`Unroofing` a Rare Toddler Rash
... unknown exposures. Interestingly, thoracic dermatome distribution has been observed in 65% to 75% of cases in two other series.2 ‘Unroofing’ Shingles (Herpes Zoster) Varicella zoster virus is a member of the herpes family that causes two specific clinical syndromes: chickenpox and shingles. In the v ...
... unknown exposures. Interestingly, thoracic dermatome distribution has been observed in 65% to 75% of cases in two other series.2 ‘Unroofing’ Shingles (Herpes Zoster) Varicella zoster virus is a member of the herpes family that causes two specific clinical syndromes: chickenpox and shingles. In the v ...
Horse sickness fever
... possibility that elephants are reservoir hosts of AHSV is questioned as a 100 elephants tested in an endemic AHS area in South Africa had high complement fixing titres to both bluetongue and AHS viruses, but no neutralizing antibodies to these viruses, indicating that the sera of elephants reacts no ...
... possibility that elephants are reservoir hosts of AHSV is questioned as a 100 elephants tested in an endemic AHS area in South Africa had high complement fixing titres to both bluetongue and AHS viruses, but no neutralizing antibodies to these viruses, indicating that the sera of elephants reacts no ...
HIV Pathogenesis and Natural Course of the Disease
... Viral Dynamics of HIV Infection ■ Viral replication is continuous in all stages (early, during clinical latency and in advanced stages) ■ Half life of a virion is about 6 hours, while an infected cell has a life span of 1.6 days ■ Daily about 1010 virions are produced and cleared from the circulati ...
... Viral Dynamics of HIV Infection ■ Viral replication is continuous in all stages (early, during clinical latency and in advanced stages) ■ Half life of a virion is about 6 hours, while an infected cell has a life span of 1.6 days ■ Daily about 1010 virions are produced and cleared from the circulati ...
Lack of CXCR3 Delays the Development of Hepatic Inflammation
... CXCL10 are produced at high levels in mice and humans infected with Leishmania donovani, but their contribution to host resistance against L. donovani is not clear. Here, using CXCR3⫺/⫺ mice, we demonstrate that, although CXCR3 regulates early immune cell trafficking and hepatic inflammation during ...
... CXCL10 are produced at high levels in mice and humans infected with Leishmania donovani, but their contribution to host resistance against L. donovani is not clear. Here, using CXCR3⫺/⫺ mice, we demonstrate that, although CXCR3 regulates early immune cell trafficking and hepatic inflammation during ...
African Horse Sickness
... possibility that elephants are reservoir hosts of AHSV is questioned as a 100 elephants tested in an endemic AHS area in South Africa had high complement fixing titres to both bluetongue and AHS viruses, but no neutralizing antibodies to these viruses, indicating that the sera of elephants reacts no ...
... possibility that elephants are reservoir hosts of AHSV is questioned as a 100 elephants tested in an endemic AHS area in South Africa had high complement fixing titres to both bluetongue and AHS viruses, but no neutralizing antibodies to these viruses, indicating that the sera of elephants reacts no ...
Selection-Driven Evolution of Emergent Dengue
... island. Isolates were derived from years with varying levels of DEN-4 prevalence. Over our sampling period there were marked evolutionary shifts in DEN-4 viral populations circulating in Puerto Rico; viral lineages were temporally clustered and the most common genotype at a particular sampling time ...
... island. Isolates were derived from years with varying levels of DEN-4 prevalence. Over our sampling period there were marked evolutionary shifts in DEN-4 viral populations circulating in Puerto Rico; viral lineages were temporally clustered and the most common genotype at a particular sampling time ...
Date:
... Listeria monocytogenes cross-contamination in a nursery. In press. American Journal of Infection Control 2003;31(5):322-4. 24. Miron D, Lev A, Colodner R, Merzel Y. Compartment syndrome of the calf as the initial manifestation of Vibrio Vulnificus associated severe infection in a child with congenit ...
... Listeria monocytogenes cross-contamination in a nursery. In press. American Journal of Infection Control 2003;31(5):322-4. 24. Miron D, Lev A, Colodner R, Merzel Y. Compartment syndrome of the calf as the initial manifestation of Vibrio Vulnificus associated severe infection in a child with congenit ...
Chronic Bacterial and Viral Infections in Neurodegenerative and
... spite of these findings, others did not find evidence of Mycoplasma species in brain tissue (N=30), CSF, or peripheral blood (N=57) of MS patients.64 Viruses have also been associated with MS. Certain viruses have been found in MS patients, such as HHV6, but these viruses have also been found at low ...
... spite of these findings, others did not find evidence of Mycoplasma species in brain tissue (N=30), CSF, or peripheral blood (N=57) of MS patients.64 Viruses have also been associated with MS. Certain viruses have been found in MS patients, such as HHV6, but these viruses have also been found at low ...
Swine Flu Fact Sheet
... illness (when an infected person is most likely to be shedding virus). However, some persons, especially children, may shed virus for 10 days or longer. Identification as a swine flu influenza A virus requires sending the specimen to CDC for laboratory testing. What can I do to protect myself from ...
... illness (when an infected person is most likely to be shedding virus). However, some persons, especially children, may shed virus for 10 days or longer. Identification as a swine flu influenza A virus requires sending the specimen to CDC for laboratory testing. What can I do to protect myself from ...
lecture 1- Agglutination reactions
... C. Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are usually poorly immunogenic. However, they may become immunogenic when single stranded or when complexed with proteins. D. Lipids In general lipids are non-immunogenic, although they may be haptens. ...
... C. Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are usually poorly immunogenic. However, they may become immunogenic when single stranded or when complexed with proteins. D. Lipids In general lipids are non-immunogenic, although they may be haptens. ...
Quarterly Report on Syphilis in Ireland
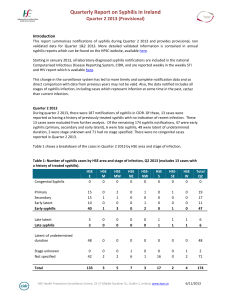
... Table 1 shows a breakdown of the cases in Quarter 2 2013 by HSE area and stage of infection. ...
... Table 1 shows a breakdown of the cases in Quarter 2 2013 by HSE area and stage of infection. ...
Identificatio of CT521 as a Frequent Target of Th1 Cells in Patients
... the central part of the protein was frequently recognized by T cells (63%). Conclusion. We have identifie a novel C. trachomatis antigen, CT521, that is frequently recognized in patients with urogenital C. trachomatis infection. The intracellular bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis remains the most prev ...
... the central part of the protein was frequently recognized by T cells (63%). Conclusion. We have identifie a novel C. trachomatis antigen, CT521, that is frequently recognized in patients with urogenital C. trachomatis infection. The intracellular bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis remains the most prev ...
PHS 398 (Rev. 11/07), Biographical Sketch Format Page
... 27. Ning, S, Huye, L. Pagano, J.S. Regulation of the transcriptional activity of the IRF7 promoter by a pathway independent of interferon signaling. J Biol Chem, 280:12262-70. 2005. 28. Yue, W. Gershburg, E. Pagano, J.S. Epstein-Barr Virus protein kinase phosphorylates EBNA2 and suppresses EBNA2 tra ...
... 27. Ning, S, Huye, L. Pagano, J.S. Regulation of the transcriptional activity of the IRF7 promoter by a pathway independent of interferon signaling. J Biol Chem, 280:12262-70. 2005. 28. Yue, W. Gershburg, E. Pagano, J.S. Epstein-Barr Virus protein kinase phosphorylates EBNA2 and suppresses EBNA2 tra ...
bloodborne pathogens program
... nausea, vomiting, fatigue, low grade fever, pain and swelling in the joints, headache and cough that may occur one to two weeks before the onset of jaundice (yellowing of the skin) and enlargement and tenderness of the liver, which can last for three to four weeks. Fatigue can last up to one year. A ...
... nausea, vomiting, fatigue, low grade fever, pain and swelling in the joints, headache and cough that may occur one to two weeks before the onset of jaundice (yellowing of the skin) and enlargement and tenderness of the liver, which can last for three to four weeks. Fatigue can last up to one year. A ...
Polyclonal Antibody Production Guidelines Introduction Since the
... combining approximately equal volumes of adjuvant and aqueous antigen solution in such a way that the oil becomes the continuous phase. If properly mixed, the antigen will be distributed over a large surface area, which increases the potential for interaction with relevant antigen presenting cells i ...
... combining approximately equal volumes of adjuvant and aqueous antigen solution in such a way that the oil becomes the continuous phase. If properly mixed, the antigen will be distributed over a large surface area, which increases the potential for interaction with relevant antigen presenting cells i ...
ADDITIONAL PRECAUTIONS
... transmission of the suspected/known organism or disease and must be instituted as soon as symptoms suggestive of an infection are noted, not only when diagnosis is confirmed. Education of staff, volunteers, residents, families and visitors is an important aspect of initiating Additional Precautions. ...
... transmission of the suspected/known organism or disease and must be instituted as soon as symptoms suggestive of an infection are noted, not only when diagnosis is confirmed. Education of staff, volunteers, residents, families and visitors is an important aspect of initiating Additional Precautions. ...
BAD BUGS Healthcare Workers and Emerging Antibiotic
... regulator of the production of toxins A and B. Gene tcdE encodes a protein that may be important for the release of toxin from the cell. Gene tcdC is a putative negative regulator of the production of toxins A and B. McDonald et al. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2433-41. ...
... regulator of the production of toxins A and B. Gene tcdE encodes a protein that may be important for the release of toxin from the cell. Gene tcdC is a putative negative regulator of the production of toxins A and B. McDonald et al. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2433-41. ...
Historical Evidence of Widespread Chytrid - Amphibia
... Abstract: Emerging infectious diseases may be contributing to the global decline of amphibian populations. In particular, chytridiomycosis, a cutaneous fungal infection of amphibians caused by the chytrid Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, gained attention in the 1990s as an apparently new pathogen. Th ...
... Abstract: Emerging infectious diseases may be contributing to the global decline of amphibian populations. In particular, chytridiomycosis, a cutaneous fungal infection of amphibians caused by the chytrid Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis, gained attention in the 1990s as an apparently new pathogen. Th ...
Spiral Bacteria in the Human Stomach: The Gastric Helicobacters
... Andre Dubois, M.D., Ph.D. Digestive Diseases Division, Department of Medicine, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Bethesda, Maryland, USA During the past decade, Helicobacter pylori has become recognized as one of the most common human pathogens, colonizing the gastric mucosa of a ...
... Andre Dubois, M.D., Ph.D. Digestive Diseases Division, Department of Medicine, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, Bethesda, Maryland, USA During the past decade, Helicobacter pylori has become recognized as one of the most common human pathogens, colonizing the gastric mucosa of a ...
BMC Infectious Diseases
... Currently three basic diagnostic methods are used in laboratories, including viral isolation, detection of the genomic sequence by a nucleic acid amplification technology assay, and detection of virus-specific antibodies [6]. However, due to labour intensiveness and high costs, the first and the sec ...
... Currently three basic diagnostic methods are used in laboratories, including viral isolation, detection of the genomic sequence by a nucleic acid amplification technology assay, and detection of virus-specific antibodies [6]. However, due to labour intensiveness and high costs, the first and the sec ...
National Congenital CMV Disease Registry
... In some instances kidney and liver function can also be affected. Close monitoring of white blood cell counts, kidney and liver function is therefore necessary during the course of treatment. There may be unexpected long-term effects of treatment, especially on growth and development, and this issue ...
... In some instances kidney and liver function can also be affected. Close monitoring of white blood cell counts, kidney and liver function is therefore necessary during the course of treatment. There may be unexpected long-term effects of treatment, especially on growth and development, and this issue ...
Preventive Health Care for Men Who Have Sex with Men
... Men who have sex with men (MSM) comprise at least 4% of males in the United States. MSM may describe themselves as gay, bisexual, or heterosexual. Because current medical practice does not always facilitate discussion of sexual behaviors, this group of men may face barriers to receiving culturally c ...
... Men who have sex with men (MSM) comprise at least 4% of males in the United States. MSM may describe themselves as gay, bisexual, or heterosexual. Because current medical practice does not always facilitate discussion of sexual behaviors, this group of men may face barriers to receiving culturally c ...
Biosafety Levels - Advanced BioFuels USA
... Biological agents are assigned to biosafety levels (BSL) based on the risk they pose to human health and the environment. Such factors as severity of disease caused by the agent routes of exposure, and virulence are used when determining the most appropriate BSL. The partial list below is provide ...
... Biological agents are assigned to biosafety levels (BSL) based on the risk they pose to human health and the environment. Such factors as severity of disease caused by the agent routes of exposure, and virulence are used when determining the most appropriate BSL. The partial list below is provide ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.