IOSR Journal Of Humanities And Social Science (IOSR-JHSS)
... prevalence is highest in sub-Saharan Africa and East Asia. Most people in these regions become infected with the hepatitis B virus during childhood and between 5–10% of the adult population are chronically infected. In the Middle East and the Indian subcontinent, an estimated 2–5% of the general pop ...
... prevalence is highest in sub-Saharan Africa and East Asia. Most people in these regions become infected with the hepatitis B virus during childhood and between 5–10% of the adult population are chronically infected. In the Middle East and the Indian subcontinent, an estimated 2–5% of the general pop ...
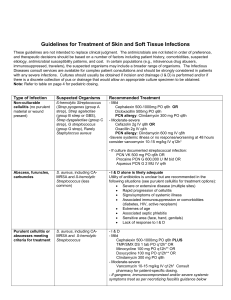
Institutional guidelines for treatment of skin and soft tissue infections
... These guidelines are not intended to replace clinical judgment. The antimicrobials are not listed in order of preference, and therapeutic decisions should be based on a number of factors including patient history, comorbidities, suspected etiology, antimicrobial susceptibility patterns, and cost. In ...
... These guidelines are not intended to replace clinical judgment. The antimicrobials are not listed in order of preference, and therapeutic decisions should be based on a number of factors including patient history, comorbidities, suspected etiology, antimicrobial susceptibility patterns, and cost. In ...
Bloodborne Pathogens Agenda
... HBV can survive for at least one week in dried blood Symptoms can occur 19 months after ...
... HBV can survive for at least one week in dried blood Symptoms can occur 19 months after ...
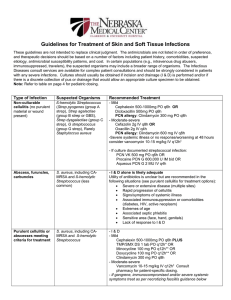
Institutional guidelines for treatment of skin and soft tissue infections
... These guidelines are not intended to replace clinical judgment. The antimicrobials are not listed in order of preference, and therapeutic decisions should be based on a number of factors including patient history, comorbidities, suspected etiology, antimicrobial susceptibility patterns, and cost. In ...
... These guidelines are not intended to replace clinical judgment. The antimicrobials are not listed in order of preference, and therapeutic decisions should be based on a number of factors including patient history, comorbidities, suspected etiology, antimicrobial susceptibility patterns, and cost. In ...
Rotavirus - Immunisation Advisory Centre
... * Diarrhoeal disease is second leading cause of death in children under 5 years (¾ million per year) ...
... * Diarrhoeal disease is second leading cause of death in children under 5 years (¾ million per year) ...
The Nasal Cavity Is a Route for Prion Infection in Hamsters
... that affect animals, including humans. These neurodegenerative diseases are notable for their ability to be transmitted from one animal to another and for their relatively long incubation periods. The natural route(s) of transmission have not been determined. The route of transmission that has been ...
... that affect animals, including humans. These neurodegenerative diseases are notable for their ability to be transmitted from one animal to another and for their relatively long incubation periods. The natural route(s) of transmission have not been determined. The route of transmission that has been ...
Interim Guidelines for Preventing Spread of Severe Acute
... Nearly 90% of SARS cases have occurred in China or Hong Kong. Only 39 probable SARS cases have been reported in the United States and none have died. The symptoms of SARS include a fever and also may include headache, a feeling of discomfort, and body aches. Some people have reported diarrhea also. ...
... Nearly 90% of SARS cases have occurred in China or Hong Kong. Only 39 probable SARS cases have been reported in the United States and none have died. The symptoms of SARS include a fever and also may include headache, a feeling of discomfort, and body aches. Some people have reported diarrhea also. ...
Pandemic
... – Advocacy for high level support is needed. The Ministry of Health should take the technical lead on this effort. – Communication strategies for community involvement in pandemic preparedness should be developed by each Member State. ...
... – Advocacy for high level support is needed. The Ministry of Health should take the technical lead on this effort. – Communication strategies for community involvement in pandemic preparedness should be developed by each Member State. ...
INVESTIGATION OF HANTAVIRUS INFECTIONS AMONG CCHFV
... Hantavirus infections causes two main febrile diseases: hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) and hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome (HCPS). Hantaviruses are transmitted by rodents. In 2009, a hantavirus outbreak occurred in the Western Black Sea region of Turkey. For the last 10 years, the ...
... Hantavirus infections causes two main febrile diseases: hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) and hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome (HCPS). Hantaviruses are transmitted by rodents. In 2009, a hantavirus outbreak occurred in the Western Black Sea region of Turkey. For the last 10 years, the ...
A Review of Potential Infectious Disease Threats to Southern
... agents identified, two have high potential to cause neonatal mortality in the southern resident population. These pathogens, marine Brucella and cetacean poxvirus, were assigned level 2 and unknown virulence ratings. Marine Brucella spp. are Gram negative bacteria closely related to better known ter ...
... agents identified, two have high potential to cause neonatal mortality in the southern resident population. These pathogens, marine Brucella and cetacean poxvirus, were assigned level 2 and unknown virulence ratings. Marine Brucella spp. are Gram negative bacteria closely related to better known ter ...
malaria educational resource for teachers
... days, the parasite will reproduce and be present in the infected person’s blood. If bitten at that point, the parasite goes into the vector to be transmitted to someone else. ...
... days, the parasite will reproduce and be present in the infected person’s blood. If bitten at that point, the parasite goes into the vector to be transmitted to someone else. ...
(2010) A low-pathogenic variant of Infectious Salmon Anemia Virus
... - the method for detection of segment 7 (Plarre et al. 2005 Dis. Aquat. Org., 66, 71-79) which has been adapted to one-step RT-PCR conditions. The validation was conducted using kidney-, heart- and gill tissues from both ISAV infected and healthy Atlantic salmon. ISAV strains represented each of the ...
... - the method for detection of segment 7 (Plarre et al. 2005 Dis. Aquat. Org., 66, 71-79) which has been adapted to one-step RT-PCR conditions. The validation was conducted using kidney-, heart- and gill tissues from both ISAV infected and healthy Atlantic salmon. ISAV strains represented each of the ...
6 Brief Resume of the intended work 6.1 Need for the study Dengue
... It is a major cause of morbidity throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the world. 1 The number of dengue cases has increased over the last three to five years, with recurring epidemics. 4 Dengue is endemic in many parts of India and epidemics are frequently reported from various parts o ...
... It is a major cause of morbidity throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the world. 1 The number of dengue cases has increased over the last three to five years, with recurring epidemics. 4 Dengue is endemic in many parts of India and epidemics are frequently reported from various parts o ...
Current and future burden of communicable diseases in the
... of the European Union and EEA/EFTA countries. The disease burden will be estimated using DALYs (DisabilityAdjusted Life Year), a health gap measure representing years of life lost (YLL) due to premature death and number of life years lost due to disability (YLD). To better represent communicable dis ...
... of the European Union and EEA/EFTA countries. The disease burden will be estimated using DALYs (DisabilityAdjusted Life Year), a health gap measure representing years of life lost (YLL) due to premature death and number of life years lost due to disability (YLD). To better represent communicable dis ...
File - April D. Beresford, RN
... Not long after MRSA was identified in England in 1961, it was found in Japan, Australia, and the USA in 1968 (Enright, Robinson, Randle, Feil, Grundmann & Spratt, 2002). In 2004, the United States was estimated to be the seventh most infected country for MRSA, behind Romania (1), Malta (2), Argentin ...
... Not long after MRSA was identified in England in 1961, it was found in Japan, Australia, and the USA in 1968 (Enright, Robinson, Randle, Feil, Grundmann & Spratt, 2002). In 2004, the United States was estimated to be the seventh most infected country for MRSA, behind Romania (1), Malta (2), Argentin ...
open farms and pet farms in ireland: a practical guide to preventing
... Visiting these venues presents a generally low, but possible, risk of visitors acquiring infection from the animals. However, where practices are poor on individual farms, risks may be higher. Open farms have been associated in the past with a number of outbreaks of infectious disease most notably, ...
... Visiting these venues presents a generally low, but possible, risk of visitors acquiring infection from the animals. However, where practices are poor on individual farms, risks may be higher. Open farms have been associated in the past with a number of outbreaks of infectious disease most notably, ...
Document
... 4. Explain why nosocomial infections are a significant challenge to the medical community. Why is it so difficult to prevent transmission of these diseases to patients? 5. Patients that contract a nosocomial infection may suffer considerably, depending on the illness. Should they be compensated for ...
... 4. Explain why nosocomial infections are a significant challenge to the medical community. Why is it so difficult to prevent transmission of these diseases to patients? 5. Patients that contract a nosocomial infection may suffer considerably, depending on the illness. Should they be compensated for ...
Chapter 15 - Laboratory Animal Boards Study Group
... 71. CDC does not apply “universal precautions” to other body fluids (feces, nasal secretions, sputum, sweat, tears, urine, and vomitus) for HBV and HIV transmission. True or False. 72. Transmission of HBV to gibbons and of non-A, non-B hepatitis to chimpanzee by saliva has been reported. True or Fal ...
... 71. CDC does not apply “universal precautions” to other body fluids (feces, nasal secretions, sputum, sweat, tears, urine, and vomitus) for HBV and HIV transmission. True or False. 72. Transmission of HBV to gibbons and of non-A, non-B hepatitis to chimpanzee by saliva has been reported. True or Fal ...
press kit - Sanofi Pasteur
... are in children under five and the disease can result in paralysis or disability and, in some cases, death. Although polio cannot be cured, vaccination against the disease is highly effective. Since the creation of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) in 1988, polio cases have decreased by ...
... are in children under five and the disease can result in paralysis or disability and, in some cases, death. Although polio cannot be cured, vaccination against the disease is highly effective. Since the creation of the Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) in 1988, polio cases have decreased by ...
feline tick-borne diseases - All Pet Care Animal Hospital
... Illinois, Ohio, and Virginia.16-18 Seasonal activity of ticks is a key component in the transmission of C felis to cats because the number of cytauxzoonosis cases increase when A americanum is more active.19 In addition, outdoor cats living in the wooded habitats, where reservoir hosts and ticks are ...
... Illinois, Ohio, and Virginia.16-18 Seasonal activity of ticks is a key component in the transmission of C felis to cats because the number of cytauxzoonosis cases increase when A americanum is more active.19 In addition, outdoor cats living in the wooded habitats, where reservoir hosts and ticks are ...
OPTIMAL CONTROL OF VECTOR-BORNE
... δ1 , δ2 : per capita recruitment rate of the host and the vector populations, respectively; density dependent factors for the recruitment rates are g(N ) (for the host) and h(P ) (for the vector) populations; β : the probability that susceptible hosts become infected after contact with an infected v ...
... δ1 , δ2 : per capita recruitment rate of the host and the vector populations, respectively; density dependent factors for the recruitment rates are g(N ) (for the host) and h(P ) (for the vector) populations; β : the probability that susceptible hosts become infected after contact with an infected v ...
Dengue, Leishmaniasis, and African Trypanosomiasis
... differentiates DHF/DSS from classic DF. Severity is classified as mild (grades I and II) or severe (grades III and IV), with the ...
... differentiates DHF/DSS from classic DF. Severity is classified as mild (grades I and II) or severe (grades III and IV), with the ...
Lancet. 1997
... schedule were similar to those previously reported. The whole-cell vaccine was highly immunogenic for fimbriae, pertactin, and filamentous haemagglutinin, but had a low antipertussis toxin response. Hypotonic hyporesponsiveness occurred significantly more frequently in the whole-cell group (p < 0.05 ...
... schedule were similar to those previously reported. The whole-cell vaccine was highly immunogenic for fimbriae, pertactin, and filamentous haemagglutinin, but had a low antipertussis toxin response. Hypotonic hyporesponsiveness occurred significantly more frequently in the whole-cell group (p < 0.05 ...
Leptospirosis

Leptospirosis (also known as field fever, rat catcher's yellows, and pretibial fever among others names) is an infection caused by corkscrew-shaped bacteria called Leptospira. Symptoms can range from none to mild such as headaches, muscle pains, and fevers; to severe with bleeding from the lungs or meningitis. If the infection causes the person to turn yellow, have kidney failure and bleeding, it is then known as Weil's disease. If it causes lots of bleeding from the lungs it is known as severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome.Up to 13 different genetic types of Leptospira may cause disease in humans. It is transmitted by both wild and domestic animals. The most common animals that spread the disease are rodents. It is often transmitted by animal urine or by water or soil containing animal urine coming into contact with breaks in the skin, eyes, mouth, or nose. In the developing world the disease most commonly occurs in farmers and poor people who live in cities. In the developed world it most commonly occurs in those involved in outdoor activities in warm and wet areas of the world. Diagnosis is typically by looking for antibodies against the bacteria or finding its DNA in the blood.Efforts to prevent the disease include protective equipment to prevent contact when working with potentially infected animals, washing after this contact, and reducing rodents in areas people live and work. The antibiotic doxycycline, when used in an effort to prevent infection among travellers, is of unclear benefit. Vaccines for animals exist for certain type of Leptospira which may decrease the risk of spread to humans. Treatment if infected is with antibiotics such as: doxycycline, penicillin, or ceftriaxone. Weil's disease and severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome result in death rates greater than 10% and 50%, respectively, even with treatment.It is estimated that seven to ten million people are infected by leptospirosis a year. The number of deaths this causes is not clear. The disease is most common in tropical areas of the world but may occur anywhere. Outbreaks may occur in slums of the developing world. The disease was first described by Weil in 1886 in Germany. Animals who are infected may have no symptoms, mild symptoms, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may vary by the type of animal. In some animals Leptospira live in the reproductive tract, leading to transmission during mating.