Bubonic Plague
... result from inhalation of infectious respiratory droplets expelled from a human or animal that has plague pneumonia. Signs of pneumonic plague include severe pneumonia accompanied by high fever, difficulty breathing and shortness of breath, and often coughing up blood. This form is characterized by ...
... result from inhalation of infectious respiratory droplets expelled from a human or animal that has plague pneumonia. Signs of pneumonic plague include severe pneumonia accompanied by high fever, difficulty breathing and shortness of breath, and often coughing up blood. This form is characterized by ...
Communicable Diseases
... How diseases are spread Direct contact - touching infected area of person Indirect - sneezing, coughing, sharing personal items Contact with vectors (animals and insects) - bites Other contact - eating contaminated foods ...
... How diseases are spread Direct contact - touching infected area of person Indirect - sneezing, coughing, sharing personal items Contact with vectors (animals and insects) - bites Other contact - eating contaminated foods ...
Swedish Vaccination Programme
... is a highly contagious and often difficult viral disease with high fever, cough and rash. Measles can lead to complications such as meningitis, ear infections or bronchitis. There is no treatment for the illness and deaths occur among unvaccinated children. ...
... is a highly contagious and often difficult viral disease with high fever, cough and rash. Measles can lead to complications such as meningitis, ear infections or bronchitis. There is no treatment for the illness and deaths occur among unvaccinated children. ...
Chapter 19
... • If patient doesn’t recover from primary tuberculosis, reactivation of bacilli can occur • Tubercles expand and drain into the bronchial tubes and upper respiratory tract • Gradually the patient experiences more severe symptoms – Violent coughing, greenish or bloody sputum, fever, anorexia, weight ...
... • If patient doesn’t recover from primary tuberculosis, reactivation of bacilli can occur • Tubercles expand and drain into the bronchial tubes and upper respiratory tract • Gradually the patient experiences more severe symptoms – Violent coughing, greenish or bloody sputum, fever, anorexia, weight ...
Communicable Diseases
... How diseases are spread Direct contact - touching infected area of person Indirect - sneezing, coughing, sharing personal items Contact with vectors (animals and insects) - bites Other contact - eating contaminated foods ...
... How diseases are spread Direct contact - touching infected area of person Indirect - sneezing, coughing, sharing personal items Contact with vectors (animals and insects) - bites Other contact - eating contaminated foods ...
Lesson Plan 1: Infectious Diseases
... 1. Understand what infectious disease is and identify common means of transmission. Infectious diseases are caused by dangerous microorganisms called pathogens. They are spread through direct contact (in body fluids), indirect contact (on surfaces and objects), and airborne transmission (e.g., by mo ...
... 1. Understand what infectious disease is and identify common means of transmission. Infectious diseases are caused by dangerous microorganisms called pathogens. They are spread through direct contact (in body fluids), indirect contact (on surfaces and objects), and airborne transmission (e.g., by mo ...
Dynamics of Disease Spread in a Predator-Prey System
... Many examples of a predator-prey interaction among species can be easily observed in ecological system throughout the world, such as a fox-rabbit relation. In a normal life, predator and prey species exhibit regular cycles of abundance or population increase and decrease. The explanation of the fluc ...
... Many examples of a predator-prey interaction among species can be easily observed in ecological system throughout the world, such as a fox-rabbit relation. In a normal life, predator and prey species exhibit regular cycles of abundance or population increase and decrease. The explanation of the fluc ...
Volume 24 - No 10: Tsukamurella
... microbiology laboratory. She began a course of vancomycin and was given a single dose of gentamicin. The Laboratory Diagnosis Four separate blood cultures drawn on admission and over the following two days all were positive for growth at one day with pleomorphic, clumped and branching Gram-positive ...
... microbiology laboratory. She began a course of vancomycin and was given a single dose of gentamicin. The Laboratory Diagnosis Four separate blood cultures drawn on admission and over the following two days all were positive for growth at one day with pleomorphic, clumped and branching Gram-positive ...
Exposure to Shingles (Herpes Zoster)
... Shingles is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. In certain people who previously had chickenpox, the virus can become active again and cause the painful rash called shingles. Incidence of shingles increases with age and immunosuppression. The rash can be in one area (localized) or every ...
... Shingles is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. In certain people who previously had chickenpox, the virus can become active again and cause the painful rash called shingles. Incidence of shingles increases with age and immunosuppression. The rash can be in one area (localized) or every ...
VIRAL HEMORRHAGIC SEPTICEMIA
... for the first time at older ages, the resultant disease is more chronic and has a more prolonged course. Losses can be severe in cold water under crowded, stressful situations, even among older fish. The disease is transmitted by contact and from fish to fish through the water (Rasmussen 1965). If p ...
... for the first time at older ages, the resultant disease is more chronic and has a more prolonged course. Losses can be severe in cold water under crowded, stressful situations, even among older fish. The disease is transmitted by contact and from fish to fish through the water (Rasmussen 1965). If p ...
Biotechnology and Human Health
... • In this activity you will model how an infectious disease is spread. You will then apply a test developed through the use of biotechnology to determine levels of infection. • Each student will receive a container of fluid. One of these containers has been contaminated. • Each student will exchange ...
... • In this activity you will model how an infectious disease is spread. You will then apply a test developed through the use of biotechnology to determine levels of infection. • Each student will receive a container of fluid. One of these containers has been contaminated. • Each student will exchange ...
Corporate Presentation October 2014 NASDAQ: TLOG
... Birinapant Clears Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) In Vivo Decrease in Circulating HBV‐DNA with Birinapant ...
... Birinapant Clears Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) In Vivo Decrease in Circulating HBV‐DNA with Birinapant ...
The Causes of Acute Fever Requiring Hospitalization in Geriatric
... temperatures and increased humidity. Third, their behavior may change, making them susceptible to new infections [15]. 4.2. Infectious Causes of Fever. This study identified lower respiratory tract, urinary tract, and skin and soft tissue infections as the most common infectious causes of fever in t ...
... temperatures and increased humidity. Third, their behavior may change, making them susceptible to new infections [15]. 4.2. Infectious Causes of Fever. This study identified lower respiratory tract, urinary tract, and skin and soft tissue infections as the most common infectious causes of fever in t ...
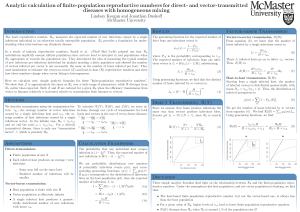
Analytic calculation of finite-population reproductive numbers for
... calculations implicitly assume infinite population sizes, and are hard to interpret in real populations when R0 approaches or exceeds the population size. They introduced the idea of measuring the typical number of new infections per infectious individual for malaria invading a finite population and ...
... calculations implicitly assume infinite population sizes, and are hard to interpret in real populations when R0 approaches or exceeds the population size. They introduced the idea of measuring the typical number of new infections per infectious individual for malaria invading a finite population and ...
Chapter 5- Infection Control Principles and Practices
... cells of a biological organism; needs a host to reproduce (bacteria can reproduce on their own) Cause colds, measles, chicken pox, polio, HIV, hepatitis, gastrointestinal infections… Difficult to treat; there are some vaccines that prevent viruses from growing in the body ...
... cells of a biological organism; needs a host to reproduce (bacteria can reproduce on their own) Cause colds, measles, chicken pox, polio, HIV, hepatitis, gastrointestinal infections… Difficult to treat; there are some vaccines that prevent viruses from growing in the body ...
2015 Tarleton NCD 091113
... Live a enuated vaccine more effec ve in inducing long‐las ng cell‐mediated & humoral immunity Lower dosage and less frequent administra on is required, leading to lower cost; Cheaper vaccines are essen al , as most humans infected with rabies live in the developing world Side effects s ...
... Live a enuated vaccine more effec ve in inducing long‐las ng cell‐mediated & humoral immunity Lower dosage and less frequent administra on is required, leading to lower cost; Cheaper vaccines are essen al , as most humans infected with rabies live in the developing world Side effects s ...
Meningitis Vaccine Waiver Form
... Can meningitis be treated? Bacterial meningitis can be treated with a number of effective antibiotics. It is important, however, that treatment be started early in the course of the disease. Appropriate antibiotic treatment of most common types of bacterial meningitis should reduce the risk of dying ...
... Can meningitis be treated? Bacterial meningitis can be treated with a number of effective antibiotics. It is important, however, that treatment be started early in the course of the disease. Appropriate antibiotic treatment of most common types of bacterial meningitis should reduce the risk of dying ...
Bug of the Month 2012 Rose Plessis
... VZIG as soon as possible, within 96 hours of exposure. VZIG may extend the incubation period to 28 days. Consult Public Health. ...
... VZIG as soon as possible, within 96 hours of exposure. VZIG may extend the incubation period to 28 days. Consult Public Health. ...
Vaccines - British Society for Immunology
... immunity degrades over time and a booster dose may be required to “top up” the level of antibodies. Vaccines are primarily preventative (given before potential exposure to a disease) but some can be effective when delivered a very short time after infection, such as with rabies.1 Importance of vacci ...
... immunity degrades over time and a booster dose may be required to “top up” the level of antibodies. Vaccines are primarily preventative (given before potential exposure to a disease) but some can be effective when delivered a very short time after infection, such as with rabies.1 Importance of vacci ...
How vaccines work.
... work fast enough to prevent the antigen from causing disease, so the child still gets sick. • However, the immune system “remembers” that antigen. If it ever enters the body again, even after many years, the immune system can produce antibodies fast enough to keep it from causing disease a second ti ...
... work fast enough to prevent the antigen from causing disease, so the child still gets sick. • However, the immune system “remembers” that antigen. If it ever enters the body again, even after many years, the immune system can produce antibodies fast enough to keep it from causing disease a second ti ...
Bloodborne Pathogens - University of Montana
... HCV is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States with an estimated 3.2 million people infected ...
... HCV is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States with an estimated 3.2 million people infected ...
Bloodborne Pathogens - University of Montana
... HCV is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States with an estimated 3.2 million people infected ...
... HCV is the most common chronic bloodborne infection in the United States with an estimated 3.2 million people infected ...
Infection prevention and control (IPC) precautions for patients
... • Healthcare workers (HCW): Hand hygiene, surgical mask, and, if splashes onto eyes are anticipated, eye protection (goggles/face shield) • Place patient at least 1 metre (3 feet) from other patients • Request patient and symptomatic accompanying persons to use of tissues when coughing or sneezing a ...
... • Healthcare workers (HCW): Hand hygiene, surgical mask, and, if splashes onto eyes are anticipated, eye protection (goggles/face shield) • Place patient at least 1 metre (3 feet) from other patients • Request patient and symptomatic accompanying persons to use of tissues when coughing or sneezing a ...
How Does Infection Occur?/The Chain of Infection
... 2. Depending on the activity performed on the patient, the nature of the patient’s illness, and the amount of exposure to blood and body fluids, other protective equipment should be worn. E.g. gown and goggles if patient is coughing, bleeding, or has drainage from wounds or body orifices. 3. Needles ...
... 2. Depending on the activity performed on the patient, the nature of the patient’s illness, and the amount of exposure to blood and body fluids, other protective equipment should be worn. E.g. gown and goggles if patient is coughing, bleeding, or has drainage from wounds or body orifices. 3. Needles ...
Leptospirosis

Leptospirosis (also known as field fever, rat catcher's yellows, and pretibial fever among others names) is an infection caused by corkscrew-shaped bacteria called Leptospira. Symptoms can range from none to mild such as headaches, muscle pains, and fevers; to severe with bleeding from the lungs or meningitis. If the infection causes the person to turn yellow, have kidney failure and bleeding, it is then known as Weil's disease. If it causes lots of bleeding from the lungs it is known as severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome.Up to 13 different genetic types of Leptospira may cause disease in humans. It is transmitted by both wild and domestic animals. The most common animals that spread the disease are rodents. It is often transmitted by animal urine or by water or soil containing animal urine coming into contact with breaks in the skin, eyes, mouth, or nose. In the developing world the disease most commonly occurs in farmers and poor people who live in cities. In the developed world it most commonly occurs in those involved in outdoor activities in warm and wet areas of the world. Diagnosis is typically by looking for antibodies against the bacteria or finding its DNA in the blood.Efforts to prevent the disease include protective equipment to prevent contact when working with potentially infected animals, washing after this contact, and reducing rodents in areas people live and work. The antibiotic doxycycline, when used in an effort to prevent infection among travellers, is of unclear benefit. Vaccines for animals exist for certain type of Leptospira which may decrease the risk of spread to humans. Treatment if infected is with antibiotics such as: doxycycline, penicillin, or ceftriaxone. Weil's disease and severe pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome result in death rates greater than 10% and 50%, respectively, even with treatment.It is estimated that seven to ten million people are infected by leptospirosis a year. The number of deaths this causes is not clear. The disease is most common in tropical areas of the world but may occur anywhere. Outbreaks may occur in slums of the developing world. The disease was first described by Weil in 1886 in Germany. Animals who are infected may have no symptoms, mild symptoms, or severe symptoms. Symptoms may vary by the type of animal. In some animals Leptospira live in the reproductive tract, leading to transmission during mating.