Set 7 Antibiotics - IUP Personal Websites
... were too powerful to administer to a sick patient. By the start of the 20th Century the search was on for a chemical that could kills germs inside a living person without harm. ...
... were too powerful to administer to a sick patient. By the start of the 20th Century the search was on for a chemical that could kills germs inside a living person without harm. ...
Rickettsia
... antibodies against MOMP and LPS antigens; both specific and sensitive Nucleic acid-based tests: PCR + gene sequencing of a variety of genes The traditional Weil-Felix test: not recommended for use ...
... antibodies against MOMP and LPS antigens; both specific and sensitive Nucleic acid-based tests: PCR + gene sequencing of a variety of genes The traditional Weil-Felix test: not recommended for use ...
Lecture 4
... Vaccination in small animals is generally less demanding. In large animals vaccination is is an elaborate task, necessitating prior organization of personnel, vaccines and equipments to be used. The general procedure for cattle vaccination is as follows: a. Beneficiaries should be informed about tim ...
... Vaccination in small animals is generally less demanding. In large animals vaccination is is an elaborate task, necessitating prior organization of personnel, vaccines and equipments to be used. The general procedure for cattle vaccination is as follows: a. Beneficiaries should be informed about tim ...
Climate Change as a Driver for Vector
... A One Health paradigm emphasizes the critical relationship between human health, animal health, and the environment in understanding the drivers of disease emergence ...
... A One Health paradigm emphasizes the critical relationship between human health, animal health, and the environment in understanding the drivers of disease emergence ...
Principles of Communicable Diseases Epidemiology
... cases at a given time expressed as a percent at a given time. Prevalence is a product of incidence x duration of disease, and is of little interest if an infectious disease is of short duration (i.e. measles), but may be of interest if an infectious disease is of long duration (i.e. chronic hepatiti ...
... cases at a given time expressed as a percent at a given time. Prevalence is a product of incidence x duration of disease, and is of little interest if an infectious disease is of short duration (i.e. measles), but may be of interest if an infectious disease is of long duration (i.e. chronic hepatiti ...
High School Infectious Disease Virtual Field Trip
... causing agents. Isolating yourself is the same as a quarantine, which is often used to isolate disease carrying individuals during an outbreak. 2. Immunity: Vaccines provide immunity for an individual against a disease, even after exposure. Using the test tube with the buffer solution, add a couple ...
... causing agents. Isolating yourself is the same as a quarantine, which is often used to isolate disease carrying individuals during an outbreak. 2. Immunity: Vaccines provide immunity for an individual against a disease, even after exposure. Using the test tube with the buffer solution, add a couple ...
Introduction Lecture PowerPoint
... in history a mother knows that the loss of one of her children before maturity is an unlikely event. • Main causes of death include: non-communicable diseases (cancer, ASCVD, obesity, diabetes, hypertension) . • Although much in decline, acutely infectious diseases are spread either by fomites or by ...
... in history a mother knows that the loss of one of her children before maturity is an unlikely event. • Main causes of death include: non-communicable diseases (cancer, ASCVD, obesity, diabetes, hypertension) . • Although much in decline, acutely infectious diseases are spread either by fomites or by ...
Preview Sample 3
... 1. An increasing number of cases of pertussis have been reported to the CDC since the 1980s. The increases are greatest among adolescents (aged 10–19 years), but an increase is also seen among infants younger than 5 months old. 2. A. Catarrhal, lasting one to two weeks, characterized by coryza, mild ...
... 1. An increasing number of cases of pertussis have been reported to the CDC since the 1980s. The increases are greatest among adolescents (aged 10–19 years), but an increase is also seen among infants younger than 5 months old. 2. A. Catarrhal, lasting one to two weeks, characterized by coryza, mild ...
Measles Signage with description
... What are vaccine recommendations during an outbreak in a healthcare setting? b) Serologic evidence of immunity Born in or after 1957: 2 doses vaccine (Indeterminate or equivocal results Born before 1957: At least 1 dose vaccine for those without serological are considered nonimmune) evidence of imm ...
... What are vaccine recommendations during an outbreak in a healthcare setting? b) Serologic evidence of immunity Born in or after 1957: 2 doses vaccine (Indeterminate or equivocal results Born before 1957: At least 1 dose vaccine for those without serological are considered nonimmune) evidence of imm ...
Nowadays, preventable infectious diseases still represent a major
... diseases are not yet accepted as contributing to improving healthy ageing. The absence of sustainability in vaccine programmes does not enable maintenance of life-long protection against such childhood diseases as measles, diphtheria, and pertussis. In the unvaccinated population the incidence of th ...
... diseases are not yet accepted as contributing to improving healthy ageing. The absence of sustainability in vaccine programmes does not enable maintenance of life-long protection against such childhood diseases as measles, diphtheria, and pertussis. In the unvaccinated population the incidence of th ...
Travel Medicine (Powerpoint presentation)
... • 3 doses given over 2-4 weeks; give last dose at least 10 days before travel and observe for 30 min after each dose • Duration of immunity unknown ...
... • 3 doses given over 2-4 weeks; give last dose at least 10 days before travel and observe for 30 min after each dose • Duration of immunity unknown ...
Middle School Infectious Disease Virtual Field Trip
... causing agents. Isolating yourself is the same as a quarantine, which is often used to isolate disease carrying individuals during an outbreak. 2. Immunity: Vaccines provide immunity for an individual against a disease, even after exposure. Using the test tube with the buffer solution, add a couple ...
... causing agents. Isolating yourself is the same as a quarantine, which is often used to isolate disease carrying individuals during an outbreak. 2. Immunity: Vaccines provide immunity for an individual against a disease, even after exposure. Using the test tube with the buffer solution, add a couple ...
Slide 1
... Tracheobronchitis Bronchiolitis Congestive heart failure Myocarditis, pericarditis Complications of sinus, middle ear, musculature Reye’s syndrome – in children Ketoacidosis – in diabetics Acute viral encephalitis – in children Guillain Barre syndrome Gastrointestinal bleeding – in children Decompen ...
... Tracheobronchitis Bronchiolitis Congestive heart failure Myocarditis, pericarditis Complications of sinus, middle ear, musculature Reye’s syndrome – in children Ketoacidosis – in diabetics Acute viral encephalitis – in children Guillain Barre syndrome Gastrointestinal bleeding – in children Decompen ...
Ch.13 Part II
... Persistence of Microbes and Pathologic Conditions • Apparent recovery of host does not always mean the microbe has been removed • Latency – after the initial symptoms in certain chronic diseases, the microbe can periodically become active and produce a recurrent disease; person may or may not shed ...
... Persistence of Microbes and Pathologic Conditions • Apparent recovery of host does not always mean the microbe has been removed • Latency – after the initial symptoms in certain chronic diseases, the microbe can periodically become active and produce a recurrent disease; person may or may not shed ...
how much do you know about fleas, ticks, mites and other biters by Vet
... In seeking to understand how disease occurs, a number of complex, often inter-related, factors must be understood. These include the presence of a disease reservoir that serves to infect the arthropod vector. We must also consider the life cycle of the pathogen, the feeding habits of the vector, cli ...
... In seeking to understand how disease occurs, a number of complex, often inter-related, factors must be understood. These include the presence of a disease reservoir that serves to infect the arthropod vector. We must also consider the life cycle of the pathogen, the feeding habits of the vector, cli ...
Bloodborne Pathogens
... A blood borne pathogen is a microorganism that is present in human blood and can cause disease in humans. These pathogens are spread through contact with infectious body fluids, such as blood, semen, or vaginal secretions. They are not spread by coughing, sneezing, or casual contact. ...
... A blood borne pathogen is a microorganism that is present in human blood and can cause disease in humans. These pathogens are spread through contact with infectious body fluids, such as blood, semen, or vaginal secretions. They are not spread by coughing, sneezing, or casual contact. ...
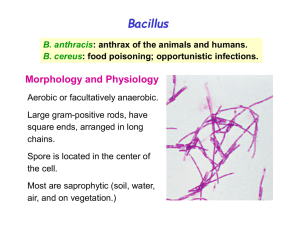
B. anthracis
... hours. The papule rapidly changes into a vesicle, then a pustule, and finally a necrotic eschar. The infection may disseminate, giving rise to septicemia. Inhalation anthrax (wool-sorters’ disease): long incubation time (2 months or more). Mediastinitis (enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes), seps ...
... hours. The papule rapidly changes into a vesicle, then a pustule, and finally a necrotic eschar. The infection may disseminate, giving rise to septicemia. Inhalation anthrax (wool-sorters’ disease): long incubation time (2 months or more). Mediastinitis (enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes), seps ...
Epidemiological Unit Introduction Mumps is an acute viral disease
... At present mumps vaccine is available only in combination with Measles and Rubella vaccines as MMR vaccine in Sri Lanka. Mumps containing vaccine is usually administered between 12 – 18 months of age. Any susceptible individual who is more than one year of age could be immunized with mumps containin ...
... At present mumps vaccine is available only in combination with Measles and Rubella vaccines as MMR vaccine in Sri Lanka. Mumps containing vaccine is usually administered between 12 – 18 months of age. Any susceptible individual who is more than one year of age could be immunized with mumps containin ...
MICROBIO320
... Create your own microbe that causes a dread disease in humans. You may or may not agree with the direction of the company, but you have a ton of student loans to payback. You must work on this project. To be successful in this mission, you must deal effectively with the following details: 1. Identif ...
... Create your own microbe that causes a dread disease in humans. You may or may not agree with the direction of the company, but you have a ton of student loans to payback. You must work on this project. To be successful in this mission, you must deal effectively with the following details: 1. Identif ...
doc - ncssm
... of people moving from one compartment to another. Assume there is a population of N individuals (N is constant over time) through which the flu is moving. The people who have the disease are called Infecteds. The people who do not yet have the disease but may catch it if they interact with an infect ...
... of people moving from one compartment to another. Assume there is a population of N individuals (N is constant over time) through which the flu is moving. The people who have the disease are called Infecteds. The people who do not yet have the disease but may catch it if they interact with an infect ...
PDF - Matheson Center For Health Care Studies
... is spread most commonly through water or food that is contaminated with infected fecal matter. It may incubate for as long as a month. With no cure existing, treatment centers on antibiotics for possible infections, analgesics, and methods to speed up recovery. There were no cases of Polio in Utah i ...
... is spread most commonly through water or food that is contaminated with infected fecal matter. It may incubate for as long as a month. With no cure existing, treatment centers on antibiotics for possible infections, analgesics, and methods to speed up recovery. There were no cases of Polio in Utah i ...
Influenza What is influenza? Influenza is an infection caused by a
... Vaccination is an effective way of avoiding the flu. Unlike other infectious diseases, the flu virus changes and different varieties occur each year. That means that vaccines need to be changed on a yearly basis. This ensures they are effective against the virus type most likely to affect the commun ...
... Vaccination is an effective way of avoiding the flu. Unlike other infectious diseases, the flu virus changes and different varieties occur each year. That means that vaccines need to be changed on a yearly basis. This ensures they are effective against the virus type most likely to affect the commun ...
Meningococcal disease

Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis (also termed meningococcus). It carries a high mortality rate if untreated but is a vaccine-preventable disease. While best known as a cause of meningitis, widespread blood infection can result in sepsis, which is a more damaging and dangerous condition. Meningitis and meningococcemia are major causes of illness, death, and disability in both developed and under-developed countries.There are approximately 2,600 cases of bacterial meningitis per year in the United States, and on average 333,000 cases in developing countries. The case fatality rate ranges between 10 and 20 percent. The incidence of endemic meningococcal disease during the last 13 years ranges from 1 to 5 per 100,000 in developed countries, and from 10 to 25 per 100,000 in developing countries. During epidemics the incidence of meningococcal disease approaches 100 per 100,000. Meningococcal vaccines have sharply reduced the incidence of the disease in developed countries.The disease's pathogenesis is not fully understood. The pathogen colonises a large number of the general population harmlessly, but in some very small percentage of individuals it can invade the blood stream, and the entire body but notably limbs and brain, causing serious illness. Over the past few years, experts have made an intensive effort to understand specific aspects of meningococcal biology and host interactions, however the development of improved treatments and effective vaccines is expected to depend on novel efforts by workers in many different fields.While meningococcal disease is not as contagious as the common cold (which is spread through casual contact), it can be transmitted through saliva and occasionally through close, prolonged general contact with an infected person.