EQUINOCTIAL vLOBE ·
... Fig. 1. Let P be the pole of the ecliptic CV" $ � vY. N the pole of the equator CV" �, cutting the ecliptic in
... Fig. 1. Let P be the pole of the ecliptic CV" $ � vY. N the pole of the equator CV" �, cutting the ecliptic in
a PDF version of the Uniglobe Manual.
... Bearing. The horizontal angle between a reference direction and another direction of interest. It is usually measured from 0° at true north clockwise through 360°. ...
... Bearing. The horizontal angle between a reference direction and another direction of interest. It is usually measured from 0° at true north clockwise through 360°. ...
The motions of the Earth
... Avoid ambiguities in date formats (DD/MM/AAAA vs MM/DD/AAAA) Ease calculations of time intervals Bypass the “October 1582” problem (Julian vs Gregorian calendars). Uses a single positive number to state both date and time with arbitrary accuracy Julian date = “number of days elapsed since January 1s ...
... Avoid ambiguities in date formats (DD/MM/AAAA vs MM/DD/AAAA) Ease calculations of time intervals Bypass the “October 1582” problem (Julian vs Gregorian calendars). Uses a single positive number to state both date and time with arbitrary accuracy Julian date = “number of days elapsed since January 1s ...
THE EVIDENCE FROM KNOSSOS ON THE MINOAN CALENDAR
... celestial events, such as sunrise and sunset at the equinoxes and solstices, from the beginning of the Middle Bronze Age (ca 2000 BCE). Thus it is likely that they had considerable knowledge of the motions of the celestial bodies much ear‐ lier. The debated dates of the Greek const ...
... celestial events, such as sunrise and sunset at the equinoxes and solstices, from the beginning of the Middle Bronze Age (ca 2000 BCE). Thus it is likely that they had considerable knowledge of the motions of the celestial bodies much ear‐ lier. The debated dates of the Greek const ...
SU3150-Astronomy - Michigan Technological University
... the same rate daily keeping their angular separation constant For this reason the Right Ascension and Declination are used as universal coordinates to document star positions in star catalogs that could be used by anyone anywhere in the world Position of the Vernal equinox too changes slightly due t ...
... the same rate daily keeping their angular separation constant For this reason the Right Ascension and Declination are used as universal coordinates to document star positions in star catalogs that could be used by anyone anywhere in the world Position of the Vernal equinox too changes slightly due t ...
The celestial sphere
... ASTR211: COORDINATES AND TIME 2. Diurnal motion of celestial bodies Stars, planets, Sun and Moon all exhibit diurnal motion across celestial sphere. ...
... ASTR211: COORDINATES AND TIME 2. Diurnal motion of celestial bodies Stars, planets, Sun and Moon all exhibit diurnal motion across celestial sphere. ...
3 - Celestial Sphere
... The celestial sphere is a model you can use to describe, explain, and predict the motion of the Sun and the stars in the sky. It models how the sky looks from Earth. Identify the underlined concepts on your celestial sphere: 1) There are imaginary points such as the North and South Celestial Poles ( ...
... The celestial sphere is a model you can use to describe, explain, and predict the motion of the Sun and the stars in the sky. It models how the sky looks from Earth. Identify the underlined concepts on your celestial sphere: 1) There are imaginary points such as the North and South Celestial Poles ( ...
Mathematical Methods in Ancient Astronomy
... character; find simple periodic functions, whose combination describes, within given limits of accuracy, the observed phenomena. While in our harmonic analysis the basic periodic functions admit, at least in principle, a direct geometric interpretation by simple harmonic oscillations, no such interp ...
... character; find simple periodic functions, whose combination describes, within given limits of accuracy, the observed phenomena. While in our harmonic analysis the basic periodic functions admit, at least in principle, a direct geometric interpretation by simple harmonic oscillations, no such interp ...
COORDINATES, TIME, AND THE SKY John Thorstensen
... equal to your latitude. Note that altitude is measured along a great-circle arc which passes through the object and the zenith. The existence of a pole implies the existence of a celestial equator, which is the set of all directions 90 degrees from (either) pole. If you stand on the north or south p ...
... equal to your latitude. Note that altitude is measured along a great-circle arc which passes through the object and the zenith. The existence of a pole implies the existence of a celestial equator, which is the set of all directions 90 degrees from (either) pole. If you stand on the north or south p ...
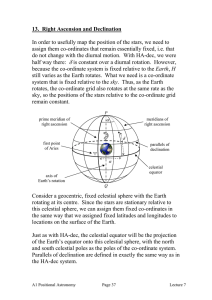
13. Right Ascension and Declination
... • RA-dec co-ordinates are harder to interpret in terms of position in the sky and object visibility than HA-dec coordinates. • RA-dec co-ordinates are still not fixed for objects which exhibit annual motion, i.e. the Sun, planets and other solar system objects. ...
... • RA-dec co-ordinates are harder to interpret in terms of position in the sky and object visibility than HA-dec coordinates. • RA-dec co-ordinates are still not fixed for objects which exhibit annual motion, i.e. the Sun, planets and other solar system objects. ...
night sky a field guide to the heavens
... beyond all expectation, what could have been named that would be more marvelous than these things, or that nations beforehand would less venture to believe could be? Nothing, me thinks: so wonderous strange had been this sight. Yet how little, you know, wearied as all are to satiety with seeing, any ...
... beyond all expectation, what could have been named that would be more marvelous than these things, or that nations beforehand would less venture to believe could be? Nothing, me thinks: so wonderous strange had been this sight. Yet how little, you know, wearied as all are to satiety with seeing, any ...
Package `moonsun`
... name of a planet (appended to dates in result) TRUE if it is inner, FALSE if outer planet period of a planet (tropical years) longitude at epoch 1990 January 0.00 (degrees) longitude of the perihelion (degrees) eccentricity of the orbit semi-major axis of the orbit (AU) inclination of the orbit (deg ...
... name of a planet (appended to dates in result) TRUE if it is inner, FALSE if outer planet period of a planet (tropical years) longitude at epoch 1990 January 0.00 (degrees) longitude of the perihelion (degrees) eccentricity of the orbit semi-major axis of the orbit (AU) inclination of the orbit (deg ...
Histograms Constructed from the Data of 239Pu Alpha
... Earlier, the shape of histograms of the results of measurements obtained in processes of different physical nature had been shown to be determined by cosmophysical factors [1]. Appearance of histograms of a similar shape is repeated periodically: these are the neara-day, near-27-days and annual peri ...
... Earlier, the shape of histograms of the results of measurements obtained in processes of different physical nature had been shown to be determined by cosmophysical factors [1]. Appearance of histograms of a similar shape is repeated periodically: these are the neara-day, near-27-days and annual peri ...
Computation of a comet`s orbit - Iowa Research Online
... time will show how close these approximations are. The reasons for this state of affairs are var ious and to give even a passable explanation of them, ana of the theories by which the many changes of position are taken into account, would require more than the entire length of this paper. I must co ...
... time will show how close these approximations are. The reasons for this state of affairs are var ious and to give even a passable explanation of them, ana of the theories by which the many changes of position are taken into account, would require more than the entire length of this paper. I must co ...
Week 1
... From our perspective on Earth the stars appear embedded on a distant 2-dimensional surface – the Celestial Sphere. ...
... From our perspective on Earth the stars appear embedded on a distant 2-dimensional surface – the Celestial Sphere. ...
presentation - CESAR Project website
... The main objective is to train students in both general science and engineering basics providing them with firsthand experience in astronomy in an IBSE learning environment Observations allow students to learn, with first-order scientific tools, the basics of an astronomical research, aiming to arou ...
... The main objective is to train students in both general science and engineering basics providing them with firsthand experience in astronomy in an IBSE learning environment Observations allow students to learn, with first-order scientific tools, the basics of an astronomical research, aiming to arou ...
The Celestial Sphere - George Mason University
... • The full 360 degrees circle is broken up into 24 hours, so one hour of RA = 15 degrees. • The lines of RA all converge at the celestial poles, so two stars one hour of RA apart will not necessarily be 15 degrees in angular separation on the sky (only if they are on the celestial equator will they ...
... • The full 360 degrees circle is broken up into 24 hours, so one hour of RA = 15 degrees. • The lines of RA all converge at the celestial poles, so two stars one hour of RA apart will not necessarily be 15 degrees in angular separation on the sky (only if they are on the celestial equator will they ...
THE CONSTELLATIONS OF THE ZODIAC G. Iafrate, M. Ramella
... Chaldean people (Babylonians) around 500 BC. This division of the ecliptic into twelve equal zones of celestial longitude ends up being the first known celestial coordinates system. The Babylonian calendar assigned each month to a sign, beginning with the position of the Sun at vernal equinox (March ...
... Chaldean people (Babylonians) around 500 BC. This division of the ecliptic into twelve equal zones of celestial longitude ends up being the first known celestial coordinates system. The Babylonian calendar assigned each month to a sign, beginning with the position of the Sun at vernal equinox (March ...
THE CONSTELLATIONS OF THE ZODIAC
... Chaldean people (Babylonians) around 500 BC. This division of the ecliptic into twelve equal zones of celestial longitude ends up being the first known celestial coordinates system. The Babylonian calendar assigned each month to a sign, beginning with the position of the Sun at vernal equinox (March ...
... Chaldean people (Babylonians) around 500 BC. This division of the ecliptic into twelve equal zones of celestial longitude ends up being the first known celestial coordinates system. The Babylonian calendar assigned each month to a sign, beginning with the position of the Sun at vernal equinox (March ...
FullText - Mediterranean Archaeology and Archaeometry
... point between the two extremes and divide the solar cycle into a warm and a hot season. The vernal and autumnal equinoxes divide the year into two halves, as do the summer and winter solstices (Hughes, 2005). Our findings on the third platform located on the northern terrace provide strong evidence ...
... point between the two extremes and divide the solar cycle into a warm and a hot season. The vernal and autumnal equinoxes divide the year into two halves, as do the summer and winter solstices (Hughes, 2005). Our findings on the third platform located on the northern terrace provide strong evidence ...
Celestial Globes Armillary Spheres
... points furthest away from the ecliptic, above and below. the highest point of a body, i.e., the sun during the summer solstice. a time when the day and night hours are equal, or where the ecliptic path crosses the celestial equator. This occurs twice in a year, spring (vernal), and in winter. ...
... points furthest away from the ecliptic, above and below. the highest point of a body, i.e., the sun during the summer solstice. a time when the day and night hours are equal, or where the ecliptic path crosses the celestial equator. This occurs twice in a year, spring (vernal), and in winter. ...
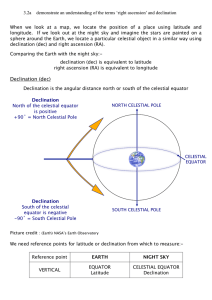
3.2a Right Ascension and Declination
... If a person was able to see the night sky shown above for a full day, the full band of stars would pass in front of them, moving steadily towards the right. The longitude reference point was more difficult. Many countries have laid claim to the Prime Meridian – the Chinese once used a gate from the ...
... If a person was able to see the night sky shown above for a full day, the full band of stars would pass in front of them, moving steadily towards the right. The longitude reference point was more difficult. Many countries have laid claim to the Prime Meridian – the Chinese once used a gate from the ...
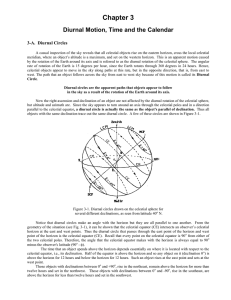
CHAPTER 3, Diurnal Motion - The College of New Jersey
... sense) from the horizon. When an object is below the horizon, it's angular distance from the horizon, or altitude, is assigned a negative value. Objects make one upper transit and one lower transit each day. For an observer in the Northern Hemisphere, both upper and lower transit will occur above th ...
... sense) from the horizon. When an object is below the horizon, it's angular distance from the horizon, or altitude, is assigned a negative value. Objects make one upper transit and one lower transit each day. For an observer in the Northern Hemisphere, both upper and lower transit will occur above th ...
Lecture 1 - Simon P Driver
... • At what local /me would the object rise and set on 1st Feb: – RA overhead on 7th Feb is ~9h (see answer to part1) – RA overhead on 1st Feb is ~8.5h (2hr per month so ~0.5hr per week) ...
... • At what local /me would the object rise and set on 1st Feb: – RA overhead on 7th Feb is ~9h (see answer to part1) – RA overhead on 1st Feb is ~8.5h (2hr per month so ~0.5hr per week) ...
Harappan Astronomy
... astronomy was based on the Sun, the Moon or the stars. There is extensive archaeological evidence that the Harappans traded with cultures in West Asia ((Kenoyer, 1998), Possehl, 2002)). The constellations as we know them today were formalised in Mesopotamia around 3000 BC ((see for example Wikipedia ...
... astronomy was based on the Sun, the Moon or the stars. There is extensive archaeological evidence that the Harappans traded with cultures in West Asia ((Kenoyer, 1998), Possehl, 2002)). The constellations as we know them today were formalised in Mesopotamia around 3000 BC ((see for example Wikipedia ...