Chapter 6: Infection Control
... your care, as well as other staff members and visitors, from acquiring an infection from someone else. ...
... your care, as well as other staff members and visitors, from acquiring an infection from someone else. ...
Chapter 25 Powerpoint Show
... List the causative agents, modes of transmission, symptoms, and treatments for tapeworms, hydatid disease, pinworms, hookworms, ascariasis, and trichinosis. ...
... List the causative agents, modes of transmission, symptoms, and treatments for tapeworms, hydatid disease, pinworms, hookworms, ascariasis, and trichinosis. ...
why? (1)
... the two viral types. This can be done either by type-specific WB or immunoassay, or PCR. ...
... the two viral types. This can be done either by type-specific WB or immunoassay, or PCR. ...
INFORMATION FOR PARENTS 2016 Recommended Immunizations
... Hepatitis A is an infection in the liver caused by hepatitis A virus. The virus is spread primarily person-to-person through the fecal-oral route. In other words, the virus is taken in by mouth from contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by the feces (stool) of an infected person. Sympto ...
... Hepatitis A is an infection in the liver caused by hepatitis A virus. The virus is spread primarily person-to-person through the fecal-oral route. In other words, the virus is taken in by mouth from contact with objects, food, or drinks contaminated by the feces (stool) of an infected person. Sympto ...
May 15, 2009
... have bees on the farm, it has been a standard practice on the farm for a number of years to apply pollen and we have continued this practice in Orchard 1 and 2. ...
... have bees on the farm, it has been a standard practice on the farm for a number of years to apply pollen and we have continued this practice in Orchard 1 and 2. ...
Clinical Infectious Diseases
... On the cover: Miracle of Hope, 2010, acrylic on canvas, by David Putnam (American, born 1958). Stanford University Positive Care Clinic, Atherton, CA. Reproduced with permission of the artist. Antiretroviral treatment in the last decade of the 20th century marked the turning of the tide in the battl ...
... On the cover: Miracle of Hope, 2010, acrylic on canvas, by David Putnam (American, born 1958). Stanford University Positive Care Clinic, Atherton, CA. Reproduced with permission of the artist. Antiretroviral treatment in the last decade of the 20th century marked the turning of the tide in the battl ...
Chapter Nine – Nutrition Quiz Clues
... Transmitted Infections; with Focus on Reducing Risks and Coping with Chronic Disease and Conditions Know what is the term used for disease causing agents (not virus, bacteria, or germs) ...
... Transmitted Infections; with Focus on Reducing Risks and Coping with Chronic Disease and Conditions Know what is the term used for disease causing agents (not virus, bacteria, or germs) ...
Evasion of Host Immune Surveillance by Hepatitis C Virus: Potential
... the development of liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, or autoimmune diseases such as mixed cryoglobulinemia and glomerulonephritis5. This persistent infection leads to the development of cirrhosis in up to 35% of patients and, as such, end-stage liver disease from HCV infection is the chief ...
... the development of liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, or autoimmune diseases such as mixed cryoglobulinemia and glomerulonephritis5. This persistent infection leads to the development of cirrhosis in up to 35% of patients and, as such, end-stage liver disease from HCV infection is the chief ...
Time to Travel? or living in a hub country?
... • Yellow fever is a viral disease that occurs in tropical regions of Africa and in par ts of South America. ...
... • Yellow fever is a viral disease that occurs in tropical regions of Africa and in par ts of South America. ...
Bloodborne Pathogens
... 35,000 people are infected annually An infected person may carry the virus for years before symptoms appear No cure and no vaccine at present ...
... 35,000 people are infected annually An infected person may carry the virus for years before symptoms appear No cure and no vaccine at present ...
Chicken pox
... A single dose of 0.5 ml sc is recommended for children age 12m-12 yrs who have not had chicken pox . This vaccine had cumulative efficacy at 70-90 % in preventing varicella in children. It is protective if it is given within 3 days of exposure ...
... A single dose of 0.5 ml sc is recommended for children age 12m-12 yrs who have not had chicken pox . This vaccine had cumulative efficacy at 70-90 % in preventing varicella in children. It is protective if it is given within 3 days of exposure ...
MAKE US TB FREE
... infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-the virus that causes AIDS) are two of the strongest risk factors. When someone has both HIV infection and TB infection, the risk of developing active TB is extremely high. IVDUs are at very high risk for developing tuberculosis because of the high in ...
... infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-the virus that causes AIDS) are two of the strongest risk factors. When someone has both HIV infection and TB infection, the risk of developing active TB is extremely high. IVDUs are at very high risk for developing tuberculosis because of the high in ...
Evolving Epidemiology of Hepatitis C Virus in the United States
... The impact of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection on health and medical care in the United States is a major problem for infectious disease physicians. Although the incidence of HCV infection has declined markedly in the past 2 decades, chronic infection in 3 million or more residents now accounts for ...
... The impact of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection on health and medical care in the United States is a major problem for infectious disease physicians. Although the incidence of HCV infection has declined markedly in the past 2 decades, chronic infection in 3 million or more residents now accounts for ...
STDs-v2
... The incubation period varies from 10 to 90 days, and even though no symptoms or lesions are noted during this time, the blood contains spirochetes and is ...
... The incubation period varies from 10 to 90 days, and even though no symptoms or lesions are noted during this time, the blood contains spirochetes and is ...
True - Blood Borne Pathogen Training
... 6. Sterile means free from all living organisms? For sterilization standards 99.99% of organisms have been killed by the process. True 7. The Hepatitis B vaccine greatly reduces the risk from the most contagious blood-borne pathogen. Hepatits is the most contagious BBP. HIV and Hep C are more deadly ...
... 6. Sterile means free from all living organisms? For sterilization standards 99.99% of organisms have been killed by the process. True 7. The Hepatitis B vaccine greatly reduces the risk from the most contagious blood-borne pathogen. Hepatits is the most contagious BBP. HIV and Hep C are more deadly ...
Infection Control 2004
... • After using the restroom • Before eating • If exposure to Bacillus anthracis suspected or proven ...
... • After using the restroom • Before eating • If exposure to Bacillus anthracis suspected or proven ...
What is AIDS? Ho Symptoms of HIV Infection
... How do people become infected with HIV and how to prevent it HIV can be transmitted in the following fluids: semen, vaginal fluid, breast milk and blood. HIV enters the ...
... How do people become infected with HIV and how to prevent it HIV can be transmitted in the following fluids: semen, vaginal fluid, breast milk and blood. HIV enters the ...
Meningococcal Meningitis and Meningococcemia
... Meningococcal meningitis and meningococcemia are rare, but serious infections caused by bacteria called Neisseria meningitides. Bacteria enter the body through the nose and throat and may cause an infection of the bloodstream (meningococcemia) and/or the lining of the brain (meningitis) and spinal c ...
... Meningococcal meningitis and meningococcemia are rare, but serious infections caused by bacteria called Neisseria meningitides. Bacteria enter the body through the nose and throat and may cause an infection of the bloodstream (meningococcemia) and/or the lining of the brain (meningitis) and spinal c ...
Official communique: Chikungunya virus
... The number of cases of Chikungunya an alphavirus transmitted by the mosquitoes Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus, continues to grow. The outbreak began in the Caribbean in December 2013 and until the present nearly 305,000 suspected cases have been reported to the Pan American Health Organization/W ...
... The number of cases of Chikungunya an alphavirus transmitted by the mosquitoes Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus, continues to grow. The outbreak began in the Caribbean in December 2013 and until the present nearly 305,000 suspected cases have been reported to the Pan American Health Organization/W ...
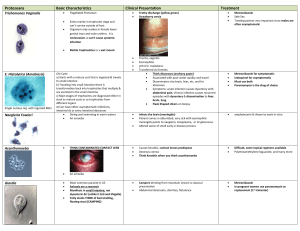
Protozoans
... a) Starts with a mature cyst that is ingested & travels to small intestine b) Traveling into small intestine there is transformation back into trophozites that multiply & are excreted in the small intestine c) Main stages of trophozites are diagnosed either in stool as mature cysts or as trophozites ...
... a) Starts with a mature cyst that is ingested & travels to small intestine b) Traveling into small intestine there is transformation back into trophozites that multiply & are excreted in the small intestine c) Main stages of trophozites are diagnosed either in stool as mature cysts or as trophozites ...
Examples of Emerging and Re-Emerging Infectious Disease
... 1950s-60s: Infectious diseases apparently receding in developed countries Antibiotics and vaccines Pesticides to control mosquitoes Improved surveillance and control measures – internationally ...
... 1950s-60s: Infectious diseases apparently receding in developed countries Antibiotics and vaccines Pesticides to control mosquitoes Improved surveillance and control measures – internationally ...
Community-Based Infectious Disease Clinics: A Tool of Engagement
... public health concern, particularly among people who inject drugs (PWID). HCV is a blood-borne viral infection of the liver affecting more than 170 million worldwide and over 300,000 in Canada, including approximately 60,000 British Columbians [1]. Approximately 20% of these individuals are co-infec ...
... public health concern, particularly among people who inject drugs (PWID). HCV is a blood-borne viral infection of the liver affecting more than 170 million worldwide and over 300,000 in Canada, including approximately 60,000 British Columbians [1]. Approximately 20% of these individuals are co-infec ...
Estimation of the Force of Infection from Current Status Data Using
... University of Antwerp, Epidemiology and Community Medicine, Center for Evaluation of Vaccination, B2610 Antwerp, Belgium Abstract Based on seroprevalence data from rubella, mumps and varicella, we show how the force of infection, the age-specific rate at which susceptible individuals contract infect ...
... University of Antwerp, Epidemiology and Community Medicine, Center for Evaluation of Vaccination, B2610 Antwerp, Belgium Abstract Based on seroprevalence data from rubella, mumps and varicella, we show how the force of infection, the age-specific rate at which susceptible individuals contract infect ...
Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting primarily the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection is often asymptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to scarring of the liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, which is generally apparent after many years. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will go on to develop liver failure, liver cancer, or life-threatening esophageal and gastric varices.HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with intravenous drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, and transfusions. An estimated 150–200 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis C. The existence of hepatitis C – originally identifiable only as a type of non-A non-B hepatitis – was suggested in the 1970s and proven in 1989. Hepatitis C infects only humans and chimpanzees. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The virus persists in the liver in about 85% of those infected. This chronic infection can be treated with medication: the standard therapy is a combination of peginterferon and ribavirin, with either boceprevir or telaprevir added in some cases. Overall, 50–80% of people treated are cured. Those who develop cirrhosis or liver cancer may require a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is the leading reason for liver transplantation, though the virus usually recurs after transplantation. No vaccine against hepatitis C is available. About 343,000 deaths due to liver cancer from hepatitis C occurred in 2013, up from 198,000 in 1990. An additional 358,000 in 2013 occurred due to cirrhosis.