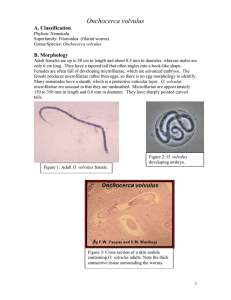
Classification
... A dosage of 150 µg/kg body weight of ivermectin (Mectizan®) is used to slowly eliminate skin microfilariae and also suppress release of microfilariae from the female worm for 1-2 years. Repeated dosages slowly kill the worms. Other drugs that are used but have sever side effects include Di-ethylcarb ...
... A dosage of 150 µg/kg body weight of ivermectin (Mectizan®) is used to slowly eliminate skin microfilariae and also suppress release of microfilariae from the female worm for 1-2 years. Repeated dosages slowly kill the worms. Other drugs that are used but have sever side effects include Di-ethylcarb ...
Answers
... viruses are airborne. (True/False) 4. Hands should always be washed with antiseptic soap in a hospital. (True/False) 5. When using antiseptic soap a quick wash will do since the soap continues to work for long periods. (True/False) 6. Uniforms should be worn directly to work and directly home with n ...
... viruses are airborne. (True/False) 4. Hands should always be washed with antiseptic soap in a hospital. (True/False) 5. When using antiseptic soap a quick wash will do since the soap continues to work for long periods. (True/False) 6. Uniforms should be worn directly to work and directly home with n ...
Citrus Virus Diseases
... lesions in the trunk and main limbs, and a more aggressive form of the disease called psorosis B (PsB) with rampant bark lesions affecting even thin branches and chlorotic blotches in old leaves. In the greenhouse, the PsA and PsB syndromes can be induced by graft inoculating healthy citrus seedling ...
... lesions in the trunk and main limbs, and a more aggressive form of the disease called psorosis B (PsB) with rampant bark lesions affecting even thin branches and chlorotic blotches in old leaves. In the greenhouse, the PsA and PsB syndromes can be induced by graft inoculating healthy citrus seedling ...
Detection of Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Hospitalized Children
... outbreaks have a defined seasonality, occurring mainly during fall and winter while in tropical and semi-tropical countries, it mainly peaks during the rainy season (7, 8). In addition to conventional viral culture techniques and serology, a recently described innovative, polymerase chain reaction ( ...
... outbreaks have a defined seasonality, occurring mainly during fall and winter while in tropical and semi-tropical countries, it mainly peaks during the rainy season (7, 8). In addition to conventional viral culture techniques and serology, a recently described innovative, polymerase chain reaction ( ...
Transmissiion and pathogenesis of Tuberculosis
... • 7-21 days after initial infection – mycobact tuberculosis multiplies within macrophages until the macrophages burst. • Then: – T cells become activated and liberate cytokines, including gamma interferon – the individual becomes tuberculin-positive – activated macrophages may release lytic enzymes ...
... • 7-21 days after initial infection – mycobact tuberculosis multiplies within macrophages until the macrophages burst. • Then: – T cells become activated and liberate cytokines, including gamma interferon – the individual becomes tuberculin-positive – activated macrophages may release lytic enzymes ...
Title: Blood thicker than water: Kinship, disease prevalence and
... members, and is relatively easy to measure, but kin-association represents a further level of population substructure that is harder to measure, particularly when association behaviours happen underground. Here, using epidemiological and molecular genetic data from a wild, high-density population of ...
... members, and is relatively easy to measure, but kin-association represents a further level of population substructure that is harder to measure, particularly when association behaviours happen underground. Here, using epidemiological and molecular genetic data from a wild, high-density population of ...
STD
... DNA test to determine if women with abnormal Pap test results need follow-up Identify women who are infected with ...
... DNA test to determine if women with abnormal Pap test results need follow-up Identify women who are infected with ...
Nursing Tips for April 2006 - LCCC-LPN
... Staph bacteria can live on the skin or in the nose of healthy individuals without causing any symptoms of disease. This is known as colonization and MRSA can also be carried in this way. However, injury to the skin (e.g. scrape or cut) can allow an opportunity for bacteria to enter the skin and caus ...
... Staph bacteria can live on the skin or in the nose of healthy individuals without causing any symptoms of disease. This is known as colonization and MRSA can also be carried in this way. However, injury to the skin (e.g. scrape or cut) can allow an opportunity for bacteria to enter the skin and caus ...
Feline Leukemia Virus (FELV)
... testing negative should be quarantined in separate quarters for several months and retested negative one or two times before being allowed to enter the household. Some modification of the test-and-removal program may be made for households or catteries in which FeLV-positive cats are retained in sep ...
... testing negative should be quarantined in separate quarters for several months and retested negative one or two times before being allowed to enter the household. Some modification of the test-and-removal program may be made for households or catteries in which FeLV-positive cats are retained in sep ...
Salmonella Typhi
... Do infected people need to be isolated or excluded from work or school? Patients with Salmonella Typhi should be excluded from all work involving food handling, day care providers, or health care until their doctor or local health department performs a series of stool cultures to ensure that no Salm ...
... Do infected people need to be isolated or excluded from work or school? Patients with Salmonella Typhi should be excluded from all work involving food handling, day care providers, or health care until their doctor or local health department performs a series of stool cultures to ensure that no Salm ...
Introduction
... immune system response than do live vaccines. • So it is likely to take several additional doses, or booster shots, to maintain a person’s immunity. • This could be a drawback in areas where people don’t have regular access to health care and can’t get booster shots on time. ...
... immune system response than do live vaccines. • So it is likely to take several additional doses, or booster shots, to maintain a person’s immunity. • This could be a drawback in areas where people don’t have regular access to health care and can’t get booster shots on time. ...
Chronic Lung Disease in Children
... • Restrict intake of fluid and Na+ • Diuretics • Bronchodilators • Steroids are almost never indicated • Infection prevention ...
... • Restrict intake of fluid and Na+ • Diuretics • Bronchodilators • Steroids are almost never indicated • Infection prevention ...
EUPHEM report: Summary of work activities - ECDC
... The recent multistate foodborne and travel-related outbreaks caused by the hepatitis A virus reiterate the importance of molecular surveillance for hepatitis A in order to understand global trends in hepatitis A virus strains and to improve the capacity of laboratory response in outbreak situations. ...
... The recent multistate foodborne and travel-related outbreaks caused by the hepatitis A virus reiterate the importance of molecular surveillance for hepatitis A in order to understand global trends in hepatitis A virus strains and to improve the capacity of laboratory response in outbreak situations. ...
ILAR Journal - Laboratory Animal Boards Study Group
... Humans and rhesus macaques develop viremia, liver damage, and can suffer more serious illness with hemorrhagic disease. Paramyxoviruses – single-stranded negative sense RNA viruses Nipah virus was first isolated in 1999, when the virus crosses from bats to pigs. The virus caused encephalitis in in ...
... Humans and rhesus macaques develop viremia, liver damage, and can suffer more serious illness with hemorrhagic disease. Paramyxoviruses – single-stranded negative sense RNA viruses Nipah virus was first isolated in 1999, when the virus crosses from bats to pigs. The virus caused encephalitis in in ...
HPE06_ch21_s3
... Pneumonia • In people who are elderly, or who have heart disease or breathing problems, flu may develop into pneumonia (noo MOHN yuh), a serious infection of the lungs. • Many people die each year from pneumonia, which can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or even fungi. ...
... Pneumonia • In people who are elderly, or who have heart disease or breathing problems, flu may develop into pneumonia (noo MOHN yuh), a serious infection of the lungs. • Many people die each year from pneumonia, which can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or even fungi. ...
Identification of HIV-1 transmission clusters in Southeastern Austria
... N and O are mostly found in West Africa and play a minor role in the worldwide HIV pandemic. Group P, which remains especially rare despite extensive screening, was up to date only found in two non-related patients of Cameroonian origin [4]. Subtypes show a geographical association. The predominant ...
... N and O are mostly found in West Africa and play a minor role in the worldwide HIV pandemic. Group P, which remains especially rare despite extensive screening, was up to date only found in two non-related patients of Cameroonian origin [4]. Subtypes show a geographical association. The predominant ...
THE PREVALENCE OF LATENT TUBERCULOSIS INFECTIONAMONG FINAL YEAR MEDICAL
... the burden of TB. The prevalence of TB in Kenya was 291 per 100,000 population in 2011 and new TB cases were estimated to be 288 per 100,000 population in the same year [1]. Over 9200 deaths were attributed to TB in the same year[1]. HCWs care for patients with open tuberculosis and hence are at ris ...
... the burden of TB. The prevalence of TB in Kenya was 291 per 100,000 population in 2011 and new TB cases were estimated to be 288 per 100,000 population in the same year [1]. Over 9200 deaths were attributed to TB in the same year[1]. HCWs care for patients with open tuberculosis and hence are at ris ...
Role of Housing Modalities on Management and Surveillance
... Axenic and associated animals are classified as gnotobiotic, meaning that they have a known, or completely defined, microflora. Rodents produced in barrier rooms in uncovered cages are not gnotobiotic because of their exposure to microorganisms both in the environment and harbored by people. Thus th ...
... Axenic and associated animals are classified as gnotobiotic, meaning that they have a known, or completely defined, microflora. Rodents produced in barrier rooms in uncovered cages are not gnotobiotic because of their exposure to microorganisms both in the environment and harbored by people. Thus th ...
Infantile respiratory syncytial virus and human rhinovirus infections: respective
... leukocytes and natural killer cells and, importantly, also trigger programmed death of infected airway epithelial cells as a mechanism of limiting viral replication and spread to neighbouring cells [39]. Airway dendritic cells carry viral antigens to local lymph nodes and present them to CD4+ T-cell ...
... leukocytes and natural killer cells and, importantly, also trigger programmed death of infected airway epithelial cells as a mechanism of limiting viral replication and spread to neighbouring cells [39]. Airway dendritic cells carry viral antigens to local lymph nodes and present them to CD4+ T-cell ...
Upper Gastro-intestinal tract: Inflammatory disease
... inflammation. No-one had taken much notice because it was such an outlandish notion. Everyone knew that bacteria couldn't survive in the stomach's acid environment. They'd been taught so at medical school. ...
... inflammation. No-one had taken much notice because it was such an outlandish notion. Everyone knew that bacteria couldn't survive in the stomach's acid environment. They'd been taught so at medical school. ...
the impact of plant age and genetics on curly top disease
... CFH, Worland, or California/Logan, and genotypic variants of these strains (Stenger and McMahon, 1997). Based on sequence similarity and severity on sugarbeet, the three strains are now designated as separate species with the names Beet severe curly top virus (BSCTV, fonnerly CFH), Beet mild curly t ...
... CFH, Worland, or California/Logan, and genotypic variants of these strains (Stenger and McMahon, 1997). Based on sequence similarity and severity on sugarbeet, the three strains are now designated as separate species with the names Beet severe curly top virus (BSCTV, fonnerly CFH), Beet mild curly t ...
Management of Infectious Diseases
... Humans are the only reservoir of infection. 2.7.2. Chickenpox is highly infectious. Characterised by a blister-like itchy rash, appears initially on the face, scalp and trunk, but can spread over the entire body. Other symptoms which may precede the rash by 48 hours include general malaise, fever an ...
... Humans are the only reservoir of infection. 2.7.2. Chickenpox is highly infectious. Characterised by a blister-like itchy rash, appears initially on the face, scalp and trunk, but can spread over the entire body. Other symptoms which may precede the rash by 48 hours include general malaise, fever an ...
No Hoof, No Horse
... wraps are maintained to prevent re-infection until the surgical drainage site has healed. The normal course of treatment varies between 2-3 weeks. White Line Disease Another hoof infection that we diagnose is white line disease or WLD. This infection occurs in the non-sensitive layer of the outer ho ...
... wraps are maintained to prevent re-infection until the surgical drainage site has healed. The normal course of treatment varies between 2-3 weeks. White Line Disease Another hoof infection that we diagnose is white line disease or WLD. This infection occurs in the non-sensitive layer of the outer ho ...
(IVIG) an effective treatment for viral myocarditis?
... Ken-Michael Bayle, D.O. With an incidence of 1 per 100,000 children, myocarditis is a rare condition, but it has a high rate of morbidity and mortality. Myocarditis is estimated to be the cause of death in about 12% of children with sudden cardiac death. Children who develop myocarditis can go on to ...
... Ken-Michael Bayle, D.O. With an incidence of 1 per 100,000 children, myocarditis is a rare condition, but it has a high rate of morbidity and mortality. Myocarditis is estimated to be the cause of death in about 12% of children with sudden cardiac death. Children who develop myocarditis can go on to ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.