Thoughts on the Internationalization of RMB Under Financial Crisis
... billions annually. RMB can also be circulated in Vietnam, five countries in mid-Asian, Russia and Pakistan, and in Kazakhstan. It has become the largest amount of cross-border circulating currency. In Mongolia, it has taken more than one third of the transaction value in cash in the bilateral trade. ...
... billions annually. RMB can also be circulated in Vietnam, five countries in mid-Asian, Russia and Pakistan, and in Kazakhstan. It has become the largest amount of cross-border circulating currency. In Mongolia, it has taken more than one third of the transaction value in cash in the bilateral trade. ...
Eco120DE- Saturday S..
... are called “monetary policy”. • “Open market operations” are a means of the government controlling the supply of money. The government (in our case the Reserve Bank of Australia or RBA) buys and sells government securities, such as government bonds to control the amount of money in the economy. • If ...
... are called “monetary policy”. • “Open market operations” are a means of the government controlling the supply of money. The government (in our case the Reserve Bank of Australia or RBA) buys and sells government securities, such as government bonds to control the amount of money in the economy. • If ...
BD104_fme_lnt_003_Ma..
... (a) A higher price level reduces the real value or purchasing power of the public’s accumulated savings balances. (b) Real value of assets with fixed money values (eg. savings accounts, bonds etc.) diminishes. (c) As a result, the public is poorer in real terms and will reduce spending. ...
... (a) A higher price level reduces the real value or purchasing power of the public’s accumulated savings balances. (b) Real value of assets with fixed money values (eg. savings accounts, bonds etc.) diminishes. (c) As a result, the public is poorer in real terms and will reduce spending. ...
Class 10 PPT
... • The demand for loanable funds in the loanable funds market increased because people are trying to finance their purchases abroad. This increased the interest rate. • This increased the supply of pesos in the foreign-currency exchange market as people are converting their pesos to ...
... • The demand for loanable funds in the loanable funds market increased because people are trying to finance their purchases abroad. This increased the interest rate. • This increased the supply of pesos in the foreign-currency exchange market as people are converting their pesos to ...
The Impact of Exchange Rate Movement on Export
... exchange rates on Firm Exports. The results showed that firms that export are more likely to be bigger, older, more productive and foreign owned. Chit & Judge (2011) examined the role of financial sector development in influencing the impact of exchange rate volatility on the exports of five emergin ...
... exchange rates on Firm Exports. The results showed that firms that export are more likely to be bigger, older, more productive and foreign owned. Chit & Judge (2011) examined the role of financial sector development in influencing the impact of exchange rate volatility on the exports of five emergin ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... Bureau of Economic Research Volume Title: Inflation: Causes and Effects
... for the erosion of purchasing power without providing for a higher real return. Under these circumstances, a rise in the United States rate of interest may not attract foreign capital. Capital markets are much more sophisticated than what is presumed by some of the simplistic theories. The evidence ...
... for the erosion of purchasing power without providing for a higher real return. Under these circumstances, a rise in the United States rate of interest may not attract foreign capital. Capital markets are much more sophisticated than what is presumed by some of the simplistic theories. The evidence ...
Document
... A. The price of a Big Mac in Hong Kong is $9.90. The price of a Big Mac in Germany is DM4.90 (DM is the abbreviation for DeutschMark or German mark). The nominal exchange rate between Hong Kong and Germany is such that 4.675 Hong Kong Dollars are necessary to buy 1 German mark. What is the real Big ...
... A. The price of a Big Mac in Hong Kong is $9.90. The price of a Big Mac in Germany is DM4.90 (DM is the abbreviation for DeutschMark or German mark). The nominal exchange rate between Hong Kong and Germany is such that 4.675 Hong Kong Dollars are necessary to buy 1 German mark. What is the real Big ...
1) Gross domestic product is calculated by summing up A) the total
... 12) If an increase in investment spending of $50 million results in a $400 million increase in equilibrium real GDP, then A) the multiplier is 0.125. B) the multiplier is 3.5. C) the multiplier is 8. D) the multiplier is 50. 13) The major shortcoming of a barter economy is A) the requirement of a do ...
... 12) If an increase in investment spending of $50 million results in a $400 million increase in equilibrium real GDP, then A) the multiplier is 0.125. B) the multiplier is 3.5. C) the multiplier is 8. D) the multiplier is 50. 13) The major shortcoming of a barter economy is A) the requirement of a do ...
ECO 202-03
... This course uses market analysis (supply and demand at the national level) to develop an understanding of the working of the macroeconomic system. The macroeconomy is analyzed by studying five national markets: output, labor, financial (credit), foreign exchange market and the money (bank reserve) m ...
... This course uses market analysis (supply and demand at the national level) to develop an understanding of the working of the macroeconomic system. The macroeconomy is analyzed by studying five national markets: output, labor, financial (credit), foreign exchange market and the money (bank reserve) m ...
the report
... Since President al-Sisi took office 2 years ago the country has enjoyed a more secure political order, although this has not translated into improved economic fundamentals. On the contrary, his repression, terrorist attacks and weak macroeconomic policies are having a dramatic impact on tourism – a ...
... Since President al-Sisi took office 2 years ago the country has enjoyed a more secure political order, although this has not translated into improved economic fundamentals. On the contrary, his repression, terrorist attacks and weak macroeconomic policies are having a dramatic impact on tourism – a ...
fixed exchange rates
... The fixed-exchange-rate regime that applied to most advanced countries from World War II until the early 1970s was called the Bretton Woods Under this system, the participating countries established narrow bands within which they pegged the nominal exchange rate, ε, between their currency and the U. ...
... The fixed-exchange-rate regime that applied to most advanced countries from World War II until the early 1970s was called the Bretton Woods Under this system, the participating countries established narrow bands within which they pegged the nominal exchange rate, ε, between their currency and the U. ...
Chapter 2
... The International Gold Standard, 1879-1913 With stable exchange rates and a common monetary policy, prices of tradable commodities were much equalized across countries. Real rates of interest also tended toward equality across a broad range of countries. On the other hand, the workings of the ...
... The International Gold Standard, 1879-1913 With stable exchange rates and a common monetary policy, prices of tradable commodities were much equalized across countries. Real rates of interest also tended toward equality across a broad range of countries. On the other hand, the workings of the ...
Living With the IMF.indd
... help temper the demand for hard currency. However, this psychological factor will have more of an impact on speculatory purchases rather than day to day demand for purchases of goods and services which currently exists. That said, with Jamaica receiving the first tranche of the IMF funds which is to ...
... help temper the demand for hard currency. However, this psychological factor will have more of an impact on speculatory purchases rather than day to day demand for purchases of goods and services which currently exists. That said, with Jamaica receiving the first tranche of the IMF funds which is to ...
Open Economy Macroeconomics
... lending can be controlled by the authorities, so can the money stock. In this sense, the money supply is a policy instrument at the disposal of the home country’s monetary authority. So money supply is an exogenous variable leaving the exchange rate to be determined endogenously by market forces. Th ...
... lending can be controlled by the authorities, so can the money stock. In this sense, the money supply is a policy instrument at the disposal of the home country’s monetary authority. So money supply is an exogenous variable leaving the exchange rate to be determined endogenously by market forces. Th ...
1. Refer to the above graph. If the supply of money was $250 billion
... They increase it because they decrease the cash and checks held by the public They increase it because the change expectations of future economic growth ...
... They increase it because they decrease the cash and checks held by the public They increase it because the change expectations of future economic growth ...
RMB - Charles Mo and Company
... US influence in the financial world China’s success at signing up so many countries as founders of the new Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank What is China’s strategy on its currency? Does China want its currency to be a reserve currency or an alternative to the US dollars? n ...
... US influence in the financial world China’s success at signing up so many countries as founders of the new Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank What is China’s strategy on its currency? Does China want its currency to be a reserve currency or an alternative to the US dollars? n ...
Currency Invoicing of US Imports - Department of Economics
... the fluctuations are largest when exports are invoiced in a third currency, invoicing in either the importer’s or the exporter’s currency dominates the strategy of invoicing in a third currency. Based on the theoretical approach developed by Donnenfeld and Zilcha and others we can derive specific pr ...
... the fluctuations are largest when exports are invoiced in a third currency, invoicing in either the importer’s or the exporter’s currency dominates the strategy of invoicing in a third currency. Based on the theoretical approach developed by Donnenfeld and Zilcha and others we can derive specific pr ...
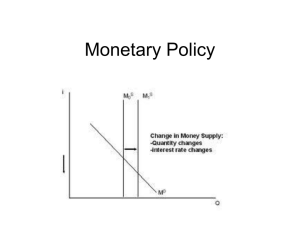
Monetary Policy
... requirements, or lowers discount rate • Real interest rates decrease • Stimulates AD (investment and consumption) • Lower interest rates lead to capital outflow, so dollar depreciates, and exports stimulated (higher AD) • Asset prices increase (housing) ...
... requirements, or lowers discount rate • Real interest rates decrease • Stimulates AD (investment and consumption) • Lower interest rates lead to capital outflow, so dollar depreciates, and exports stimulated (higher AD) • Asset prices increase (housing) ...
Syllabus - NIT Mizoram
... Exchange rate as an instrument of adjustment, Basic exchange rate concepts: spot, forward, real, nominal, fixed, flexible, etc. Models of exchange rate determination, current account and capital account models; A historic perspective of International Monetary systems of the post-world war era, Brett ...
... Exchange rate as an instrument of adjustment, Basic exchange rate concepts: spot, forward, real, nominal, fixed, flexible, etc. Models of exchange rate determination, current account and capital account models; A historic perspective of International Monetary systems of the post-world war era, Brett ...
RISK MANAGEMENT
... be put under strain as customers take longer to pay. Suppliers will weaken without prompt payment. Foreign exchange rates may also become increasingly volatile. The enforceability of euro derivatives/country of bank counterparty may be put under strain as well, if the contagion spreads. There may al ...
... be put under strain as customers take longer to pay. Suppliers will weaken without prompt payment. Foreign exchange rates may also become increasingly volatile. The enforceability of euro derivatives/country of bank counterparty may be put under strain as well, if the contagion spreads. There may al ...
Balance of Payments and Exchange Rates
... • Between 1959 and 1985, inflation in Switzerland or Germany has not been as high as in France, so France (the French Franc) experienced a real appreciation with respect to these 2 currencies. However in the long run (over the years), the nominal exchange rate (F/DM or F/SF) also depreciated to acco ...
... • Between 1959 and 1985, inflation in Switzerland or Germany has not been as high as in France, so France (the French Franc) experienced a real appreciation with respect to these 2 currencies. However in the long run (over the years), the nominal exchange rate (F/DM or F/SF) also depreciated to acco ...
ECO 120- Macroeconomics
... are called “monetary policy”. • “Open market operations” are a means of the government controlling the supply of money. The government (in our case the Reserve Bank of Australia or RBA) buys and sells government securities, such as government bonds to control the amount of money in the economy. • If ...
... are called “monetary policy”. • “Open market operations” are a means of the government controlling the supply of money. The government (in our case the Reserve Bank of Australia or RBA) buys and sells government securities, such as government bonds to control the amount of money in the economy. • If ...
Exchange rate
.jpg?width=300)
In finance, an exchange rate (also known as a foreign-exchange rate, forex rate, FX rate or Agio) between two currencies is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another. It is also regarded as the value of one country’s currency in terms of another currency. For example, an interbank exchange rate of 119 Japanese yen (JPY, ¥) to the United States dollar (US$) means that ¥119 will be exchanged for each US$1 or that US$1 will be exchanged for each ¥119. In this case it is said that the price of a dollar in terms of yen is ¥119, or equivalently that the price of a yen in terms of dollars is $1/119.Exchange rates are determined in the foreign exchange market, which is open to a wide range of different types of buyers and sellers where currency trading is continuous: 24 hours a day except weekends, i.e. trading from 20:15 GMT on Sunday until 22:00 GMT Friday. The spot exchange rate refers to the current exchange rate. The forward exchange rate refers to an exchange rate that is quoted and traded today but for delivery and payment on a specific future date.In the retail currency exchange market, a different buying rate and selling rate will be quoted by money dealers. Most trades are to or from the local currency. The buying rate is the rate at which money dealers will buy foreign currency, and the selling rate is the rate at which they will sell the currency. The quoted rates will incorporate an allowance for a dealer's margin (or profit) in trading, or else the margin may be recovered in the form of a commission or in some other way. Different rates may also be quoted for cash (usually notes only), a documentary form (such as traveler's cheques) or electronically (such as a credit card purchase). The higher rate on documentary transactions has been justified to compensate for the additional time and cost of clearing the document, while the cash is available for resale immediately. Some dealers on the other hand prefer documentary transactions because of the security concerns with cash.