Neurodevelopment I
... A central question in developmental biology is how form and pattern emerge from the simple beginnings of a fertilized egg. Are cell fates somehow predetermined or do cells and tissues interact with one another to orchestrate developmental processes (induction)? Embryonic induction was first shown un ...
... A central question in developmental biology is how form and pattern emerge from the simple beginnings of a fertilized egg. Are cell fates somehow predetermined or do cells and tissues interact with one another to orchestrate developmental processes (induction)? Embryonic induction was first shown un ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... b. Postganglionic neuron- The cell body of this neuron is located in an autonomic ganglion outside the CNS. 2. Only three types of structures are innervated by the autonomic nervous system (ANS). a. Smooth muscle (viscera, blood vessels, etc.) b. Cardiac Muscle c. Glands d. Note: some research paper ...
... b. Postganglionic neuron- The cell body of this neuron is located in an autonomic ganglion outside the CNS. 2. Only three types of structures are innervated by the autonomic nervous system (ANS). a. Smooth muscle (viscera, blood vessels, etc.) b. Cardiac Muscle c. Glands d. Note: some research paper ...
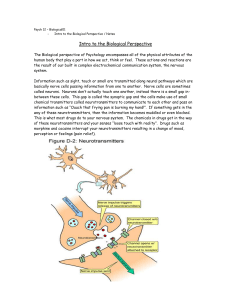
Intro to the Biological Perspective
... Divisions of the Nervous System Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system. But they do not fit together to create a single, simple nervous system that serves only one function. Ours is a nervous system with many different parts or divisions. The major divisions of the nervous system are ...
... Divisions of the Nervous System Neurons are the building blocks of the nervous system. But they do not fit together to create a single, simple nervous system that serves only one function. Ours is a nervous system with many different parts or divisions. The major divisions of the nervous system are ...
Development of the Central Nervous System I. Macrscopic
... Multiple cues in axon guidance Growth Cone Requires both Microtubule (tubulin) and microfilament (actin) - based cytoskeletal changes Signaling through surface receptors ...
... Multiple cues in axon guidance Growth Cone Requires both Microtubule (tubulin) and microfilament (actin) - based cytoskeletal changes Signaling through surface receptors ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... There is great diversity in nervous system organization among animals; some even lack nervous systems (e.g., sponges). Vertebrate nervous systems are highly centralized and cephalized Vertebrate nervous systems are structurally and functionally diverse, however, they all have distinct central and pe ...
... There is great diversity in nervous system organization among animals; some even lack nervous systems (e.g., sponges). Vertebrate nervous systems are highly centralized and cephalized Vertebrate nervous systems are structurally and functionally diverse, however, they all have distinct central and pe ...
DIVERSITY OF LIFE Diversity: how many and what types The origin
... would record a spike of positive charge inside the axon and a fraction of a second later, the second in line would record a spike of positive charge the degree of change in electrical potential in the cell did not respond to changes in stimulation of nerve, but did impact the frequency—the nerve i ...
... would record a spike of positive charge inside the axon and a fraction of a second later, the second in line would record a spike of positive charge the degree of change in electrical potential in the cell did not respond to changes in stimulation of nerve, but did impact the frequency—the nerve i ...
Press Release
... Each cell type has a unique molecular fingerprint - a combination of regulatory genes that are active in a cell and give it its identity. The similarities between the fingerprints of vasotocin and RFamide-secreting cells in zebrafish and Platynereis are so big that they are difficult to explain by c ...
... Each cell type has a unique molecular fingerprint - a combination of regulatory genes that are active in a cell and give it its identity. The similarities between the fingerprints of vasotocin and RFamide-secreting cells in zebrafish and Platynereis are so big that they are difficult to explain by c ...
Notes - Unit 2
... Portions of Virginia’s Chesapeake Bay have become “Dead Zones”, regions without enough oxygen to support life. After about 50 years and more than $100 million spent there has been almost no improvement or recovery! While parts of the New York Harbor are still contaminated, greatly reducing any wildl ...
... Portions of Virginia’s Chesapeake Bay have become “Dead Zones”, regions without enough oxygen to support life. After about 50 years and more than $100 million spent there has been almost no improvement or recovery! While parts of the New York Harbor are still contaminated, greatly reducing any wildl ...
Nerves, Hormones, and Homeostasis
... • Homeostasis: The process of maintaining the internal conditions of an organism between acceptable limits. • Hypothalamus: A part in the brain that controls many automatic functions in the body, most important is the body’s “internal thermostat”. • Negative feedback mechanisms: are self-regulating ...
... • Homeostasis: The process of maintaining the internal conditions of an organism between acceptable limits. • Hypothalamus: A part in the brain that controls many automatic functions in the body, most important is the body’s “internal thermostat”. • Negative feedback mechanisms: are self-regulating ...
Feedback Mechanisms and Types of Neurons
... – Insulin is released into blood – Causes cells to absorb glucose & liver to store ...
... – Insulin is released into blood – Causes cells to absorb glucose & liver to store ...
Nervous
... accompanied by inhibition of the back thigh muscles (flexor muscles) that flex the lower leg (pull it toward the body). This inhibition involves a second nerve circuit: The sensory neurons from the quadriceps form synapses not only with motor neurons but also with interneurons in the spinal cord ...
... accompanied by inhibition of the back thigh muscles (flexor muscles) that flex the lower leg (pull it toward the body). This inhibition involves a second nerve circuit: The sensory neurons from the quadriceps form synapses not only with motor neurons but also with interneurons in the spinal cord ...
The Nervous System
... contractions of GI tract smooth muscle secretions of GI tract organs (stomach acid ...
... contractions of GI tract smooth muscle secretions of GI tract organs (stomach acid ...
Excretory and Nervous Systems 2012
... The functions of the nervous system are accomplished by the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system. The peripheral nervous system, which consists of nerves and supporting cells, collects information about the body’s external and internal environment. The central nervous system, whi ...
... The functions of the nervous system are accomplished by the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system. The peripheral nervous system, which consists of nerves and supporting cells, collects information about the body’s external and internal environment. The central nervous system, whi ...
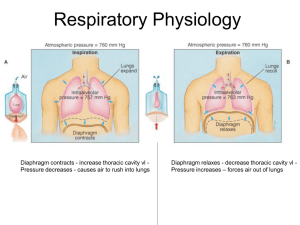
Respiratory Physiology
... 1 - bicarbonate (HCO3) - 70% formed when CO2 (released by cells making ATP) combines with H2O (due to the enzyme in red blood cells called carbonic anhydrase) as shown in the diagram below ...
... 1 - bicarbonate (HCO3) - 70% formed when CO2 (released by cells making ATP) combines with H2O (due to the enzyme in red blood cells called carbonic anhydrase) as shown in the diagram below ...
zn-1 (Only cell products will be distributed
... We have been asked by NICHD to ensure that all investigators include an acknowledgment in publications that benefit from the use of the DSHB's products. We suggest that the following statement be used: “The (select: hybridoma, monoclonal antibody, or protein capture reagent,) developed by [Investiga ...
... We have been asked by NICHD to ensure that all investigators include an acknowledgment in publications that benefit from the use of the DSHB's products. We suggest that the following statement be used: “The (select: hybridoma, monoclonal antibody, or protein capture reagent,) developed by [Investiga ...
02. Peripheral Nervous System
... nervous system outside of CNS. ► Nerves carry information between the organs and CNS (sensory and motor neurons). ► Includes afferent neurons and efferent neurons. ► Afferent – neurons that collect information and transmit it toward the CNS. ► Efferent – neurons that transmit information away from t ...
... nervous system outside of CNS. ► Nerves carry information between the organs and CNS (sensory and motor neurons). ► Includes afferent neurons and efferent neurons. ► Afferent – neurons that collect information and transmit it toward the CNS. ► Efferent – neurons that transmit information away from t ...
Early embryology
... Marsupials do not produce a shelled egg. The egg, which is poorly supplied with yolk, is retained for a time within the reproductive tract of the mother. The embryo penetrates the wall of the uterus. The yolk sac provides a rudimentary connection to the mother's blood supply from which it receives f ...
... Marsupials do not produce a shelled egg. The egg, which is poorly supplied with yolk, is retained for a time within the reproductive tract of the mother. The embryo penetrates the wall of the uterus. The yolk sac provides a rudimentary connection to the mother's blood supply from which it receives f ...
Lab 8: Chick 72 hours Lab 8: Chick, 72 hours
... Digestive system and endoderm derivatives • At 72 hours the endodermal derivatives such as the lung buds begin to rapidly expand into the mesenchyme of mesoderm origin. • The esophagus, p g , stomach,, liver and duodenum are just beginning to form. Try to trace the connections between these tissues ...
... Digestive system and endoderm derivatives • At 72 hours the endodermal derivatives such as the lung buds begin to rapidly expand into the mesenchyme of mesoderm origin. • The esophagus, p g , stomach,, liver and duodenum are just beginning to form. Try to trace the connections between these tissues ...
Organization and Regulation of Body Systems Tissues, Organs and Nervous, Endocrine and Reproductive
... Critical role in the reward system , makes you feel good. (also implicated in Parkinson's and schizophrenia) Why are Nicotine, Cocaine, and Heroin Addictive Nicotine causes neurons to release dopamine Cocaine blocks the reentering of dopamine back into the presynaptic neuron, leaving these neu ...
... Critical role in the reward system , makes you feel good. (also implicated in Parkinson's and schizophrenia) Why are Nicotine, Cocaine, and Heroin Addictive Nicotine causes neurons to release dopamine Cocaine blocks the reentering of dopamine back into the presynaptic neuron, leaving these neu ...
Eye induction
... differentiate into GCs. However, if early cells are either mixed with late progenitors, or exposed to media from cultures of later progenitors they tend to take on the later fate. Notch-delta signaling is another extrinsic feedback mechanism. Inactive notch promotes neuronal differentiation and upre ...
... differentiate into GCs. However, if early cells are either mixed with late progenitors, or exposed to media from cultures of later progenitors they tend to take on the later fate. Notch-delta signaling is another extrinsic feedback mechanism. Inactive notch promotes neuronal differentiation and upre ...
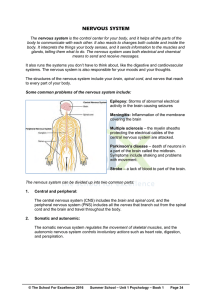
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Myelin sheath: Many neuron axons are myelinated, and without the coating, called the myelin sheath, interference may occur, like that which can be experienced when a movie is being played and a lawn mower outside is in operation. Myelin is a white, fatty substance that coats and helps insulate the a ...
... Myelin sheath: Many neuron axons are myelinated, and without the coating, called the myelin sheath, interference may occur, like that which can be experienced when a movie is being played and a lawn mower outside is in operation. Myelin is a white, fatty substance that coats and helps insulate the a ...
Chapter 35 Directed Reading
... The human nervous system is separated into two major divisions: ______________ and _____________ nervous systems. The _____________ nervous system (CNS) relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information and includes the _____________ and the ___________ ___________. The ______________ ...
... The human nervous system is separated into two major divisions: ______________ and _____________ nervous systems. The _____________ nervous system (CNS) relays messages, processes information, and analyzes information and includes the _____________ and the ___________ ___________. The ______________ ...
PDF
... canonical Wnt9b signalling is able to regulate both progenitor cell expansion and differentiation in the developing kidney. ...
... canonical Wnt9b signalling is able to regulate both progenitor cell expansion and differentiation in the developing kidney. ...
Neuronal self-avoidance

Neuronal self-avoidance, or isoneural avoidance, is an important property of neurons which consists in the tendency of branches (dendrites and axons) arising from a single soma (also called isoneuronal or sister branches) to turn away from one another. The arrangements of branches within neuronal arbors are established during development and result in minimal crossing or overlap as they spread over a territory, resulting in the typical fasciculated morphology of neurons (Fig 1).In opposition, branches from different neurons can overlap freely with one another. This propriety demands that neurons are able to discriminate “self,” which they avoid, from “non-self” branches, with which they coexist. This neuronal self-recognition is attained through families of cell recognition molecules which work as individual barcodes, allowing the discrimination of any other nearby branch as either “self” or “non-self”.Self-avoidance ensures that dendritic territories are covered completely and yet non-redundantly guaranteeing that branches achieve functionally appropriate coverage of input or output territories.Neuronal communication requires the coordinated assembly of axons, dendrites, and synapses. Therefore, self-avoidance is necessary for proper neuronal wiring and postnatal development and, together with Neuronal tiling (heteroneuronal avoidance), is a crucial spacing mechanism for patterning neural circuits that results in complete and nonredundant innervation of sensory or synaptic space.