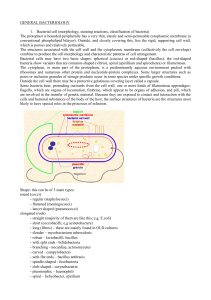
GENERAL BACTERIOLOGY 1. Bacterial cell
... Some bacteria, develop a highly resistant resting phase or endospore, whereby the organism can survive in a dormant state through a long period of starvation or other adverse environmental conditions. The process does not involve multiplication: in sporulation, each vegetative cell forms only one sp ...
... Some bacteria, develop a highly resistant resting phase or endospore, whereby the organism can survive in a dormant state through a long period of starvation or other adverse environmental conditions. The process does not involve multiplication: in sporulation, each vegetative cell forms only one sp ...
adaptation of an indigenous very virulent infectious bursal disease
... cells at 24 hours after sub-culturing were used for infection with vvIBDV, as described by Ahasan et al. (2002). The growth medium of each flask was removed and cell monolayer was washed twice with prewarmed phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Then the Vero cells were infected by 0.25 ml of IBDV using ...
... cells at 24 hours after sub-culturing were used for infection with vvIBDV, as described by Ahasan et al. (2002). The growth medium of each flask was removed and cell monolayer was washed twice with prewarmed phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Then the Vero cells were infected by 0.25 ml of IBDV using ...
Differential Immune Responses to New World and Old World
... in the TCRV-infected mouse model [65]. By transplanting wild-type bone-marrow cells into irradiated type I IFN receptor knockout mice (IFNAR−/− ), Oestereich and colleagues have shown that this new mouse model can recapitulate some important features of severe Lassa fever in humans, including T cell ...
... in the TCRV-infected mouse model [65]. By transplanting wild-type bone-marrow cells into irradiated type I IFN receptor knockout mice (IFNAR−/− ), Oestereich and colleagues have shown that this new mouse model can recapitulate some important features of severe Lassa fever in humans, including T cell ...
the romanian hepatitis action paper
... diseases to IDU and HCV antibody testing for HIV-infected persons are being provided but in an unsystematic manner. In 2008, the screening of the health status of the population included only transaminases, which may or may not be an indicator for hepatitis. Patients with normal ALT were not tested ...
... diseases to IDU and HCV antibody testing for HIV-infected persons are being provided but in an unsystematic manner. In 2008, the screening of the health status of the population included only transaminases, which may or may not be an indicator for hepatitis. Patients with normal ALT were not tested ...
Restricted Biological Agents
... Below is a list of agents restricted for export by the U.S. Government. Be aware that this list is not exhaustive but is limited to biological agents likely to be used at VUMC that have export control restrictions. ...
... Below is a list of agents restricted for export by the U.S. Government. Be aware that this list is not exhaustive but is limited to biological agents likely to be used at VUMC that have export control restrictions. ...
HIV/AIDS – CLINICAL MANAGEMENT
... Infant: AZT syrup 2mg/kg/QID for first six weeks, 8 to 12 hours after birth LSCS Postpartum care Breast feeding with ART ...
... Infant: AZT syrup 2mg/kg/QID for first six weeks, 8 to 12 hours after birth LSCS Postpartum care Breast feeding with ART ...
SNAP Cats snapcats.org Provided by the Cornell Feline Health
... common sign, but sneezing and nasal discharge may also occur. The bacteria are transmitted through direct contact with an infected cat, and the highest rates of infection are in cats between five weeks and nine months of age, especially those residing in multiple-cat environments with a history of r ...
... common sign, but sneezing and nasal discharge may also occur. The bacteria are transmitted through direct contact with an infected cat, and the highest rates of infection are in cats between five weeks and nine months of age, especially those residing in multiple-cat environments with a history of r ...
Free PDF
... • Neutropenic patients experience FUO due to localized and disseminated infections, but the etiology is usually identified in only 40-50% of cases. The more common diagnosis in these patients are bacterial infection, pneumonia, and infection of the skin or other soft tissues. Usually antibiotic ther ...
... • Neutropenic patients experience FUO due to localized and disseminated infections, but the etiology is usually identified in only 40-50% of cases. The more common diagnosis in these patients are bacterial infection, pneumonia, and infection of the skin or other soft tissues. Usually antibiotic ther ...
diagnostic field guide for bacterial and viral diseases of paddy
... yellowish green and show mottled appearance alongwith slight twisting. The older leaves turn orange -yellow and interveinal chlorosis is observed starting from the margin of the leaf blade. The infected leaves often dry up quickly. In-the field, disease symptoms initially seen in localized spot in y ...
... yellowish green and show mottled appearance alongwith slight twisting. The older leaves turn orange -yellow and interveinal chlorosis is observed starting from the margin of the leaf blade. The infected leaves often dry up quickly. In-the field, disease symptoms initially seen in localized spot in y ...
Why Vaccines and Therapies for HIV are So1
... T-cell CTL recognize 9 specific amino acid sequences in all viral proteins--both variable and conserved antigens Nancy L. Haigwood Seattle Biomedical Research Institute ...
... T-cell CTL recognize 9 specific amino acid sequences in all viral proteins--both variable and conserved antigens Nancy L. Haigwood Seattle Biomedical Research Institute ...
Disseminate and fatal cytomegalovirus disease with thymitis in
... HAART should be considered in the differential IRD diagnosis since they have different management and prognosis. ...
... HAART should be considered in the differential IRD diagnosis since they have different management and prognosis. ...
ip0a901 №5
... Ask the client about allergic reactions before selecting an antiseptic solution Wash first with soap and water if visibly soiled Apply antiseptic starting from the operative site and working outward in a circular motion for several inches ...
... Ask the client about allergic reactions before selecting an antiseptic solution Wash first with soap and water if visibly soiled Apply antiseptic starting from the operative site and working outward in a circular motion for several inches ...
Flavitrack: an annotated database of flavivirus
... strain. It is thus critically important to distinguish the common features of these viruses, as well as differences that may be associated with lethality. Flavitrack was designed to ease the identification of conserved functional areas, using methodology previously developed in this group (Negi et a ...
... strain. It is thus critically important to distinguish the common features of these viruses, as well as differences that may be associated with lethality. Flavitrack was designed to ease the identification of conserved functional areas, using methodology previously developed in this group (Negi et a ...
Comparison of the transmission characteristics of low and high
... Low pathogenicity avian influenza A strains (LPAI) of the H5 and H7 type are noted for their ability to transform into highly pathogenic counterparts (HPAI). Here we compare the transmission characteristics in poultry of LPAI H5N2 (A/Chicken/Pennsylvania/83) and corresponding HPAI virus by means of t ...
... Low pathogenicity avian influenza A strains (LPAI) of the H5 and H7 type are noted for their ability to transform into highly pathogenic counterparts (HPAI). Here we compare the transmission characteristics in poultry of LPAI H5N2 (A/Chicken/Pennsylvania/83) and corresponding HPAI virus by means of t ...
Invasive Mucormycosis in Chronic Granulomatous Disease
... and multiple granuloma formations. Lungs and chest wall are the most frequent sites of infection in these patients. Aspergillus spp. is the most commonly isolated pathogen. Other sites of infection include bone, brain, and liver. Extension of infection to the vertebrae, with or without spinal cord i ...
... and multiple granuloma formations. Lungs and chest wall are the most frequent sites of infection in these patients. Aspergillus spp. is the most commonly isolated pathogen. Other sites of infection include bone, brain, and liver. Extension of infection to the vertebrae, with or without spinal cord i ...
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) FOR LENTIVIRAL
... vector-derived reagents are generated in human cells where there is the possibility of recombination to form wild type HIV-1. As such, they should be handled as potentially infectious material. Description: Lentiviral vectors defined by the presence of HIV-derived cis elements which are flanked by l ...
... vector-derived reagents are generated in human cells where there is the possibility of recombination to form wild type HIV-1. As such, they should be handled as potentially infectious material. Description: Lentiviral vectors defined by the presence of HIV-derived cis elements which are flanked by l ...
The papillomavirus life cycle
... et al., 2003; Peh et al., 2002). HPV2 and closely related supergroup A papillomaviruses are the primary cause of common warts. The second major group of human papillomaviruses are contained within supergroup B. Viruses from the B1 subgroup such as HPV5 (also known as Beta papillomaviruses) (de Villi ...
... et al., 2003; Peh et al., 2002). HPV2 and closely related supergroup A papillomaviruses are the primary cause of common warts. The second major group of human papillomaviruses are contained within supergroup B. Viruses from the B1 subgroup such as HPV5 (also known as Beta papillomaviruses) (de Villi ...
Document
... Is antigen presentation by hepatocytes sufficient alone for immune activation to cause rejection/hepatitis? ...
... Is antigen presentation by hepatocytes sufficient alone for immune activation to cause rejection/hepatitis? ...
- VibrioNet
... The worst epidemic of cholera in recent history between 2010 and 2013 in Haiti caused the death of more than 8,000 Haitians. While Vibrio cholera is mainly considered as the responsible pathogenic agent, the actual pathogen is a temperate phage that upon successful infection of its Vibrio host turns ...
... The worst epidemic of cholera in recent history between 2010 and 2013 in Haiti caused the death of more than 8,000 Haitians. While Vibrio cholera is mainly considered as the responsible pathogenic agent, the actual pathogen is a temperate phage that upon successful infection of its Vibrio host turns ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.