Chapter24 - Web.UVic.ca
... and to the right. This shift indicates that firms are prepared to supply the same level of output at lower prices (because their costs have fallen). As the AS curve shifts down, the equilibrium level of GDP rises and the equilibrium price level falls. This process continues until Y = Y*, at which po ...
... and to the right. This shift indicates that firms are prepared to supply the same level of output at lower prices (because their costs have fallen). As the AS curve shifts down, the equilibrium level of GDP rises and the equilibrium price level falls. This process continues until Y = Y*, at which po ...
Inflation IER
... When lotto began in 1987 the first division prize was worth $1,000,000. It could buy five houses. Today a first division prize of $1,000,000 can only buy two. The value of lotto prizes have gone down and the price of lotto tickets have gone up. ...
... When lotto began in 1987 the first division prize was worth $1,000,000. It could buy five houses. Today a first division prize of $1,000,000 can only buy two. The value of lotto prizes have gone down and the price of lotto tickets have gone up. ...
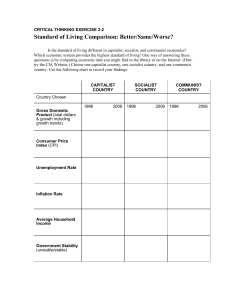
critical thinking exercise 2-2
... (https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html), which gives a surprisingly complete collection of economic and demographic data. As students search these sources, they can record the latest information they find. Even if they cannot find the answers, encourage them to note ...
... (https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/index.html), which gives a surprisingly complete collection of economic and demographic data. As students search these sources, they can record the latest information they find. Even if they cannot find the answers, encourage them to note ...
Document
... MACROECONOMICS SAMPLE QUESTIONS 1. Suppose that people expect inflation to equal 3 percent, but in fact prices rise by 5 percent. The following effects are already observed. Explain how this unexpectedly high inflation rate would have these effects: a) a homeowner that financed her home by borrowing ...
... MACROECONOMICS SAMPLE QUESTIONS 1. Suppose that people expect inflation to equal 3 percent, but in fact prices rise by 5 percent. The following effects are already observed. Explain how this unexpectedly high inflation rate would have these effects: a) a homeowner that financed her home by borrowing ...
PROBLEM SET 3 14.02 Introductory Macroeconomics March 9, 2005 Due March 16, 2005
... March 9, 2005 Due March 16, 2005 I. Answer each as True, False, or Uncertain, providing some explanation for your choice. 1. The aggregate demand curve is downward sloping because people demand fewer goods at higher prices. 2. The neutrality of money implies that monetary policy cannot a¤ect the out ...
... March 9, 2005 Due March 16, 2005 I. Answer each as True, False, or Uncertain, providing some explanation for your choice. 1. The aggregate demand curve is downward sloping because people demand fewer goods at higher prices. 2. The neutrality of money implies that monetary policy cannot a¤ect the out ...
Assignments 1 Instructor: Sireen Abdelqader Student Name
... A healthy economy is characterized as one with a high and steady level of economic growth, a high level of employment and low unemployment, and stable (or gently rising) prices. ...
... A healthy economy is characterized as one with a high and steady level of economic growth, a high level of employment and low unemployment, and stable (or gently rising) prices. ...
Chap010
... – Real GDP is the inflation-adjusted value of GDP or the value of output measured in constant prices. – Nominal GDP is measured in current prices. ...
... – Real GDP is the inflation-adjusted value of GDP or the value of output measured in constant prices. – Nominal GDP is measured in current prices. ...
Neo Classical versus Keynesian LRAS curves
... unemployed at any specific time even though jobs are available. If a recession was to occur due, perhaps, to a significant fall in exports, then output would fall below _____ ______________. Unemployment will rise as businesses shed jobs. But more significantly, as the general price level has fallen ...
... unemployed at any specific time even though jobs are available. If a recession was to occur due, perhaps, to a significant fall in exports, then output would fall below _____ ______________. Unemployment will rise as businesses shed jobs. But more significantly, as the general price level has fallen ...
than Meets the Eye? - National Academy of Social Insurance
... Direct price controls introduced in 1987 to replace indirect controls through ...
... Direct price controls introduced in 1987 to replace indirect controls through ...
CHAPTER 13 C Level Questions 1. In the sticky
... In the sticky-price model, describe the aggregate supply curve in the following special cases. How do these cases compare to the short-run aggregate supply curve discussed in Chapter ...
... In the sticky-price model, describe the aggregate supply curve in the following special cases. How do these cases compare to the short-run aggregate supply curve discussed in Chapter ...
Elasticity of Airline Industries
... Baltimore and Cleveland The average one-way ticket went from $193 to $56 Traffic increased from 89 passengers a day in each direction to 781 ...
... Baltimore and Cleveland The average one-way ticket went from $193 to $56 Traffic increased from 89 passengers a day in each direction to 781 ...
Name:
... saving represents income not spent. Planned investment is an injection because it is spending on capital goods that businesses plan to make regardless of their current level of income. If the two are unequal, there will be a discrepancy between spending and production that will result in ...
... saving represents income not spent. Planned investment is an injection because it is spending on capital goods that businesses plan to make regardless of their current level of income. If the two are unequal, there will be a discrepancy between spending and production that will result in ...
GDP - Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco
... • Consumer Price Index (CPI) • Producer Price Index (PPI) • Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index (PCEPI) ...
... • Consumer Price Index (CPI) • Producer Price Index (PPI) • Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index (PCEPI) ...
Why is this true? In an open economy, net exports being negative
... Comparative advantage is a normative argument (what a country should do). Evidence suggests that world trade patterns conform more to the principle of absolute advantage, also known as competitive advantage. [Added, but not required explanation]: This is partly because Ricardo’s comparative advantag ...
... Comparative advantage is a normative argument (what a country should do). Evidence suggests that world trade patterns conform more to the principle of absolute advantage, also known as competitive advantage. [Added, but not required explanation]: This is partly because Ricardo’s comparative advantag ...
Sticky Prices and the New Keynesian Model
... received returns of gold and silver for goods which they have sent to Cadiz. They are thereby enabled to employ more workmen than formerly, who never dream of demanding higher wages, but are glad of employment from such good paymasters. [The artisan] ...carries his money to the market, where he find ...
... received returns of gold and silver for goods which they have sent to Cadiz. They are thereby enabled to employ more workmen than formerly, who never dream of demanding higher wages, but are glad of employment from such good paymasters. [The artisan] ...carries his money to the market, where he find ...
describing trends
... The American economy picked up in the first quarter. The price of oil topped out for the year. Gold prices plummet in South Africa. Pharmaxis shares plunge 52 per cent. India’s GDP bottomed out. Shares rally on Spanish auction. Bay Area home prices soar in buyer bidding wars. Pick up = to improve in ...
... The American economy picked up in the first quarter. The price of oil topped out for the year. Gold prices plummet in South Africa. Pharmaxis shares plunge 52 per cent. India’s GDP bottomed out. Shares rally on Spanish auction. Bay Area home prices soar in buyer bidding wars. Pick up = to improve in ...
click - U of T : Economics
... Most of us were taught that price inflation is driven by a fundamental imbalance: too much money chasing too few goods. In Canada, the data seem to support this theory. Real economic growth wallowed below 2 per cent for most of last year, and average weekly earnings rose a paltry 1.4 per cent in the ...
... Most of us were taught that price inflation is driven by a fundamental imbalance: too much money chasing too few goods. In Canada, the data seem to support this theory. Real economic growth wallowed below 2 per cent for most of last year, and average weekly earnings rose a paltry 1.4 per cent in the ...
FRBSF E L CONOMIC ETTER
... increase.This implies that recorded house prices may not be as representative of actual housing values in bad times as they are in good times.This is important because when people make economic decisions that depend on house values, they tend to rely on observed prices to estimate those values. For ...
... increase.This implies that recorded house prices may not be as representative of actual housing values in bad times as they are in good times.This is important because when people make economic decisions that depend on house values, they tend to rely on observed prices to estimate those values. For ...
Chapter 3: Economic Challenges Facing Contemporary Business.
... – Demand-pull inflation - Excessive consumer demand. ...
... – Demand-pull inflation - Excessive consumer demand. ...