Lesson Plan - The Vaccine Makers Project
... the same pathogen with different genes for their surface antigens (multiple genotypes). Chronic infection – a pathogen remains in cells and replicates indefinitely Continuous replication causes low levels of virus to be produced indefinitely resulting in chronic infection. Hepatitis B virus is an ex ...
... the same pathogen with different genes for their surface antigens (multiple genotypes). Chronic infection – a pathogen remains in cells and replicates indefinitely Continuous replication causes low levels of virus to be produced indefinitely resulting in chronic infection. Hepatitis B virus is an ex ...
A sudden rash and blisters on the left leg in Bali
... independent of oxygen and can cause cellular damage by forming aberrant cross-links in cellular DNA, resulting in inhibition of DNA synthesis. In type II reactions, psoralen and oxygen form free radicals, resulting in epidermal, dermal, and endothelial cell membrane damage that manifests as oedema, ...
... independent of oxygen and can cause cellular damage by forming aberrant cross-links in cellular DNA, resulting in inhibition of DNA synthesis. In type II reactions, psoralen and oxygen form free radicals, resulting in epidermal, dermal, and endothelial cell membrane damage that manifests as oedema, ...
Novel Inflammatory Markers, Clinical Risk Factors and Virus Type
... isolates are divided into 2 major groups, A and B, due to differences in the amino acid sequence of the attachment G protein. The 2 major groups usually circulate simultaneously, but the proportion of infection caused by group A or B viruses differ from season to season9 with type A seasons generall ...
... isolates are divided into 2 major groups, A and B, due to differences in the amino acid sequence of the attachment G protein. The 2 major groups usually circulate simultaneously, but the proportion of infection caused by group A or B viruses differ from season to season9 with type A seasons generall ...
Nosocomial Rotavirus Infection: Epidemiology, Clinical
... Rotavirus (RV) is the major causative agent of gastroenteritis in young children, and nosocomial rotavirus (NRV) transmission has been reported. However, limited data are available in Thailand. The routine detection of RV antigen in the stool has been performed in hospitalized children with diarrhea ...
... Rotavirus (RV) is the major causative agent of gastroenteritis in young children, and nosocomial rotavirus (NRV) transmission has been reported. However, limited data are available in Thailand. The routine detection of RV antigen in the stool has been performed in hospitalized children with diarrhea ...
Transmission dynamics of an emerging infectious disease in wildlife
... disease outbreak occurred at a koi farm in the United Kingdom in 1996. CyHV-3 was first isolated in 1998 (Hedrick et al., 2000) and was identified as a novel virus belonging to the family Herpesviridae (Aoki et al., 2007). The CyHV-3 disease had spread to fish farms around the world by the early 200 ...
... disease outbreak occurred at a koi farm in the United Kingdom in 1996. CyHV-3 was first isolated in 1998 (Hedrick et al., 2000) and was identified as a novel virus belonging to the family Herpesviridae (Aoki et al., 2007). The CyHV-3 disease had spread to fish farms around the world by the early 200 ...
How to Manage UTI in the Elderley and Systemic Disease
... confusion (delirium), lethargy, agitation, collapse 15%, no fever and no leukocytosis deteriorate more rapidly from infection bacteremic UTI in the elderly often present respiratory symptoms, treated as ‘Pneumonia’ ...
... confusion (delirium), lethargy, agitation, collapse 15%, no fever and no leukocytosis deteriorate more rapidly from infection bacteremic UTI in the elderly often present respiratory symptoms, treated as ‘Pneumonia’ ...
Epidemiology and Infection 132, 999-1000.
... effects of various vaccination schedules on the time course of outbreaks of meningococcal disease, it was drawn to our attention by a reader of this journal that a particular statement concerning vaccine efficacy may have not been entirely accurate. The statement in question was "there exist capsula ...
... effects of various vaccination schedules on the time course of outbreaks of meningococcal disease, it was drawn to our attention by a reader of this journal that a particular statement concerning vaccine efficacy may have not been entirely accurate. The statement in question was "there exist capsula ...
Restricted Anti-infective Indications CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE
... of GUIDANCE-DS which is an essential element of restricted anti-infective management Intensive care antimicrobial liaison rounds (twice weekly at JHH, weekly at other sites) will continue across HNE Health at all intensive care units. Area Clinical Practice Guidelines and pathways for pneumonia, S. ...
... of GUIDANCE-DS which is an essential element of restricted anti-infective management Intensive care antimicrobial liaison rounds (twice weekly at JHH, weekly at other sites) will continue across HNE Health at all intensive care units. Area Clinical Practice Guidelines and pathways for pneumonia, S. ...
Mycobacterium arupense infection in HIV
... patient,12 pulmonary infection in malignant patient,13 osteomyelitis of the wrist,14 were reported due to infection with M. arupense. To our knowledge, the present study is the first report of pulmonary infections in two independent HIV-infected patients in a developing country. Our patients illustra ...
... patient,12 pulmonary infection in malignant patient,13 osteomyelitis of the wrist,14 were reported due to infection with M. arupense. To our knowledge, the present study is the first report of pulmonary infections in two independent HIV-infected patients in a developing country. Our patients illustra ...
Latent Tuberculosis Infection
... No. The administration of a tuberculin skin test cannot, by itself, cause reactivity to future tuberculin skin testing in persons who have not been infected with TB. However, repeated skin testing can cause the false impression of recent infection (TST conversion) in persons who had actually been in ...
... No. The administration of a tuberculin skin test cannot, by itself, cause reactivity to future tuberculin skin testing in persons who have not been infected with TB. However, repeated skin testing can cause the false impression of recent infection (TST conversion) in persons who had actually been in ...
Document
... •Treatment is supportive, using either oral or intravenous rehydration , For severe cases: •Intravenous fluids and blood transfusions •The rate of infection has increased dramatically over the last 50 years, with around 50–100 million people being infected yearly. •Is a global disease currently is e ...
... •Treatment is supportive, using either oral or intravenous rehydration , For severe cases: •Intravenous fluids and blood transfusions •The rate of infection has increased dramatically over the last 50 years, with around 50–100 million people being infected yearly. •Is a global disease currently is e ...
Virus-Bacteria Interactions: An Emerging Topic in Human Infection
... reducing the likelihood of pathogenic bacterial proliferation or virus attachment. Other components, like mucus or enzymatic secretions, may also interfere or assist the infection process. To circumvent this, rather than compete for host cell binding sites, some viruses can utilize bacterial ligands ...
... reducing the likelihood of pathogenic bacterial proliferation or virus attachment. Other components, like mucus or enzymatic secretions, may also interfere or assist the infection process. To circumvent this, rather than compete for host cell binding sites, some viruses can utilize bacterial ligands ...
Overview of Surgical Site Infectionsfile_download
... postoperative surveillance.6 An estimated 47% to 84% of SSIs occur after discharge7 and, therefore, go undetected by hospital infection surveillance programs. SSIs increase the hospital length of stay by an average of 7.5 days. A CDC report using data from 2002 estimated that annual U.S. hospital co ...
... postoperative surveillance.6 An estimated 47% to 84% of SSIs occur after discharge7 and, therefore, go undetected by hospital infection surveillance programs. SSIs increase the hospital length of stay by an average of 7.5 days. A CDC report using data from 2002 estimated that annual U.S. hospital co ...
Virology Lectures Virology - College of Veterinary Medicine
... Viruses: They are the smallest and simplest form of life on earth, which can replicate only in living susceptible cells. Viruses consist of : 1.A nucleic acid genome either DNA or RNA. 2.A protein coat (capsid) that enclosed the genome. 3.In some cases a lipid membrane (envelope). ...
... Viruses: They are the smallest and simplest form of life on earth, which can replicate only in living susceptible cells. Viruses consist of : 1.A nucleic acid genome either DNA or RNA. 2.A protein coat (capsid) that enclosed the genome. 3.In some cases a lipid membrane (envelope). ...
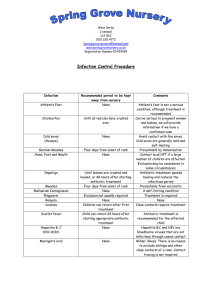
Infection Control
... Athlete’s foot is not a serious condition, although treatment is recommended Can be serious to pregnant women and babies, we will provide information if we have a confirmed case Avoid contact with the sores. Cold sores are generally mild and self-limiting Preventable by immunisation Contact local HP ...
... Athlete’s foot is not a serious condition, although treatment is recommended Can be serious to pregnant women and babies, we will provide information if we have a confirmed case Avoid contact with the sores. Cold sores are generally mild and self-limiting Preventable by immunisation Contact local HP ...
CIP Consulting LLC Basic and Intermediate Infection Prevention
... EIA (Enzyme immunoassay) This procedure uses known specific antibodies which are reacted with a patient specimen. If the unknown patient antigen reacts with the antibody, a visible result can be observed by an enzymatic reaction. (i.e., Influenza A virus antibody, HIV, Strep kit) Advantage – rapid t ...
... EIA (Enzyme immunoassay) This procedure uses known specific antibodies which are reacted with a patient specimen. If the unknown patient antigen reacts with the antibody, a visible result can be observed by an enzymatic reaction. (i.e., Influenza A virus antibody, HIV, Strep kit) Advantage – rapid t ...
Virus transmission via food - Institute of Food Technologists
... whereas the rotaviruses contain double-stranded RNA. Human enteric viruses containing DNA are known, but none have been proven to be transmitted via food or water. The outer surface of the particle is a highly specific protein coat that protects the RNA, interacts with a susceptible host cell to ini ...
... whereas the rotaviruses contain double-stranded RNA. Human enteric viruses containing DNA are known, but none have been proven to be transmitted via food or water. The outer surface of the particle is a highly specific protein coat that protects the RNA, interacts with a susceptible host cell to ini ...
Ebola - DevelopmentEducation.ie
... hasten their death. This misinformation means that people who are diagnosed sometimes flee, rejecting the treatment that might save their lives Changing behaviours: Concern is also warning locals not to eat bush meat from the likes of monkeys and particularly fruit bats who act as the host of the Eb ...
... hasten their death. This misinformation means that people who are diagnosed sometimes flee, rejecting the treatment that might save their lives Changing behaviours: Concern is also warning locals not to eat bush meat from the likes of monkeys and particularly fruit bats who act as the host of the Eb ...
Heartland Virus–Associated Death in Tennessee
... failure. HRTV antigen was detected by immunohistochemistry in a bone marrow biopsy collected from one of the first casepatients on hospital day 2, whereas the current patient had HRTV antigen detected at autopsy (hospital day 15) in lymph nodes and spleen, but notably not bone marrow, suggesting that ...
... failure. HRTV antigen was detected by immunohistochemistry in a bone marrow biopsy collected from one of the first casepatients on hospital day 2, whereas the current patient had HRTV antigen detected at autopsy (hospital day 15) in lymph nodes and spleen, but notably not bone marrow, suggesting that ...
Five postulates for resolving outbreaks of infectious disease
... the isolation and characterization of a demonstrably identical pathogenic strain from every case, but in practice this is rarely achieved. Even if the meaning of the term ‘isolate’ is widened from the successful culture of a micro-organism to include detection of segments of its genome or of a speci ...
... the isolation and characterization of a demonstrably identical pathogenic strain from every case, but in practice this is rarely achieved. Even if the meaning of the term ‘isolate’ is widened from the successful culture of a micro-organism to include detection of segments of its genome or of a speci ...
Sexually Transmitted Infections - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Viral infections can not be treated with antibiotics. Once they are in your system, they are not going away. Any medication taken is for the symptoms only. The virus will still be there. What does it mean to be asymptomatic? It means there may not be any symptoms, but it can still be spread from per ...
... Viral infections can not be treated with antibiotics. Once they are in your system, they are not going away. Any medication taken is for the symptoms only. The virus will still be there. What does it mean to be asymptomatic? It means there may not be any symptoms, but it can still be spread from per ...
PREZCOBIX™ (darunavir/cobicistat)
... program, where darunavir was co-administered with ritonavir 100 mg once or twice daily, the most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 5 percent) of at least moderate intensity (greater than or equal to Grade 2) were diarrhea, nausea, rash, headache, abdominal pain and vomitin ...
... program, where darunavir was co-administered with ritonavir 100 mg once or twice daily, the most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 5 percent) of at least moderate intensity (greater than or equal to Grade 2) were diarrhea, nausea, rash, headache, abdominal pain and vomitin ...
Chronic Hepatitis B Infection - National Medical Research Council
... to hepatitis B virus infection.1 The first edition of the MOH clinical practice guidelines on chronic hepatitis B infection was published in 2003 to provide guidance on the prevention, management and treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection. This second edition of the guidelines updates as well as ...
... to hepatitis B virus infection.1 The first edition of the MOH clinical practice guidelines on chronic hepatitis B infection was published in 2003 to provide guidance on the prevention, management and treatment of chronic hepatitis B infection. This second edition of the guidelines updates as well as ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.