Plant and Soil
... Many N2-fixing organisms can turn off nitrogenase activity in the presence of N H ] and turn it on again when the N H 4 is exhausted. One of the most interesting systems for accomplishing this is by covalent modification of one subunit of dinitrogenase reductase by dinitrogenase reductase ADP-ribosy ...
... Many N2-fixing organisms can turn off nitrogenase activity in the presence of N H ] and turn it on again when the N H 4 is exhausted. One of the most interesting systems for accomplishing this is by covalent modification of one subunit of dinitrogenase reductase by dinitrogenase reductase ADP-ribosy ...
AP Biology Exam
... d. Excite groups of muscles uncontrollably e. None of the above 16. Which of the following phyla does not have coelomates? a. Aschelminthes b. Annelida c. Arthropoda d. Mollusca e. None of the above 17. The Ames test is best used to detect ________________. a. Drug resistance b. Mutation c. Bacteria ...
... d. Excite groups of muscles uncontrollably e. None of the above 16. Which of the following phyla does not have coelomates? a. Aschelminthes b. Annelida c. Arthropoda d. Mollusca e. None of the above 17. The Ames test is best used to detect ________________. a. Drug resistance b. Mutation c. Bacteria ...
Fungal denitrification and nitric oxide reductase cytochrome P450nor
... assimilatory nitrate-reducing system is ubiquitously distributed among plants and micro-organisms to provide the nitrogen atoms of nitrate as nutrition for life. Assimilatory and dissimilatory nitrate-reducing systems were previously thought to function independently of one another. Therefore, invol ...
... assimilatory nitrate-reducing system is ubiquitously distributed among plants and micro-organisms to provide the nitrogen atoms of nitrate as nutrition for life. Assimilatory and dissimilatory nitrate-reducing systems were previously thought to function independently of one another. Therefore, invol ...
CHEMISTRY OF p-ELEMENTS - Львівський національний
... respiration. It takes part in all kinds of matter renewal. The reactions of oxygen with lipids, proteins and with glucose for the first time are the source of energy for living organisms. While oxygen (O2) is necessary for life, oxygen as ozone (O3) is highly toxic. On the other hand, ozone is an im ...
... respiration. It takes part in all kinds of matter renewal. The reactions of oxygen with lipids, proteins and with glucose for the first time are the source of energy for living organisms. While oxygen (O2) is necessary for life, oxygen as ozone (O3) is highly toxic. On the other hand, ozone is an im ...
Nutritional Requirements of Streptococcus salivarius
... 196I). Unlike S. bovis, S. salivarius could not utilize thioglycollic acid, thiourea, thiouracil and sulphide. Both organisms failed to utilize methionine, sulphate and sulphite. It is not known how streptococci synthesize their sulphur-containing amino acids. An interesting question is how Streptoc ...
... 196I). Unlike S. bovis, S. salivarius could not utilize thioglycollic acid, thiourea, thiouracil and sulphide. Both organisms failed to utilize methionine, sulphate and sulphite. It is not known how streptococci synthesize their sulphur-containing amino acids. An interesting question is how Streptoc ...
The Enzymes of Ammonia Assimilation and their
... The activities of GS, NADP-GOGAT and NADP-GDH in extracts of members of the ‘herbicola’, ‘carotovora’ and ‘amylovora’ clusters, grown with different sources of nitrogen, are shown in Table 1. NAD-GOGAT, NAD-GDH and corresponding amidotransferases and dehydrogenases (both NAD- and NADP-linked) able t ...
... The activities of GS, NADP-GOGAT and NADP-GDH in extracts of members of the ‘herbicola’, ‘carotovora’ and ‘amylovora’ clusters, grown with different sources of nitrogen, are shown in Table 1. NAD-GOGAT, NAD-GDH and corresponding amidotransferases and dehydrogenases (both NAD- and NADP-linked) able t ...
Honors Chemistry: Ch. 12 – Stoichiometry Some useful terms
... 4.) Calculate the mass of silver needed to react with chlorine to produce 84 g of silver chloride (Hint: Write a balanced equation first). 5.) Calculate the number of liters of oxygen gas needed to produce 15.0 liters of dinitrogen trioxide. Assume all gases are at STP. 2N2(g) + 3O2(g) 2N2O3(g) 6. ...
... 4.) Calculate the mass of silver needed to react with chlorine to produce 84 g of silver chloride (Hint: Write a balanced equation first). 5.) Calculate the number of liters of oxygen gas needed to produce 15.0 liters of dinitrogen trioxide. Assume all gases are at STP. 2N2(g) + 3O2(g) 2N2O3(g) 6. ...
Communication
... Oxidized low density lipoprotein (LDL) may be of central importance in triggering atherosclerosis. One potential pathway involves the production of nitric oxide (NO) by vascular wall endothelial cells and macrophages. NO reacts with superoxide to form peroxynitrite (ONOO2), a potent agent of LDL oxi ...
... Oxidized low density lipoprotein (LDL) may be of central importance in triggering atherosclerosis. One potential pathway involves the production of nitric oxide (NO) by vascular wall endothelial cells and macrophages. NO reacts with superoxide to form peroxynitrite (ONOO2), a potent agent of LDL oxi ...
BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Problem Unit Seven
... Module 1: Amino Acid Metabolism, I. Nitrogen Metabolism ...
... Module 1: Amino Acid Metabolism, I. Nitrogen Metabolism ...
Gel Electrophoresis and Amino Acid Analysis of the Nonprotein
... amino acids present, followed by proline, arginine, and alanine. These five amino acids contributed 70 mol% of the total free amino acids. Upon hydrolysis, there was a remarkable increase in glycine to 35 mol%, while aspartic and glutamic acids remained at about 20 mol%, the level found in the free ...
... amino acids present, followed by proline, arginine, and alanine. These five amino acids contributed 70 mol% of the total free amino acids. Upon hydrolysis, there was a remarkable increase in glycine to 35 mol%, while aspartic and glutamic acids remained at about 20 mol%, the level found in the free ...
COMPOUNDS OF CARBON CONTAINING NITROGEN
... oxygen atom as a part of the functional group. Now, you will learn about organic compounds containing nitrogen atom as a part of the functional group. An historical importance can be associated with these compounds as the first ever organic compound synthesised in the laboratory was urea which conta ...
... oxygen atom as a part of the functional group. Now, you will learn about organic compounds containing nitrogen atom as a part of the functional group. An historical importance can be associated with these compounds as the first ever organic compound synthesised in the laboratory was urea which conta ...
Chapter 16: Amines and Amides
... • Name the longest chain attached to the nitrogen. • Replace the final –e with –amine. • Number the chain so the carbon bonded to the nitrogen has the lowest possible number. • Number the other substituents on the carbon chain. • An italic “N” is used as a prefix for a substituent on nitrogen. • Exa ...
... • Name the longest chain attached to the nitrogen. • Replace the final –e with –amine. • Number the chain so the carbon bonded to the nitrogen has the lowest possible number. • Number the other substituents on the carbon chain. • An italic “N” is used as a prefix for a substituent on nitrogen. • Exa ...
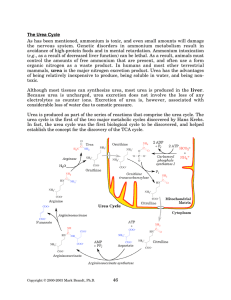
The Urea Cycle - Rose
... The other four enzymes are part of the actual cycle. The cycle begins with the addition of carbamoyl phosphate to ornithine by ornithine transcarbamoylase to produce citrulline. Citrulline then leaves the mitochondria using a specific transporter, because the remaining reactions occur in the cytopla ...
... The other four enzymes are part of the actual cycle. The cycle begins with the addition of carbamoyl phosphate to ornithine by ornithine transcarbamoylase to produce citrulline. Citrulline then leaves the mitochondria using a specific transporter, because the remaining reactions occur in the cytopla ...
Plant and Soil. 182:
... were impaired in growth on histidine and 7-aminobutyrate as sole carbon and nitrogen source. As the catabolism of these amino acids occurs predominantly through glutamate, our results indicate that mutants are also impaired in their ability to use histidine and 7-aminobutyrate as a nitrogen source. ...
... were impaired in growth on histidine and 7-aminobutyrate as sole carbon and nitrogen source. As the catabolism of these amino acids occurs predominantly through glutamate, our results indicate that mutants are also impaired in their ability to use histidine and 7-aminobutyrate as a nitrogen source. ...
File - cpprashanths Chemistry
... b) Medicines are more effective in colloidal state. c) Alum is added to purify muddy water a) Because the particle size is so small that no scattering of light is possible. 1M b) A colloidal state has a larger surface area. Thus medicines in colloidal state are effectively adsorbed and assimilated a ...
... b) Medicines are more effective in colloidal state. c) Alum is added to purify muddy water a) Because the particle size is so small that no scattering of light is possible. 1M b) A colloidal state has a larger surface area. Thus medicines in colloidal state are effectively adsorbed and assimilated a ...
12 - einstein classes
... The trihalides are predominantly covalent and, like NH3, have a tetrahedral structure with one position occupied by a lone pair. The exceptions are BiF3 which is ionic and the other halides of Bi and SbF3 which are intermediate in character. The trihalides typically hydrolyse readily with water, but ...
... The trihalides are predominantly covalent and, like NH3, have a tetrahedral structure with one position occupied by a lone pair. The exceptions are BiF3 which is ionic and the other halides of Bi and SbF3 which are intermediate in character. The trihalides typically hydrolyse readily with water, but ...
Nitrogenous Wastes
... OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0† ...
... OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0† ...
NCERT Solution - Mywayteaching
... Lattice energy is directly proportional to the charge carried by an ion. When a metal combines with oxygen, the lattice energy of the oxide involving O2− ion is much more than the oxide involving O− ion. Hence, the oxide having O2− ions are more stable than oxides having O−. Hence, we can say that f ...
... Lattice energy is directly proportional to the charge carried by an ion. When a metal combines with oxygen, the lattice energy of the oxide involving O2− ion is much more than the oxide involving O− ion. Hence, the oxide having O2− ions are more stable than oxides having O−. Hence, we can say that f ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... Nitrogen fixation can be performed by rhizobia soil bacteria in symbiosis with legume plants. This process has been extensively studied, and the entire genome sequences of select Rhizobiaceae bacteria (such as Azorhizobium, Allorhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, Mesorhizobium, Rhizobium, and Sinorhizobium) ...
... Nitrogen fixation can be performed by rhizobia soil bacteria in symbiosis with legume plants. This process has been extensively studied, and the entire genome sequences of select Rhizobiaceae bacteria (such as Azorhizobium, Allorhizobium, Bradyrhizobium, Mesorhizobium, Rhizobium, and Sinorhizobium) ...
Nitrogen and Oxygen Family
... Nitrogen differs from the rest of the members of this group due to its smaller size , high electronegativity, high ionisation enthalpy and non–availability of d orbitals. Nitrogen has unique ability to form p–p multiple bonds with itself and with other elements having small size and high electrone ...
... Nitrogen differs from the rest of the members of this group due to its smaller size , high electronegativity, high ionisation enthalpy and non–availability of d orbitals. Nitrogen has unique ability to form p–p multiple bonds with itself and with other elements having small size and high electrone ...
In silico site of metabolism prediction for human UGT
... Overfitting often occurs when a model uses more terms than necessary (Hawkins, 2004). Because the degree of degeneracy of our defined descriptors can be high, models built using all of them could be easily overfitting. Therefore, it is important to select a subset of relevant and non-redundant featu ...
... Overfitting often occurs when a model uses more terms than necessary (Hawkins, 2004). Because the degree of degeneracy of our defined descriptors can be high, models built using all of them could be easily overfitting. Therefore, it is important to select a subset of relevant and non-redundant featu ...
Dr. Murad`s Abstract
... blood pressure, increase blood flow to tissues, alter’ memory and behavior, decrease blood clotting, etc. The list of effects of nitric oxide that are independent of cyclic GMP formation is also growing at a rapid rate. For example, nitric oxide can interact with transition metals such as iron, thio ...
... blood pressure, increase blood flow to tissues, alter’ memory and behavior, decrease blood clotting, etc. The list of effects of nitric oxide that are independent of cyclic GMP formation is also growing at a rapid rate. For example, nitric oxide can interact with transition metals such as iron, thio ...
organonitrogen compounds i. amines
... The cleavage reaction of Equation 23-2 reveals other useful generalizations. Whatever its source, a parent molecular ion, M + , has one unpaired electron and is properly described as an odd-electron ion (a radical cation). When a parent molecular ion fragments, it does so hornolytically, as shown in ...
... The cleavage reaction of Equation 23-2 reveals other useful generalizations. Whatever its source, a parent molecular ion, M + , has one unpaired electron and is properly described as an odd-electron ion (a radical cation). When a parent molecular ion fragments, it does so hornolytically, as shown in ...