Judgment
... It's meaning all the complex changes in the living tissues due to infection not led to death to living tissues lead in the end to recovery of there changes . The inflammation caused by :a – Different chemical substances e.g. acids and alkaline . b – Toxins or poisoning and other pathogenic microorga ...
... It's meaning all the complex changes in the living tissues due to infection not led to death to living tissues lead in the end to recovery of there changes . The inflammation caused by :a – Different chemical substances e.g. acids and alkaline . b – Toxins or poisoning and other pathogenic microorga ...
Principles of Asepsis - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... chapter, you will learn about disease-causing microorganisms, how the body defends itself against infections, and ways that infections might occur. You will also learn about antibiotic-resistant organisms and the importance of educating patients regarding the proper use of antibiotics. The chapter f ...
... chapter, you will learn about disease-causing microorganisms, how the body defends itself against infections, and ways that infections might occur. You will also learn about antibiotic-resistant organisms and the importance of educating patients regarding the proper use of antibiotics. The chapter f ...
Lesson Plan 1: Infectious Diseases
... 3. Explain to students that they will develop a jingle to teach elementary school children. Emphasize that the jingle should be age appropriate, catchy, and educational. Ask students to follow the instructions on the worksheet and raise their hand if they have questions. 4. Call on groups to share t ...
... 3. Explain to students that they will develop a jingle to teach elementary school children. Emphasize that the jingle should be age appropriate, catchy, and educational. Ask students to follow the instructions on the worksheet and raise their hand if they have questions. 4. Call on groups to share t ...
The CDC says that there is not a limit on how many vaccines the
... have allergic reactions to vaccination. This is very rare but possible. Some vaccinations have potential side effects. The Centers for Disease Control on Prevention (CDC) monitors vaccinations before and after they are licensed and evaluates their safety. They will discontinue or change a vaccine if ...
... have allergic reactions to vaccination. This is very rare but possible. Some vaccinations have potential side effects. The Centers for Disease Control on Prevention (CDC) monitors vaccinations before and after they are licensed and evaluates their safety. They will discontinue or change a vaccine if ...
31st Annual Meeting of the European Society for Pediatric Infectious
... studies and were able to discuss their findings with other junior colleagues and European research group leaders. During the Research Masterclass, some of the young trainees also participated in chairing the scientific sessions. The meeting also provided an opportunity to network with colleagues fro ...
... studies and were able to discuss their findings with other junior colleagues and European research group leaders. During the Research Masterclass, some of the young trainees also participated in chairing the scientific sessions. The meeting also provided an opportunity to network with colleagues fro ...
Combating Infections
... • The sebaceous glands in your skin make an oily substance called sebum. Too much sebum can clog up the hair follicle. This allows bacteria to grow and multiply. • White blood cells rush to fight the infection. ...
... • The sebaceous glands in your skin make an oily substance called sebum. Too much sebum can clog up the hair follicle. This allows bacteria to grow and multiply. • White blood cells rush to fight the infection. ...
Gastrointestinal and hepatobiliary system pathology
... • Leukoplakia is clinical term for a persistent white lesion • Erythroplakia is clinical term for a persistent red lesion • Malignant oral neoplasms ...
... • Leukoplakia is clinical term for a persistent white lesion • Erythroplakia is clinical term for a persistent red lesion • Malignant oral neoplasms ...
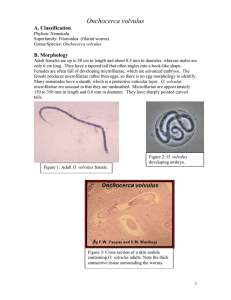
Classification
... be infected. This disease usually causes blindness and disfigurement. Both the adult worms and the microfilariae can cause the disease. The adults generally cause no symptoms, except the growth of subcutaneous nodules called onchocercomas. Onchocercomas are formed from collagen fibers encompassing a ...
... be infected. This disease usually causes blindness and disfigurement. Both the adult worms and the microfilariae can cause the disease. The adults generally cause no symptoms, except the growth of subcutaneous nodules called onchocercomas. Onchocercomas are formed from collagen fibers encompassing a ...
Slide 1
... 3. Causes of re-emerging of the problem of the infectious diseases 4. Microbiological Classification of Infectious Diseases. 5. Means of Transmission of Infectious Diseases. 6. The action of pathogen in infectious process (pathogenicity) 7. What is infectivity ,virulence, Immunogenicity and incubati ...
... 3. Causes of re-emerging of the problem of the infectious diseases 4. Microbiological Classification of Infectious Diseases. 5. Means of Transmission of Infectious Diseases. 6. The action of pathogen in infectious process (pathogenicity) 7. What is infectivity ,virulence, Immunogenicity and incubati ...
Presentation PPT - University of California | Office of The President
... Maryland. 2009-2010: two large outbreaks, one with 3,000 people. Index case recently returned from UK where mumps outbreak was occurring. 2006 multi state outbreak: >6,500 cases. Predominantly affected college-age students in midwest. ...
... Maryland. 2009-2010: two large outbreaks, one with 3,000 people. Index case recently returned from UK where mumps outbreak was occurring. 2006 multi state outbreak: >6,500 cases. Predominantly affected college-age students in midwest. ...
Vice Consul
... patient. Then organise a plan of examination with basic and additional methods, after that prescribe the adequate treatment due to concrete disease. Thus, for case of plague will be necessary to put patient in isolative ward, also student must remember that maximum incubative period of plaque is 6 d ...
... patient. Then organise a plan of examination with basic and additional methods, after that prescribe the adequate treatment due to concrete disease. Thus, for case of plague will be necessary to put patient in isolative ward, also student must remember that maximum incubative period of plaque is 6 d ...
Immunopathology Type III: Immune Complex Disease
... mitigated by affinity purification, which lowers the dose of foreign protein by getting rid of irrelevant stuff; and by chopping off and discarding the Fc part, using only F(ab) or F(ab2). ASK YOURSELF: Would you think there was any advantage to removing the Fc portions of these therapeutic antibodi ...
... mitigated by affinity purification, which lowers the dose of foreign protein by getting rid of irrelevant stuff; and by chopping off and discarding the Fc part, using only F(ab) or F(ab2). ASK YOURSELF: Would you think there was any advantage to removing the Fc portions of these therapeutic antibodi ...
11. Interstitial lung diseases
... In pediatric patients Letterer-Siwe disease Hand-Schüller-Christian disease In adults Histiocytosis X Eosinophilic granuloma ...
... In pediatric patients Letterer-Siwe disease Hand-Schüller-Christian disease In adults Histiocytosis X Eosinophilic granuloma ...
Opportunistic Infections in HIV Disease
... system HIV infects helper T-cells (also known as CD4+ cells) The infected CD4+ cells become “HIV factories” Infected CD4+ cells die because of HIV infection itself and because of the immune response directed at destroying HIV After years of ongoing infection, immune exhaustion leads to massive CD4+ ...
... system HIV infects helper T-cells (also known as CD4+ cells) The infected CD4+ cells become “HIV factories” Infected CD4+ cells die because of HIV infection itself and because of the immune response directed at destroying HIV After years of ongoing infection, immune exhaustion leads to massive CD4+ ...
Tuberculosis Part 2 2016
... Inducers: RIF’s; Anti-seizure drugs; Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTI’s) Inhibitors: Sit on the enzyme preventing it from working: Erythromycins; azols; protease inhibitors; boosters of protease inhibitors i.e. Ritonavir & Cobicistat. In the presence of inhibitors, the drug cle ...
... Inducers: RIF’s; Anti-seizure drugs; Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTI’s) Inhibitors: Sit on the enzyme preventing it from working: Erythromycins; azols; protease inhibitors; boosters of protease inhibitors i.e. Ritonavir & Cobicistat. In the presence of inhibitors, the drug cle ...
Modelling infectious diseases - Faculty of Medicine
... If the reproductive number is smaller than one, the disease will not persist but will manifest itself in outbreaks of varying size triggered by importations of the disease. ...
... If the reproductive number is smaller than one, the disease will not persist but will manifest itself in outbreaks of varying size triggered by importations of the disease. ...
WWS 598 / POP 508
... participation (10%). Reading: Please do the reading – before or after the relevant lecture - but sometime during the course. Topics are likely to come up in the exams. Readings are listed in the schedule and also available on Blackboard. Presentation: There will be a presentation on April 15 – I’ve ...
... participation (10%). Reading: Please do the reading – before or after the relevant lecture - but sometime during the course. Topics are likely to come up in the exams. Readings are listed in the schedule and also available on Blackboard. Presentation: There will be a presentation on April 15 – I’ve ...
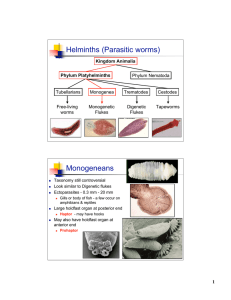
Helminths (Parasitic worms) Monogeneans
... Second Intermediate Host: Aquatic (freshwater) vegetation, including water chestnuts, water caltrope, lotus, and ...
... Second Intermediate Host: Aquatic (freshwater) vegetation, including water chestnuts, water caltrope, lotus, and ...
C-43_Webb - Advocate Health Care
... patterns. This case is important because, as demonstrated by our patient, SLE is an evolving disease and recognizing the varied symptomotology and the differential diagnosis in regards to these patients can lead to sooner diagnosis and mitigation of long term organ dysfunction and failure. There sho ...
... patterns. This case is important because, as demonstrated by our patient, SLE is an evolving disease and recognizing the varied symptomotology and the differential diagnosis in regards to these patients can lead to sooner diagnosis and mitigation of long term organ dysfunction and failure. There sho ...
Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan
... caused by a virus present in blood and other body fluids of infected persons. The HBV infection is caused by a specific virus known as Hepatitis B virus (HBV). The incubation period for this virus can be as long as 176 days with an average of 120. The symptoms may include anorexia, malaise, nausea, ...
... caused by a virus present in blood and other body fluids of infected persons. The HBV infection is caused by a specific virus known as Hepatitis B virus (HBV). The incubation period for this virus can be as long as 176 days with an average of 120. The symptoms may include anorexia, malaise, nausea, ...
Patology pathology of infections hepatitis Atypical pneumonia
... epidemics: Asia, Indian subcontinent (more common than HAV), sub-Saharan Africa, Mexico • Fatal outcome in pregnant (20%) ...
... epidemics: Asia, Indian subcontinent (more common than HAV), sub-Saharan Africa, Mexico • Fatal outcome in pregnant (20%) ...
Zoonosis Update - American Veterinary Medical Association
... rickettsii; however, these are not known to cause clinical illness in humans or laboratory mammals, including dogs and rodents.2 Epidemiology of RMSF in Dogs Rocky Mountain spotted fever tends to be more common in young (≤ 3 years old ) dogs, and > 80% of clinical cases occur in dogs that are freque ...
... rickettsii; however, these are not known to cause clinical illness in humans or laboratory mammals, including dogs and rodents.2 Epidemiology of RMSF in Dogs Rocky Mountain spotted fever tends to be more common in young (≤ 3 years old ) dogs, and > 80% of clinical cases occur in dogs that are freque ...
African trypanosomiasis

African trypanosomiasis or sleeping sickness is a parasitic disease of humans and other animals. It is caused by protozoa of the species Trypanosoma brucei. There are two types that infect humans, Trypanosoma brucei gambiense (T.b.g) and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense (T.b.r.). T.b.g causes over 98% of reported cases. Both are usually transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly and are most common in rural areas.Initially, in the first stage of the disease, there are fevers, headaches, itchiness, and joint pains. This begins one to three weeks after the bite. Weeks to months later the second stage begins with confusion, poor coordination, numbness and trouble sleeping. Diagnosis is via finding the parasite in a blood smear or in the fluid of a lymph node. A lumbar puncture is often needed to tell the difference between first and second stage disease.Prevention of severe disease involves screening the population at risk with blood tests for T.b.g. Treatment is easier when the disease is detected early and before neurological symptoms occur. Treatment of the first stage is with the medications pentamidine or suramin. Treatment of the second stage involves: eflornithine or a combination of nifurtimox and eflornithine for T.b.g. While melarsoprol works for both it is typically only used for T.b.r. due to serious side effects.The disease occurs regularly in some regions of sub-Saharan Africa with the population at risk being about 70 million in 36 countries. As of 2010 it caused around 9,000 deaths per year, down from 34,000 in 1990. An estimated 30,000 people are currently infected with 7000 new infections in 2012. More than 80% of these cases are in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Three major outbreaks have occurred in recent history: one from 1896 to 1906 primarily in Uganda and the Congo Basin and two in 1920 and 1970 in several African countries. Other animals, such as cows, may carry the disease and become infected.