Week 27, 2012
... to pay attention to personal, child and infant hygiene in order to reduce the risk of enterovirus infection. If children develop precursor symptoms of enterovirus infection with severe complications, they should be immediately sent to a large hospital for medical attention in order to grasp the best ...
... to pay attention to personal, child and infant hygiene in order to reduce the risk of enterovirus infection. If children develop precursor symptoms of enterovirus infection with severe complications, they should be immediately sent to a large hospital for medical attention in order to grasp the best ...
Task 05 - SHE - Infectious diseases
... A "mysterious" disease began silently spreading in a small town in Victoria on 26 December 2015. It was later identified as an outbreak of Disease X. The first patients who contracted Disease X developed an illness characterized by fever, black stools, and vomiting. All of these patients succumbed t ...
... A "mysterious" disease began silently spreading in a small town in Victoria on 26 December 2015. It was later identified as an outbreak of Disease X. The first patients who contracted Disease X developed an illness characterized by fever, black stools, and vomiting. All of these patients succumbed t ...
Combating endemic diseases of farmed animals for
... colleagues from Queen’s University Belfast and the Agri Food and Biosciences Institute in Northern Ireland, has found that some degree of resistance to Bovine TB is inherited and the team has also identified genetic markers associated with resistance. These results mean that it might be possible to ...
... colleagues from Queen’s University Belfast and the Agri Food and Biosciences Institute in Northern Ireland, has found that some degree of resistance to Bovine TB is inherited and the team has also identified genetic markers associated with resistance. These results mean that it might be possible to ...
lyme disease - City of Pasadena
... Lyme disease usually does not occur until the tick has been attached for 24 hours or more. Both the adults and nymphs can pass the disease to humans. Nymphs are more likely to spread Lyme disease because their small size makes them more difficult to spot. Ticks usually live in cool, moist areas, and ...
... Lyme disease usually does not occur until the tick has been attached for 24 hours or more. Both the adults and nymphs can pass the disease to humans. Nymphs are more likely to spread Lyme disease because their small size makes them more difficult to spot. Ticks usually live in cool, moist areas, and ...
epidemiological overview of tuberculosis - epidat
... 1 infectious sources infected 20 persons during the 2-year period the case remained infectious before death or spontaneous bacteriological conversion. When intervention introduced • Duration of infectiousness reduced • Transmission decreased • Relation between prevalence and incidence disturbed. In ...
... 1 infectious sources infected 20 persons during the 2-year period the case remained infectious before death or spontaneous bacteriological conversion. When intervention introduced • Duration of infectiousness reduced • Transmission decreased • Relation between prevalence and incidence disturbed. In ...
Reading Guide for Week 1 – Bio260
... And we built on that foundation to try to understand how vaccine-preventable diseases like whooping cough (pertussis), influenza, measles, and HAIs like Clostridium difficile, Staphylococcus aureus, and members of the family Enterobacteriaceae are transmitted. We learned about how to describe the ra ...
... And we built on that foundation to try to understand how vaccine-preventable diseases like whooping cough (pertussis), influenza, measles, and HAIs like Clostridium difficile, Staphylococcus aureus, and members of the family Enterobacteriaceae are transmitted. We learned about how to describe the ra ...
Lyme Disease - Mt. Lebanon
... reservoirs for the bacteria that rarely become ill. The first case of Lyme disease in the United States was described in 1969 in a Wisconsin grouse hunter. The disease got its name after an outbreak occurred in 1975 in children from Lyme, Connecticut, but the bacteria responsible for causing the dis ...
... reservoirs for the bacteria that rarely become ill. The first case of Lyme disease in the United States was described in 1969 in a Wisconsin grouse hunter. The disease got its name after an outbreak occurred in 1975 in children from Lyme, Connecticut, but the bacteria responsible for causing the dis ...
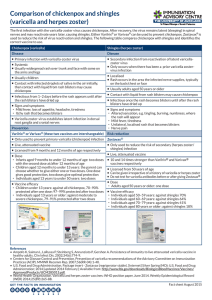
Comparison of chickenpox and shingles (varicella and herpes zoster)
... The first infection with the varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox. After recovery, the virus remains latent (sleeping) in spinal nerves and may reactivate years later, causing shingles. Either Varilrix® or Varivax® can be used to prevent chickenpox. Zostavax® is used to reduce the risk of virus ...
... The first infection with the varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox. After recovery, the virus remains latent (sleeping) in spinal nerves and may reactivate years later, causing shingles. Either Varilrix® or Varivax® can be used to prevent chickenpox. Zostavax® is used to reduce the risk of virus ...
INFLUENZA VACCINE VACCINATION OF PRETERM INFANTS In
... evidence exists of risk from vaccinating pregnant women with inactivated virus or bacterial vaccines or toxoids. Live vaccines pose a theoretical risk to the fetus; live-attenuated virus and liver bacterial vaccines are generally contraindicated during pregnancy. Benefits of vaccinating pregnant wom ...
... evidence exists of risk from vaccinating pregnant women with inactivated virus or bacterial vaccines or toxoids. Live vaccines pose a theoretical risk to the fetus; live-attenuated virus and liver bacterial vaccines are generally contraindicated during pregnancy. Benefits of vaccinating pregnant wom ...
Introduction to Epidemiology and the Modules
... imperfect tests – and the personal decisions that are often necessary. • Uses simple and conditional probabilities and concepts of relative risk (ratio of risk for those with and without genetic risk factor) ...
... imperfect tests – and the personal decisions that are often necessary. • Uses simple and conditional probabilities and concepts of relative risk (ratio of risk for those with and without genetic risk factor) ...
Lecture Outline
... • Typically has a slow progressive rise and a gradual fall. • Might be initiated by a single infected person in a population. ...
... • Typically has a slow progressive rise and a gradual fall. • Might be initiated by a single infected person in a population. ...
Hand, foot and mouth disease Hand, foot and mouth disease
... infection which causes blisters on the inside the mouth, hands, feet and also can be on the buttocks and nappy area. It is most commonly caused by one of the human coxsackieviruses, part of a group of viruses called enteroviruses. If Enterovirus 71 is the particular virus causing hand, foot and mout ...
... infection which causes blisters on the inside the mouth, hands, feet and also can be on the buttocks and nappy area. It is most commonly caused by one of the human coxsackieviruses, part of a group of viruses called enteroviruses. If Enterovirus 71 is the particular virus causing hand, foot and mout ...
Goat Health - Lee County Extension
... • Blocking the vein will make the blood build up inside it and it will stand out like a cord or rope under the skin. • Put the needle into the vein. Check that the needle is in the vein by pulling the plunger of the syringe, back a little when blood should show in the barrel. • Remove your hand from ...
... • Blocking the vein will make the blood build up inside it and it will stand out like a cord or rope under the skin. • Put the needle into the vein. Check that the needle is in the vein by pulling the plunger of the syringe, back a little when blood should show in the barrel. • Remove your hand from ...
course of the disease
... • The vaccine reaction is transitory and will resolve in 4-6 weeks. In the case of false positive after the use of killed vaccines, retest the flock. • The HI test will eliminate the false positive reactions. TREATMENT 1. Marketing broilers with a low incidence of disease may be more economical than ...
... • The vaccine reaction is transitory and will resolve in 4-6 weeks. In the case of false positive after the use of killed vaccines, retest the flock. • The HI test will eliminate the false positive reactions. TREATMENT 1. Marketing broilers with a low incidence of disease may be more economical than ...
Take a shot for good health
... Visit anthem.com for more ways to get healthy — and stay healthy. Certain factual or statistical information was derived from the following sources: 1 Centers for Disease Control, “Immunization Recommendations, United States – 2011,” cdc.gov, updated June 2011, accessed November 2011. 2 National Ins ...
... Visit anthem.com for more ways to get healthy — and stay healthy. Certain factual or statistical information was derived from the following sources: 1 Centers for Disease Control, “Immunization Recommendations, United States – 2011,” cdc.gov, updated June 2011, accessed November 2011. 2 National Ins ...
Epidemiology
... imperfect tests – and the personal decisions that are often necessary. • Uses simple and conditional probabilities and concepts of relative risk (ratio of risk for those with and without genetic risk factor) ...
... imperfect tests – and the personal decisions that are often necessary. • Uses simple and conditional probabilities and concepts of relative risk (ratio of risk for those with and without genetic risk factor) ...
Outer Membrane Vesicle of Bacteria: Friend or Foe?
... has been documented that polysaccharide(PS) (from bacterial capsule or LPS)-protein conjugates are usually immunogens in mice and rabbits as well as in humans. Many studies have shown that these conjugated vaccines elicit humoral and cellular to many pathogens in humans including N. meningitidis, V. ...
... has been documented that polysaccharide(PS) (from bacterial capsule or LPS)-protein conjugates are usually immunogens in mice and rabbits as well as in humans. Many studies have shown that these conjugated vaccines elicit humoral and cellular to many pathogens in humans including N. meningitidis, V. ...
Measles, Mumps and Rubella
... • Cough, chorya, conjunctivitis • Rash is maculopapular lasting 5-4 days • 30% or more who have the disease will have complications ...
... • Cough, chorya, conjunctivitis • Rash is maculopapular lasting 5-4 days • 30% or more who have the disease will have complications ...
this PDF file
... illnesses were prevented between 1994 and 2014 due to vaccination. The measles vaccine has decreased childhood deaths from measles by 74%. The ingredients in vaccines are safe in the amounts used. Ingredients, such as thimerosal, formaldehyde, and aluminum, can be harmful in large doses, but they ar ...
... illnesses were prevented between 1994 and 2014 due to vaccination. The measles vaccine has decreased childhood deaths from measles by 74%. The ingredients in vaccines are safe in the amounts used. Ingredients, such as thimerosal, formaldehyde, and aluminum, can be harmful in large doses, but they ar ...
bacteriology1 review 2016 AY
... occur frequently and cause recurrent disease while acquiring drugresistance. ...
... occur frequently and cause recurrent disease while acquiring drugresistance. ...
Outbreak Management - International Federation of Infection Control
... the occurrence of the disease among persons, place, or time, as well as determining specific attack rates • Formulate recommendations to prevent further transmission ...
... the occurrence of the disease among persons, place, or time, as well as determining specific attack rates • Formulate recommendations to prevent further transmission ...
skin and soft tissue infections
... Primary diseasedisseminationcontrol or active disease (lungs, LNs, pleurisy, CNS—tuberculomas, basilar meningitis, GI, GU— uterine, kidneys, bone—Potts disease, neck LN—Scrofula), HIV, miliary ...
... Primary diseasedisseminationcontrol or active disease (lungs, LNs, pleurisy, CNS—tuberculomas, basilar meningitis, GI, GU— uterine, kidneys, bone—Potts disease, neck LN—Scrofula), HIV, miliary ...
IBC Form - UM Research
... A pathogen that can cause human or animal disease but is unlikely to be a serious hazard to laboratory workers, the community, livestock or the environment Laboratory exposure may cause serious infection. Infectious risk is via direct contact, ingestion or inhalation. Effective treatment, preventive ...
... A pathogen that can cause human or animal disease but is unlikely to be a serious hazard to laboratory workers, the community, livestock or the environment Laboratory exposure may cause serious infection. Infectious risk is via direct contact, ingestion or inhalation. Effective treatment, preventive ...
Meningococcal disease

Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis (also termed meningococcus). It carries a high mortality rate if untreated but is a vaccine-preventable disease. While best known as a cause of meningitis, widespread blood infection can result in sepsis, which is a more damaging and dangerous condition. Meningitis and meningococcemia are major causes of illness, death, and disability in both developed and under-developed countries.There are approximately 2,600 cases of bacterial meningitis per year in the United States, and on average 333,000 cases in developing countries. The case fatality rate ranges between 10 and 20 percent. The incidence of endemic meningococcal disease during the last 13 years ranges from 1 to 5 per 100,000 in developed countries, and from 10 to 25 per 100,000 in developing countries. During epidemics the incidence of meningococcal disease approaches 100 per 100,000. Meningococcal vaccines have sharply reduced the incidence of the disease in developed countries.The disease's pathogenesis is not fully understood. The pathogen colonises a large number of the general population harmlessly, but in some very small percentage of individuals it can invade the blood stream, and the entire body but notably limbs and brain, causing serious illness. Over the past few years, experts have made an intensive effort to understand specific aspects of meningococcal biology and host interactions, however the development of improved treatments and effective vaccines is expected to depend on novel efforts by workers in many different fields.While meningococcal disease is not as contagious as the common cold (which is spread through casual contact), it can be transmitted through saliva and occasionally through close, prolonged general contact with an infected person.