Economics, by R. Glenn Hubbard and Anthony Patrick O`Brien
... Price Level Effect: P =>QDM at each i (DM ) People care about purchasing power of money, real money balances = X = M/P ...
... Price Level Effect: P =>QDM at each i (DM ) People care about purchasing power of money, real money balances = X = M/P ...
ECONOMIC ENVIRO NMENT MAY 2011 SOLUTIONS
... GDP does not include non-marketed output e.g. housework GDP does not include illegal businesses or some transactions for the informal sector GDP does not account for externalities – positive or negative GDP does not measure economic inequality ...
... GDP does not include non-marketed output e.g. housework GDP does not include illegal businesses or some transactions for the informal sector GDP does not account for externalities – positive or negative GDP does not measure economic inequality ...
GDP – Gross Domestic Product
... • Result 1: The producer makes higher profits and tends to expand production and hire more people. • Result 2: The newly employed workers increase spending, and the total demand in a economy increases. ...
... • Result 1: The producer makes higher profits and tends to expand production and hire more people. • Result 2: The newly employed workers increase spending, and the total demand in a economy increases. ...
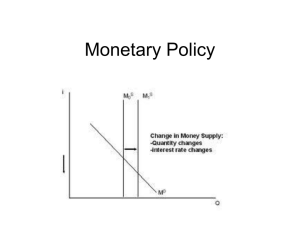
Monetary Policy
... • Stimulates AD (investment and consumption) • Lower interest rates lead to capital outflow, so dollar depreciates, and exports stimulated (higher AD) • Asset prices increase (housing) ...
... • Stimulates AD (investment and consumption) • Lower interest rates lead to capital outflow, so dollar depreciates, and exports stimulated (higher AD) • Asset prices increase (housing) ...
Chapter 28 - Weber State University
... c. interest rates and saving. d. money supply and the price level. 19. The Reagan administration’s experiment with supply-side economics produced a historic period of economic expansion that was accompanied by a. falling real interest rates. b. high unemployment rates. c. a dramatic increase in the ...
... c. interest rates and saving. d. money supply and the price level. 19. The Reagan administration’s experiment with supply-side economics produced a historic period of economic expansion that was accompanied by a. falling real interest rates. b. high unemployment rates. c. a dramatic increase in the ...
What happens when the Fed buys bonds?
... rate) decreases businesses and consumers are more likely to take out loans consumers and businesses borrow money and use it for consumption and investment spending C and I AD RGDP and PL ...
... rate) decreases businesses and consumers are more likely to take out loans consumers and businesses borrow money and use it for consumption and investment spending C and I AD RGDP and PL ...
DEFLATION – A PROBLEM OF THE SOCIO
... conventional manner. The problem may further be complicated, for example, following a collapse in asset prices, the result of which as a rule is the need to make structural reforms. In a deflationary situation irrevocable receivables of the central bank grow and probably strengthen their aversion to ...
... conventional manner. The problem may further be complicated, for example, following a collapse in asset prices, the result of which as a rule is the need to make structural reforms. In a deflationary situation irrevocable receivables of the central bank grow and probably strengthen their aversion to ...
UNIT 15 REVIEW GAME
... Portion of the business cycle when millions are out of work, many businesses fail, and the economy operates at far below capacity. depression ...
... Portion of the business cycle when millions are out of work, many businesses fail, and the economy operates at far below capacity. depression ...
WHATDUNIT? The Great Depression Mystery
... Industrial Overproduction • Wages not keeping up with inflation – Thus fewer people able to buy expensive goods ...
... Industrial Overproduction • Wages not keeping up with inflation – Thus fewer people able to buy expensive goods ...
Inflation - Murphonomics
... a rural Chinese farmer. Young people may benefit more from falling prices of mobile phones and electronic goods relative to old people. Therefore, the basket of goods may not be representative. Also, as it is updated once a year, it may soon become outdated for changes in spending habits. 2. Changes ...
... a rural Chinese farmer. Young people may benefit more from falling prices of mobile phones and electronic goods relative to old people. Therefore, the basket of goods may not be representative. Also, as it is updated once a year, it may soon become outdated for changes in spending habits. 2. Changes ...
study guide > the ascent of money part 1
... COMPARATIVELY SPEAKING FAILING TO PAY DEBT OBLIGATIONS IN MEMPHIS HAVE LESS _______________ STIGMA AND IT IS CONSIDERABLY ________________ TO RID YOURSELF OF DEBT PAYMENTS. WHAT IS THE PHILOSOPHY BEHIND THE EASE OF BANKRUPTCY IN THE UNITED STATES? ...
... COMPARATIVELY SPEAKING FAILING TO PAY DEBT OBLIGATIONS IN MEMPHIS HAVE LESS _______________ STIGMA AND IT IS CONSIDERABLY ________________ TO RID YOURSELF OF DEBT PAYMENTS. WHAT IS THE PHILOSOPHY BEHIND THE EASE OF BANKRUPTCY IN THE UNITED STATES? ...
the federal reserve and the money supply
... 1. Changes in money demand: most important are changes in Y and changes in price level. We leave P on one side, to return later (crucial role in long run). But other things equal, higher Y leads to higher money demand (more transactions), and hence to higher interest rate. This is the LM relationshi ...
... 1. Changes in money demand: most important are changes in Y and changes in price level. We leave P on one side, to return later (crucial role in long run). But other things equal, higher Y leads to higher money demand (more transactions), and hence to higher interest rate. This is the LM relationshi ...
The dangers of deflation: The pendulum swings to the pit | The
... The perversity of the low-inflation world is shown by the fact that the catalyst for the latest deflation scare is in itself a largely positive development. The price of a barrel of oil has fallen from $115 at the end of June to about $85 today, prompting a sharp drop in headline inflation (core inf ...
... The perversity of the low-inflation world is shown by the fact that the catalyst for the latest deflation scare is in itself a largely positive development. The price of a barrel of oil has fallen from $115 at the end of June to about $85 today, prompting a sharp drop in headline inflation (core inf ...
Ch. 13 Study Guide Multiple Choice ____ 1. Which of the following
... A. Producers raise prices to meet existing demand. B. The economy is in a wage-price spiral. C. Too much money is in circulation. D. Demand for goods and services exceeds existing supply. 4. How has the distribution of income in the United States changed over the last 20 years? A. It has become more ...
... A. Producers raise prices to meet existing demand. B. The economy is in a wage-price spiral. C. Too much money is in circulation. D. Demand for goods and services exceeds existing supply. 4. How has the distribution of income in the United States changed over the last 20 years? A. It has become more ...
AP Macro Economics Monetary Policy When a commercial bank
... Assume the legal reserve ratio is 25 percent and the Fourth National Bank borrows $10,000 from the Federal Reserve Bank in its district. As a result commercial bank reserves are increased by $10,000. ...
... Assume the legal reserve ratio is 25 percent and the Fourth National Bank borrows $10,000 from the Federal Reserve Bank in its district. As a result commercial bank reserves are increased by $10,000. ...