptor leads to the activation of a particular set of genes, including protein kinase R, and Mx proteins,2 which exert potent direct antiviral effects. Other type I IFN–stimulated gene products, such as IFN-␥, activate downstream elements of the ...
... immune responses.1 Signaling through the type I IFN receptor leads to the activation of a particular set of genes, including protein kinase R, and Mx proteins,2 which exert potent direct antiviral effects. Other type I IFN–stimulated gene products, such as IFN-␥, activate downstream elements of the ...
Smallpox vaccine
... fatality rate among persons vaccinated less than 10 years before exposure was 1.3%; it was 7% among those vaccinated 11 to 20 years prior, and 11% among those vaccinated 20 or more years prior to infection. By contrast, 52% of unvaccinated persons died.[37] There are side effects and risks associate ...
... fatality rate among persons vaccinated less than 10 years before exposure was 1.3%; it was 7% among those vaccinated 11 to 20 years prior, and 11% among those vaccinated 20 or more years prior to infection. By contrast, 52% of unvaccinated persons died.[37] There are side effects and risks associate ...
Fresco-part
... Studies have shown that both of these compounds have significant effects on harmful microorganisms and biofilm infections. In addition, thymol can reduce bacterial resistance to common drugs such as penicillin. Thymol has been shown to be an effective fungicide, particularly against fluconazol (Difu ...
... Studies have shown that both of these compounds have significant effects on harmful microorganisms and biofilm infections. In addition, thymol can reduce bacterial resistance to common drugs such as penicillin. Thymol has been shown to be an effective fungicide, particularly against fluconazol (Difu ...
Working with Blood and Body Fluids Guidelines - Staff
... contamination or transmission. For example, when carrying out experiments using human blood products, when cleaning toilets or administering first-aid. ...
... contamination or transmission. For example, when carrying out experiments using human blood products, when cleaning toilets or administering first-aid. ...
[9.1] ( 33 KB/Downloaded:176)
... increase the number of epidemiologists, who have been comprised mostly of public health doctors, and convert their level from non-regular workers to regular workers. Further, the government will create a post of "infection prevention and control" official, so that excellent experts can be guaranteed ...
... increase the number of epidemiologists, who have been comprised mostly of public health doctors, and convert their level from non-regular workers to regular workers. Further, the government will create a post of "infection prevention and control" official, so that excellent experts can be guaranteed ...
Viruses of Bacteria
... This chapter focuses on the viruses that infect bacterial cells. Use this reading guide to help you focus on the key ideas in the chapter. 1. What are the general characteristics of all viruses? ...
... This chapter focuses on the viruses that infect bacterial cells. Use this reading guide to help you focus on the key ideas in the chapter. 1. What are the general characteristics of all viruses? ...
New Evidence of Long-lasting Persistence of Ebola Virus Genetic
... to as the Postebogui cohort). Recruitment is ongoing, and enrollment is conducted at various times after discharge from Ebola treatment centers. After subjects provide informed consent, clinical examination, psychological assessment, and social assessment are performed, and semen specimens are obtai ...
... to as the Postebogui cohort). Recruitment is ongoing, and enrollment is conducted at various times after discharge from Ebola treatment centers. After subjects provide informed consent, clinical examination, psychological assessment, and social assessment are performed, and semen specimens are obtai ...
Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease
... Hemorrhagic Disease is the most important infectious disease of white-tailed deer, and outbreaks occur almost every year in the Southeast. It is caused by either of two closely related viruses, epizootic hemorrhagic disease (EHD) virus or bluetongue virus. Because disease features produced by these ...
... Hemorrhagic Disease is the most important infectious disease of white-tailed deer, and outbreaks occur almost every year in the Southeast. It is caused by either of two closely related viruses, epizootic hemorrhagic disease (EHD) virus or bluetongue virus. Because disease features produced by these ...
Combating Infections
... of deaths in developing countries. • However, these diseases account for only 8% of deaths in rich countries. ...
... of deaths in developing countries. • However, these diseases account for only 8% of deaths in rich countries. ...
Blood and Body Fluid Exposure, 1240.00
... 1. Should an exposure incident occur, contact Employee Health via HURT Line (4878). Immediate reporting is expected from workforce members sustaining a percutaneous, mucosal or cutaneous exposure to patient blood or body fluids (e.g. needle puncture or body fluid splash to mouth, nose, eyes, or non ...
... 1. Should an exposure incident occur, contact Employee Health via HURT Line (4878). Immediate reporting is expected from workforce members sustaining a percutaneous, mucosal or cutaneous exposure to patient blood or body fluids (e.g. needle puncture or body fluid splash to mouth, nose, eyes, or non ...
GRANT WOOD AEA
... infected body fluids of unrecognized carriers than from contact with the fluids from recognized individuals because precautions are not always followed. In instances where GWAEA employees have direct contact with children in the delivery of services, universal precautions must at all times be follo ...
... infected body fluids of unrecognized carriers than from contact with the fluids from recognized individuals because precautions are not always followed. In instances where GWAEA employees have direct contact with children in the delivery of services, universal precautions must at all times be follo ...
Basic Presentation HIV/AIDS
... The HIV infected person may, or may not have AIDS. They may, or may not, have signs or symptoms of illness but are still infectious to others. ...
... The HIV infected person may, or may not have AIDS. They may, or may not, have signs or symptoms of illness but are still infectious to others. ...
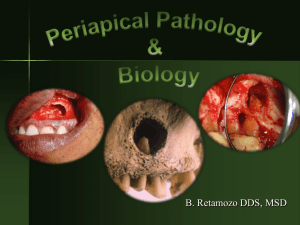
Asymptomatic Apical Periodontitis
... A lesion with highly vascular tissue containing macrophages, fibroblasts, collagen, and immune cells (neutrophils, plasma cells, T and B cells, lymphocytes, eosinophils ...
... A lesion with highly vascular tissue containing macrophages, fibroblasts, collagen, and immune cells (neutrophils, plasma cells, T and B cells, lymphocytes, eosinophils ...
PYREXIA OF UNKNOWN ORIGIN
... with advanced HIV infection for the first time with prominent constitutional symptoms.Careful evaluation for Ois is unrevealing.Within weeks of nstarting ART a fatal disease process becomes apparent Advanced HIV infection can produce fever and wt loss /constitutional symptoms without underlying OI ...
... with advanced HIV infection for the first time with prominent constitutional symptoms.Careful evaluation for Ois is unrevealing.Within weeks of nstarting ART a fatal disease process becomes apparent Advanced HIV infection can produce fever and wt loss /constitutional symptoms without underlying OI ...
Monitoring surgical wounds for infection
... During your stay in hospital, the nurse who changes your wound dressings will check for any signs of infection. If you are concerned about your wound, tell the nurse who is looking after you. Don’t be tempted to remove your dressing, or touch your wound or wound drain. You could accidentally transfe ...
... During your stay in hospital, the nurse who changes your wound dressings will check for any signs of infection. If you are concerned about your wound, tell the nurse who is looking after you. Don’t be tempted to remove your dressing, or touch your wound or wound drain. You could accidentally transfe ...
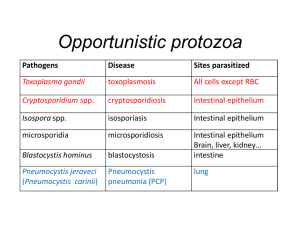
Biology of Select Zoonotic Protozoan Infections
... coccidial vaccines is required due to the species-specific immunity that is induced, since cross-species protection is relatively weak. The development of new vaccines for coccidiosis focuses on the identification of species-specific antigens and the generation of the recombinant vaccines. Several s ...
... coccidial vaccines is required due to the species-specific immunity that is induced, since cross-species protection is relatively weak. The development of new vaccines for coccidiosis focuses on the identification of species-specific antigens and the generation of the recombinant vaccines. Several s ...
Report on the 14th International Congress on Infectious Diseases
... After all, a “One Health” methodology is the only way to accurately report what is happening in the world of emerging disease and to alert people to the spread of new diseases that may affect them directly or put human or animal food crop supplies at risk. ProMED’s commitment to One Health principle ...
... After all, a “One Health” methodology is the only way to accurately report what is happening in the world of emerging disease and to alert people to the spread of new diseases that may affect them directly or put human or animal food crop supplies at risk. ProMED’s commitment to One Health principle ...
Viruses & Bacteria
... infection by producing antibodies to the virus envelope’s glycoprotein. a) An antibody is a protein secreted by cells in the immune system in response to a foreign substance in the body. b) However, mutations in viruses often change their glycoproteins & make it difficult for the antibodies to recog ...
... infection by producing antibodies to the virus envelope’s glycoprotein. a) An antibody is a protein secreted by cells in the immune system in response to a foreign substance in the body. b) However, mutations in viruses often change their glycoproteins & make it difficult for the antibodies to recog ...
control of aphid vector spread of lily symptomless virus and lily
... Emulsions were prepared shortly before use and then applied with a knapsack sprayer (Birchmeijer Helico nozzles 1.2) at a pressure of 400 kPa and at a volume equivalent to 400 L/ha. Spraying was carried out in calm weather to minimise spray drift. The equivalent dosages were 3.1 (0.78 %) and 6.25 L/ ...
... Emulsions were prepared shortly before use and then applied with a knapsack sprayer (Birchmeijer Helico nozzles 1.2) at a pressure of 400 kPa and at a volume equivalent to 400 L/ha. Spraying was carried out in calm weather to minimise spray drift. The equivalent dosages were 3.1 (0.78 %) and 6.25 L/ ...
Zoonoses on the Arabian Peninsula. A review Running title: Zoonos
... Cystic echinococcosis or cystic hydatid disease is certainly one of the most wide spread and important global helminth zoonoses. The parasite Echinococcus granulosus is found in a wide spectrum of intermediate hosts like sheep, goats, camels, cattle, pigs and equids. Wild intermediate hosts like ce ...
... Cystic echinococcosis or cystic hydatid disease is certainly one of the most wide spread and important global helminth zoonoses. The parasite Echinococcus granulosus is found in a wide spectrum of intermediate hosts like sheep, goats, camels, cattle, pigs and equids. Wild intermediate hosts like ce ...
molecular interactions of chikungunya virus non
... and nsP4-nsP4). Further, ELISA was also performed using Strep fusion protein as bait and His fusion as prey proteins on Streptactin microtitre plates. The complex was detected with anti-His antibodies and appearance of blue colour after addition of TMB as substrate indicated the presence of interact ...
... and nsP4-nsP4). Further, ELISA was also performed using Strep fusion protein as bait and His fusion as prey proteins on Streptactin microtitre plates. The complex was detected with anti-His antibodies and appearance of blue colour after addition of TMB as substrate indicated the presence of interact ...
abortion diseases of range cattle
... was in the fetus, is probably undetectable at the time of abortion. Further, if the fetus remains in the uterus for any length of time after death, postmortem degeneration will hide lesions. Fetal membranes, which are most often first and most consistently affected are frequently unavailable for exa ...
... was in the fetus, is probably undetectable at the time of abortion. Further, if the fetus remains in the uterus for any length of time after death, postmortem degeneration will hide lesions. Fetal membranes, which are most often first and most consistently affected are frequently unavailable for exa ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.





![[9.1] ( 33 KB/Downloaded:176)](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003968942_1-aafe3949c3ed624043c60aacbcfe0e03-300x300.png)