MEDICAL BACTERIOLOGY
... 1. Acquire knowledge of human culture and the physical and natural world a. This class focuses on the mechanisms used by bacteria to cause disease in humans and other animals. b. In order to better understand the processes by which infectious disease is produced, we also will discuss the role of the ...
... 1. Acquire knowledge of human culture and the physical and natural world a. This class focuses on the mechanisms used by bacteria to cause disease in humans and other animals. b. In order to better understand the processes by which infectious disease is produced, we also will discuss the role of the ...
Ferrell
... leading infectious cause of blindness. The disease spreads from person to person by the bite of a blackfly. When a blackfly bites a person who has onchocerciasis, microscopic worm larvae (called microfilariae) in the infected person's skin enter and infect the blackfly. The larvae develop over 2 wee ...
... leading infectious cause of blindness. The disease spreads from person to person by the bite of a blackfly. When a blackfly bites a person who has onchocerciasis, microscopic worm larvae (called microfilariae) in the infected person's skin enter and infect the blackfly. The larvae develop over 2 wee ...
Infection severity - University of Georgia
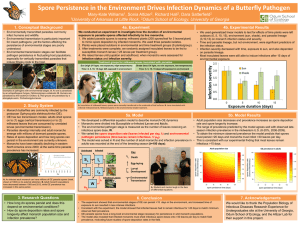
... 1. We added parasite spores to swamp milkweed plants (200 spores/leaf for 5 leaves/plant) to mimic spore deposition by infected monarchs. We used three parasite isolates. 2. Plants were placed outdoors in environmental and time treatment groups (6 plants/group). 3. After treatments were complete, we ...
... 1. We added parasite spores to swamp milkweed plants (200 spores/leaf for 5 leaves/plant) to mimic spore deposition by infected monarchs. We used three parasite isolates. 2. Plants were placed outdoors in environmental and time treatment groups (6 plants/group). 3. After treatments were complete, we ...
Full recovery from Baylisascaris procyonis
... not obtained from our patient because of his benign clinical course; his case thus remains probable, rather than confirmed. Probable cases can be ascertained by a rise in serum or CSF antibody, as detected by an ELISA (11) performed at the Department of Comparative Pathobiology, Purdue University. O ...
... not obtained from our patient because of his benign clinical course; his case thus remains probable, rather than confirmed. Probable cases can be ascertained by a rise in serum or CSF antibody, as detected by an ELISA (11) performed at the Department of Comparative Pathobiology, Purdue University. O ...
Unit E Master Outline
... High-Risk Groups for AIDS – EVERYONE who participates in risky behaviors. Transmission by: 1. Sex with someone who is HIV positive 2. Sharing needles with infected IV drug users 3. At birth from infected mother Cannot be spread by: 1. Casual contact 2. Through air, feces, food, urine or water ...
... High-Risk Groups for AIDS – EVERYONE who participates in risky behaviors. Transmission by: 1. Sex with someone who is HIV positive 2. Sharing needles with infected IV drug users 3. At birth from infected mother Cannot be spread by: 1. Casual contact 2. Through air, feces, food, urine or water ...
Colonization Versus Infection - The Association of Physicians of India
... upper urinary tract is sterile and the difficulty arises from collection of the specimen which may get contaminated with colonizers when passing through the lower urinary tract and urethra. Hence colony counts help in identifying patients who need treatment. Significant bacteriuria is defined as a s ...
... upper urinary tract is sterile and the difficulty arises from collection of the specimen which may get contaminated with colonizers when passing through the lower urinary tract and urethra. Hence colony counts help in identifying patients who need treatment. Significant bacteriuria is defined as a s ...
COMMON GASTROINTESTINAL PROBLEMS
... Esophagitis is a general term for any inflammation, irritation or swelling of the esophagus, which is the tube that leads from the back of the mouth to the stomach. It is frequently caused by a backflow of stomach acid to the esophagus. This is commonly called“heartburn”or GERD (gastroesophageal ref ...
... Esophagitis is a general term for any inflammation, irritation or swelling of the esophagus, which is the tube that leads from the back of the mouth to the stomach. It is frequently caused by a backflow of stomach acid to the esophagus. This is commonly called“heartburn”or GERD (gastroesophageal ref ...
Hepatitis B
... Many people are recommended to receive hepatitis A vaccine, including people at increased risk for exposure to hepatitis A virus infection and people who are more likely to get seriously ill if infected with the virus ...
... Many people are recommended to receive hepatitis A vaccine, including people at increased risk for exposure to hepatitis A virus infection and people who are more likely to get seriously ill if infected with the virus ...
Sources and spread of infection
... population and the virulence of the organism. C/C ratio is low in typhoid or dysentery where cases hugely outnumber carriers. C/C ratio is high say, for Staphyloccus where carriers greatly outnumber cases ...
... population and the virulence of the organism. C/C ratio is low in typhoid or dysentery where cases hugely outnumber carriers. C/C ratio is high say, for Staphyloccus where carriers greatly outnumber cases ...
STDs PPT
... 1. Most people with an STD experience painful symptoms. False. Most people who are infected with an STD, do not notice any symptoms until they visit their doctor or suffer from infertility. 2. Abstinence is the best way to prevent STDs. True. Abstinence from sexual intercourse is the most effective ...
... 1. Most people with an STD experience painful symptoms. False. Most people who are infected with an STD, do not notice any symptoms until they visit their doctor or suffer from infertility. 2. Abstinence is the best way to prevent STDs. True. Abstinence from sexual intercourse is the most effective ...
Part 2
... Estimate rates of infections and cryptic infections from observations Test management strategies based on the detection of symptomatic individuals ...
... Estimate rates of infections and cryptic infections from observations Test management strategies based on the detection of symptomatic individuals ...
Infectious disease control in the workplace
... Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) are acquired from close contact with an infected person's body fluids. Some examples include administering first aid, sharing needles, unprotected sexual contact, blood transfusions (rarely), tattooing or piercing. Prevention for the bloodborne diseases includes effectiv ...
... Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) are acquired from close contact with an infected person's body fluids. Some examples include administering first aid, sharing needles, unprotected sexual contact, blood transfusions (rarely), tattooing or piercing. Prevention for the bloodborne diseases includes effectiv ...
Tickborne Diseases - Alabama Department of Public Health
... rickettsiosis, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, southern tick-associated rash illness, and tularemia. What are the symptoms? Many tickborne diseases have similar signs and symptoms, which include fever/chills, aches and pains, and rash. Rashes may appear as circular, “bull’s eye,” skin ulcer, gener ...
... rickettsiosis, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, southern tick-associated rash illness, and tularemia. What are the symptoms? Many tickborne diseases have similar signs and symptoms, which include fever/chills, aches and pains, and rash. Rashes may appear as circular, “bull’s eye,” skin ulcer, gener ...
5._Malabsorption
... small intestinal mucosa. The later release gamma interferon and activate the release of metalloproteinases that can damage the intestinal mucosa. ...
... small intestinal mucosa. The later release gamma interferon and activate the release of metalloproteinases that can damage the intestinal mucosa. ...
RT Infections II
... Also needs to be on buffered medium (pH restrictions) Slow growth (2-5 days) o PCR: used by reference lab for identification (most human infections caused by Philadelphia strain) o Microscopic exam of tissue required: since Gram stain not useful ...
... Also needs to be on buffered medium (pH restrictions) Slow growth (2-5 days) o PCR: used by reference lab for identification (most human infections caused by Philadelphia strain) o Microscopic exam of tissue required: since Gram stain not useful ...
Infectious disease
... generally found in a particular area; malaria, for example, is said to be endemic to tropical and subtropical regions. This use differs from that of the related word "epidemic" in that it indicates a more or less constant presence in a particular population or area rather than a sudden, severe outbr ...
... generally found in a particular area; malaria, for example, is said to be endemic to tropical and subtropical regions. This use differs from that of the related word "epidemic" in that it indicates a more or less constant presence in a particular population or area rather than a sudden, severe outbr ...
Lecture 22
... • Symptoms: Blurred vision occurs in 1 to 2 days; progressive flaccid paralysis follows for 1 to 10 days, possibly resulting in death from respiratory and cardiac failure. • Several serological types of botulinal toxin - differed in their virulence – The toxin is heat labile and is destroyed by boil ...
... • Symptoms: Blurred vision occurs in 1 to 2 days; progressive flaccid paralysis follows for 1 to 10 days, possibly resulting in death from respiratory and cardiac failure. • Several serological types of botulinal toxin - differed in their virulence – The toxin is heat labile and is destroyed by boil ...
Problem 06- Fever
... organ infection. Varicella zoster (Chicken pox): o Respiratory spread, infectious -2 to +5 days, exclude from school until lesions crust, almost always symptomatic o Fever, Rash: Papules → Vesicles → Pustules → Crusts o Complications: Secondary bacterial infection (staph/ strep), may lead to necro ...
... organ infection. Varicella zoster (Chicken pox): o Respiratory spread, infectious -2 to +5 days, exclude from school until lesions crust, almost always symptomatic o Fever, Rash: Papules → Vesicles → Pustules → Crusts o Complications: Secondary bacterial infection (staph/ strep), may lead to necro ...
Schistosomiasis

Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharzia, snail fever, and Katayama fever, is a disease caused by parasitic worms of the Schistosoma type. It may infect the urinary tract or the intestines. Signs and symptoms may include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody stool, or blood in the urine. In those who have been infected for a long time, liver damage, kidney failure, infertility, or bladder cancer may occur. In children it may cause poor growth and learning difficulty.The disease is spread by contact with water contaminated with the parasites. These parasites are released from infected freshwater snails. The disease is especially common among children in developing countries as they are more likely to play in contaminated water. Other high risk groups include farmers, fishermen, and people using unclean water for their daily chores. It belongs to the group of helminth infections. Diagnosis is by finding the eggs of the parasite in a person's urine or stool. It can also be confirmed by finding antibodies against the disease in the blood.Methods to prevent the disease include improving access to clean water and reducing the number of snails. In areas where the disease is common entire groups may be treated all at once and yearly with the medication praziquantel. This is done to decrease the number of people infected and therefore decrease the spread of the disease. Praziquantel is also the treatment recommended by the World Health Organization for those who are known to be infected.Schistosomiasis affects almost 210 million people worldwide, and an estimated 12,000 to 200,000 people die from it a year. The disease is most commonly found in Africa, as well as Asia and South America. Around 700 million people, in more than 70 countries, live in areas where the disease is common. Schistosomiasis is second only to malaria, as a parasitic disease with the greatest economic impact. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease.