The Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC)
... 6. How many flu vaccines should you get this upcoming year? Not said yet by PHAC, but a seasonal flu shot for sure and maybe a swine flu shot. ...
... 6. How many flu vaccines should you get this upcoming year? Not said yet by PHAC, but a seasonal flu shot for sure and maybe a swine flu shot. ...
HEALTH NOTICE There has been a reported case of RSV
... sneezing, and fever typically develop 1 to 3 days later. Wheezing may also occur. In very young infants, irritability, decreased activity, and breathing difficulties may be the only symptoms of infection. Most otherwise healthy infants infected with RSV do not need to be hospitalized. In most cases, ...
... sneezing, and fever typically develop 1 to 3 days later. Wheezing may also occur. In very young infants, irritability, decreased activity, and breathing difficulties may be the only symptoms of infection. Most otherwise healthy infants infected with RSV do not need to be hospitalized. In most cases, ...
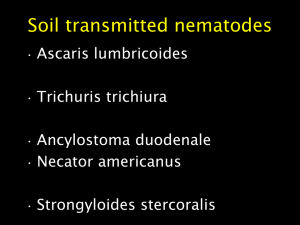
Filariasis
... parasitise humans • Occur in a wide range of habitats lymph glands, deep connective tissue, subcutaneous tissue or mesenteries • Intermediate host or vector (insect) • Adult worms parasites of vertebrate hosts which produce characteristic larvae known as microfilariae ...
... parasitise humans • Occur in a wide range of habitats lymph glands, deep connective tissue, subcutaneous tissue or mesenteries • Intermediate host or vector (insect) • Adult worms parasites of vertebrate hosts which produce characteristic larvae known as microfilariae ...
STD - Illinois State University Department of Psychology
... In more than 90 percent of cases, the infections are harmless and go away without treatment. Related to the occurrence of pre-cancerous cells on the cervix. Persistent HPV infection is found in most cases of cervical cancer. A new vaccine, Gardasil, protects against four HPV types, which together ca ...
... In more than 90 percent of cases, the infections are harmless and go away without treatment. Related to the occurrence of pre-cancerous cells on the cervix. Persistent HPV infection is found in most cases of cervical cancer. A new vaccine, Gardasil, protects against four HPV types, which together ca ...
Prezentace aplikace PowerPoint
... MX inficated at about 15th SV-40 – – first vaccines against polio were contaminated by them – by transmission from tissue cultures from laboratory monkeys – no clinical cases Clinical sy – primary infection is asymptomatic, mild LRTI,cystitis. Reactivation in ID or pregnant BK : uretral stenosis in ...
... MX inficated at about 15th SV-40 – – first vaccines against polio were contaminated by them – by transmission from tissue cultures from laboratory monkeys – no clinical cases Clinical sy – primary infection is asymptomatic, mild LRTI,cystitis. Reactivation in ID or pregnant BK : uretral stenosis in ...
Bio-Terrorism and the Respiratory Therapist
... • Occurrence: 400 cases annually in US, mostly among travelers. 21 million cases worldwide. 5% asymptomatic, but carriers (“Typhoid Mary”) • Presentation: Fever, Chills, Delerium, Malaise; Diarrhea/vomiting uncommon. • DX: Blood/stool C&S, clinical presentation, Recent history (e.g., travel). 12-30% ...
... • Occurrence: 400 cases annually in US, mostly among travelers. 21 million cases worldwide. 5% asymptomatic, but carriers (“Typhoid Mary”) • Presentation: Fever, Chills, Delerium, Malaise; Diarrhea/vomiting uncommon. • DX: Blood/stool C&S, clinical presentation, Recent history (e.g., travel). 12-30% ...
Bio-Terrorism and the Respiratory Therapist
... • Occurrence: 400 cases annually in US, mostly among travelers. 21 million cases worldwide. 5% asymptomatic, but carriers (“Typhoid Mary”) • Presentation: Fever, Chills, Delerium, Malaise; Diarrhea/vomiting uncommon. • DX: Blood/stool C&S, clinical presentation, Recent history (e.g., travel). 12-30% ...
... • Occurrence: 400 cases annually in US, mostly among travelers. 21 million cases worldwide. 5% asymptomatic, but carriers (“Typhoid Mary”) • Presentation: Fever, Chills, Delerium, Malaise; Diarrhea/vomiting uncommon. • DX: Blood/stool C&S, clinical presentation, Recent history (e.g., travel). 12-30% ...
Guidelines - Amoebiasis - 2011 - Alberta Health
... of death in developing countries and is a common cause of diarrhea in travellers and recent immigrants. Invasive amoebiasis is mainly a disease of young adults. It is rarely seen in children under the age of five years. Rates of cyst passage, most often based on the morphology of the cysts, vary acc ...
... of death in developing countries and is a common cause of diarrhea in travellers and recent immigrants. Invasive amoebiasis is mainly a disease of young adults. It is rarely seen in children under the age of five years. Rates of cyst passage, most often based on the morphology of the cysts, vary acc ...
Staphylococcal Infections
... N. meningitidis is a significant cause of bacterial meningitis, particularly among children younger than 2 years of age. The organism is a common colonizer of the oropharynx and is spread by the respiratory route. Approximately 10% of the population is colonized at any one time, and each episode of ...
... N. meningitidis is a significant cause of bacterial meningitis, particularly among children younger than 2 years of age. The organism is a common colonizer of the oropharynx and is spread by the respiratory route. Approximately 10% of the population is colonized at any one time, and each episode of ...
Obstetric and perinatal infections2012
... mothers become infected and then carry the virus. This is preventable by giving the vaccine plus specific immunoglobulin to the newborn. Hepatitis C, in contrast, is not usually transmitted in this way, and <5% of children with carrier mothers are infected. Human milk may contain rubella virus, CMV, ...
... mothers become infected and then carry the virus. This is preventable by giving the vaccine plus specific immunoglobulin to the newborn. Hepatitis C, in contrast, is not usually transmitted in this way, and <5% of children with carrier mothers are infected. Human milk may contain rubella virus, CMV, ...
Home hygiene, pets and other domestic animals
... infected with Salmonella spp. showed that, in 34% of homes, there was also illness in another family member. The data indicated that environmental sources, infected family members and also pets, are more significant risk factors for development of salmonellosis in these children than contaminated fo ...
... infected with Salmonella spp. showed that, in 34% of homes, there was also illness in another family member. The data indicated that environmental sources, infected family members and also pets, are more significant risk factors for development of salmonellosis in these children than contaminated fo ...
zoonotic disease in cats – general information
... Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) and Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) are contagious between cats, but neither of them can infect humans, nor can the human virus infect cats. However, FeLV and FIV suppress the cat's immune system, making him or her more susceptible to zoonotic infections which could ...
... Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) and Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) are contagious between cats, but neither of them can infect humans, nor can the human virus infect cats. However, FeLV and FIV suppress the cat's immune system, making him or her more susceptible to zoonotic infections which could ...
Quick Guide for Clinicians - Communicable Disease Control and
... including making PEP recommendations for antibiotic therapy, vaccination or both. *High risk close contacts for PEP are infants <1 year old, 3rd trimester pregnant women, and persons who may expose them, including health care workers. *Clinicians may be asked to provide PEP and/or vaccinations to hi ...
... including making PEP recommendations for antibiotic therapy, vaccination or both. *High risk close contacts for PEP are infants <1 year old, 3rd trimester pregnant women, and persons who may expose them, including health care workers. *Clinicians may be asked to provide PEP and/or vaccinations to hi ...
transmission of disease
... * Person to person or serial transfer transmission: Def: the spread of a disease agent through contact between infection and susceptible persons. Examples of disease: measles, syphilis, gonorrhea. *mode of transmission The mechanism of transfer of an infective agent from the reservoir to a suscepti ...
... * Person to person or serial transfer transmission: Def: the spread of a disease agent through contact between infection and susceptible persons. Examples of disease: measles, syphilis, gonorrhea. *mode of transmission The mechanism of transfer of an infective agent from the reservoir to a suscepti ...
Herpes B Virus Information for Labs Handling Non
... and cynomolgus monkeys, any of which can harbor latent B virus infection and appear to be natural hosts for the virus. Monkeys infected with B virus usually have no or only mild symptoms, but in humans the infection can be fatal. Most commonly, transmission of B virus infection occurs by animal bite ...
... and cynomolgus monkeys, any of which can harbor latent B virus infection and appear to be natural hosts for the virus. Monkeys infected with B virus usually have no or only mild symptoms, but in humans the infection can be fatal. Most commonly, transmission of B virus infection occurs by animal bite ...
HIV Infection in Children and Adolescents
... host cell genome activation of host cell virion production and release spread to other cells This viremic phase preceeds antibody response and is ...
... host cell genome activation of host cell virion production and release spread to other cells This viremic phase preceeds antibody response and is ...
Trichinosis

Trichinosis, trichinellosis or trichiniasis is a parasitic disease caused by roundworms of the genus Trichinella. Several subspecies cause human disease, but T. spiralis is the most known. Infection may occur without symptoms, while intestinal invasion can cause diarrhea, abdominal pain or vomiting. Larval migration into muscle tissue (one week after being infected) can cause edema of the face or around the eyes, conjunctivitis, fever, muscle pains, splinter hemorrhages, rashes, and peripheral eosinophilia. Life-threatening cases can result in myocarditis, central nervous system involvement, and pneumonitis. Larval encystment in the muscles causes pain and weakness, followed by slow progression of symptoms.Trichinosis is mainly caused by eating undercooked meat containing encysted larval Trichinella. In the stomach the larvae are exposed to stomach acid and pepsin which releases them from their cysts. They then start invading wall of the small intestine, where they develop into adult worms. Females are 2.2 mm in length; males 1.2 mm. The life span in the small intestine is about four weeks. After 1 week, the females release more larvae that migrate to voluntarily controlled muscles where they encyst. Diagnosis is usually made based on symptoms, and is confirmed by serology or by finding encysted or non-encysted larvae in biopsy or autopsy samples.The best way to prevent trichinellosis is to cook meat to safe temperatures. Using food thermometers can make sure the temperature inside the meat is high enough to kill the parasites. The meat should not be tasted until it is completely cooked. Once infection has been verified treatment with antiparasitic drugs such as albendazole or mebendazole should be started at once. A fast response may help kill adult worms and thereby stop further release of larvae. Once the larvae have established in muscle cells, usually by 3 to 4 weeks after infection, treatment may not completely get rid of the infection or symptoms. Both drugs are considered safe but have been associated with side effects such as bone marrow suppression. Patients on longer courses should be monitored though regular blood counts to detect adverse effects quickly and then discontinue treatment. Both medicines should be treated with caution during pregnancy or children under the age of 2 years, but the WHO weighs the benefits of treatment higher than the risks. In addition to antiparasitic medication, treatment with steroids is sometimes required in severe cases.Trichinosis can be acquired by eating both domestic and wild animals, but is not soil-transmitted.