Bell Work
... List two reasons why the population began to grow List the new forms of technology that resulted in more crops ...
... List two reasons why the population began to grow List the new forms of technology that resulted in more crops ...
Feudalism in Medieval Europe
... catholic church Often of noble birth Just below pope in the hierarchy of church Had power within church and social ...
... catholic church Often of noble birth Just below pope in the hierarchy of church Had power within church and social ...
Feudalism and manor is the back bone of medieval Europe Why did
... ◦Farms field (3 sets of farm field so they can do a crop rotation) ...
... ◦Farms field (3 sets of farm field so they can do a crop rotation) ...
Feudal Hierarchy - 8th Grade Social Studies Page
... • either a king or a queen which was typically in power based on lineage • powerful noblemen and women who owned large tracts of land • a person who is given a manor from a lord or king • a specially trained soldier who fights for a lord and vassal • men who learned from a relative how to produce a ...
... • either a king or a queen which was typically in power based on lineage • powerful noblemen and women who owned large tracts of land • a person who is given a manor from a lord or king • a specially trained soldier who fights for a lord and vassal • men who learned from a relative how to produce a ...
10. 13.2 Notes Feudalism
... Women: receive land in a dowry –remains the property of her husband Lords: ...
... Women: receive land in a dowry –remains the property of her husband Lords: ...
THE FEUDAL MODEL Definition
... who granted land was a lord, and the one who received land was a vassal. A fief could include large agricultural lands (and the peasants and serfs who worked them), towns, villages, or even church properties. The vassal was expected to support the lord’s interests on and off the battlefield. In ...
... who granted land was a lord, and the one who received land was a vassal. A fief could include large agricultural lands (and the peasants and serfs who worked them), towns, villages, or even church properties. The vassal was expected to support the lord’s interests on and off the battlefield. In ...
Feudalism
... Social Classes Those who fought – Nobles and Knights Those who prayed – Men and women of the Church Those who worked – Peasants and Serfs ...
... Social Classes Those who fought – Nobles and Knights Those who prayed – Men and women of the Church Those who worked – Peasants and Serfs ...
Chapter 24 Feudal Society
... for the right to farm, worked on a manor. • Serfs and their descendants also worked on a manor, but they were a noble’s property. • While serfs could not be driven off the land and did not have to serve in the army, they could only gain their freedom by escaping or buying their freedom. ...
... for the right to farm, worked on a manor. • Serfs and their descendants also worked on a manor, but they were a noble’s property. • While serfs could not be driven off the land and did not have to serve in the army, they could only gain their freedom by escaping or buying their freedom. ...
Manorial System
... • An economic system in the Middle Ages that was built around large estates called manors • Included a village and the land surrounding it ...
... • An economic system in the Middle Ages that was built around large estates called manors • Included a village and the land surrounding it ...
Feudalism in Europe
... fighters of all. They were the Vikings, or Norsemen. The Vikings raided villages and monasteries. By around the year 1000, though, the Vikings had settled down in many parts of Europe. They adopted Christianity and stopped raiding to become traders and farmers. The Magyars were Turkish nomads. They ...
... fighters of all. They were the Vikings, or Norsemen. The Vikings raided villages and monasteries. By around the year 1000, though, the Vikings had settled down in many parts of Europe. They adopted Christianity and stopped raiding to become traders and farmers. The Magyars were Turkish nomads. They ...
FEUDALISM
... • Developed out of the need for protection from invaders – People wanted land and protection, and there was no central gov’t (Rome had fallen) • Nobles could no longer count on their king for protection, so they had to find a way to defend their own lands – Built castles for defense • Early castles ...
... • Developed out of the need for protection from invaders – People wanted land and protection, and there was no central gov’t (Rome had fallen) • Nobles could no longer count on their king for protection, so they had to find a way to defend their own lands – Built castles for defense • Early castles ...
FEUDALISM
... • Developed out of the need for protection from invaders – People wanted land and protection, and there was no central gov’t (Rome had fallen) • Nobles could no longer count on their king for protection, so they had to find a way to defend their own lands – Built castles for defense • Early castles ...
... • Developed out of the need for protection from invaders – People wanted land and protection, and there was no central gov’t (Rome had fallen) • Nobles could no longer count on their king for protection, so they had to find a way to defend their own lands – Built castles for defense • Early castles ...
Document
... The feudal system was a political and social system. A related system governed medieval economics. This system was called the manorial system because it was built around large estates called manors. Lords, Peasants, and Serfs ...
... The feudal system was a political and social system. A related system governed medieval economics. This system was called the manorial system because it was built around large estates called manors. Lords, Peasants, and Serfs ...
feudalism - TriciaWood
... – Manor lords gave the peasants protection and plots of land for themselves and their families – In return, the peasants had to farm the lord’s land, along with other services • Most of the peasants were serfs – Serfs = peasants who are legally bound to the land, the manor on which they serve – They ...
... – Manor lords gave the peasants protection and plots of land for themselves and their families – In return, the peasants had to farm the lord’s land, along with other services • Most of the peasants were serfs – Serfs = peasants who are legally bound to the land, the manor on which they serve – They ...
Constructing the Pyramid Feudal Power
... • An economic system in the Middle Ages that was built around large estates called manors • Included a village and the land surrounding it ...
... • An economic system in the Middle Ages that was built around large estates called manors • Included a village and the land surrounding it ...
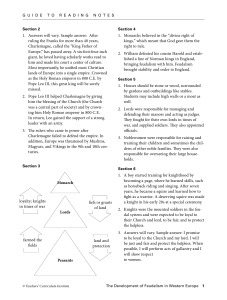
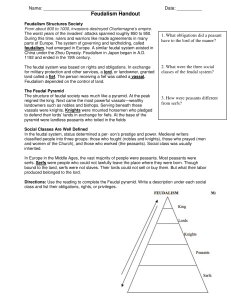
Name: -____ - cloudfront.net
... laborers, and commoners. Most of the work in the feudal estate was performed by laborers called serfs. In return for their work and dedication, the feudal lord would defend the serfs from enemy attacks. Serfs had NO freedom. They belonged to the land and worked for the master who owned the land. ...
... laborers, and commoners. Most of the work in the feudal estate was performed by laborers called serfs. In return for their work and dedication, the feudal lord would defend the serfs from enemy attacks. Serfs had NO freedom. They belonged to the land and worked for the master who owned the land. ...
Feudalism Handout - John Bowne High School
... Social Classes Are Well Defined In the feudal system, status determined a per- son’s prestige and power. Medieval writers classified people into three groups: those who fought (nobles and knights), those who prayed (men and women of the Church), and those who worked (the peasants). Social class was ...
... Social Classes Are Well Defined In the feudal system, status determined a per- son’s prestige and power. Medieval writers classified people into three groups: those who fought (nobles and knights), those who prayed (men and women of the Church), and those who worked (the peasants). Social class was ...
13-2-Feudalism-in
... • Magyars and Muslims Attack from the East and South• Magyars- Nomads attacked from the east – Attacked villages and monasteries – Did not settle in conquered land, took slaves and ...
... • Magyars and Muslims Attack from the East and South• Magyars- Nomads attacked from the east – Attacked villages and monasteries – Did not settle in conquered land, took slaves and ...
II. Feudalism
... II. Feudalism A. The period of invasions allowed local lords to seize power 1. Lords possessed large amounts of land 2. Feudalism developed as a military, political, and economic system based on the holding of land 3. Lords would give small pieces of land (fief) to vassals in exchange for military ...
... II. Feudalism A. The period of invasions allowed local lords to seize power 1. Lords possessed large amounts of land 2. Feudalism developed as a military, political, and economic system based on the holding of land 3. Lords would give small pieces of land (fief) to vassals in exchange for military ...
Ch 7 Notes on Feudalism
... • The manorial system was the economic equivalent of feudalism. Everything was done on the manor. Only iron, salt, and tar imported. • The lord of the manor shared the land with several peasants. His land or 1/3 was called the domain. • The cultivating process used three large fields. Only two were ...
... • The manorial system was the economic equivalent of feudalism. Everything was done on the manor. Only iron, salt, and tar imported. • The lord of the manor shared the land with several peasants. His land or 1/3 was called the domain. • The cultivating process used three large fields. Only two were ...
TCI 2 - Development of Feudalism
... C. a line of Norman kings D. an end to the feudal system 10. Social class in the Middle Ages was determined mainly by A. birth. B. wealth. C. religion. D. education. 11. What is the best title for this list? • Head money • tallage • fee when a woman married A. Gifts from Kings to Vassals B. Taxes Pa ...
... C. a line of Norman kings D. an end to the feudal system 10. Social class in the Middle Ages was determined mainly by A. birth. B. wealth. C. religion. D. education. 11. What is the best title for this list? • Head money • tallage • fee when a woman married A. Gifts from Kings to Vassals B. Taxes Pa ...
My Social Studies Teacher
... The Manorial System • Medieval landholding nobles were a military elite who needed the time to pursue the arts of war. • Peasants worked the lords’ landed estates on the fiefs of the vassals. • These estates provided the needed economic support for the nobles. ...
... The Manorial System • Medieval landholding nobles were a military elite who needed the time to pursue the arts of war. • Peasants worked the lords’ landed estates on the fiefs of the vassals. • These estates provided the needed economic support for the nobles. ...
Serfdom

Serfdom is the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism. It was a condition of bondage, which developed primarily during the High Middle Ages in Europe and lasted in some countries until the mid-19th century.Serfs who occupied a plot of land were required to work for the Lord of the Manor who owned that land, and in return were entitled to protection, justice and the right to exploit certain fields within the manor to maintain their own subsistence. Serfs were often required not only to work on the lord's fields, but also his mines, forests and roads. The manor formed the basic unit of feudal society, and the Lord of the manor and his serfs were bound legally, economically, and socially. Serfs formed the lowest social class of feudal society.The decline of serfdom in Western Europe has sometimes been attributed to the Black Death, which reached Europe in 1347, although the decline had begun before that date. Serfdom became increasingly rare in most of Western Europe after the Renaissance, but conversely, it grew strong in Central and Eastern Europe, where it had previously been less common (this phenomenon was known as ""later serfdom"").In Eastern Europe the institution persisted until the mid-19th century. In the Austrian Empire serfdom was abolished by the 1781 Serfdom Patent; corvée continued to exist until 1848. Serfdom was abolished in Russia in 1861. In Finland, Norway and Sweden, feudalism was not established, and serfdom did not exist; however, serfdom-like institutions did exist in both Denmark (the stavnsbånd, from 1733 to 1788) and its vassal Iceland (the more restrictive vistarband, from 1490 until 1894).According to Joseph R. Strayer, the concept of feudalism can also be applied to the societies of ancient Persia, ancient Mesopotamia, Egypt (Sixth to Twelfth dynasty), Muslim India, China (Zhou Dynasty and end of Han Dynasty) and Japan during the Shogunate. James Lee and Cameron Campbell describe the Chinese Qing Dynasty (1644–1912) as also maintaining a form of serfdom.Tibet is described by Melvyn Goldstein to have had serfdom until 1959, but whether or not the Tibetan form of peasant tenancy that qualified as serfdom was widespread is contested. Bhutan is described by Tashi Wangchuk, a Bhutanese civil servant, as abolishing serfdom officially by 1959, but Wangchuk believes less than or about 10% of poor peasants were in copyhold situations.The United Nations 1956 Supplementary Convention on the Abolition of Slavery also prohibits serfdom as a form of slavery.