Extra Review MC Questions for
... B a household deposits part of its income into an account for their children’s university fees C a bank purchases government bonds D a farmer purchases a new tractor Q6. Which of the following is a basic theory of NEW-CLASSICAL economic analysis? A the economy may be in equilibrium at less than pote ...
... B a household deposits part of its income into an account for their children’s university fees C a bank purchases government bonds D a farmer purchases a new tractor Q6. Which of the following is a basic theory of NEW-CLASSICAL economic analysis? A the economy may be in equilibrium at less than pote ...
Beginning Activity
... • Creeping inflation – 1 to 3% per year • Galloping inflation – 100 to 300% per year • Hyperinflation – 500% and up – Ex. Hungary’s currency inflation went up to 828 octillion to 1 because it printed money to pay its bills. – What currency rule does that violate? ...
... • Creeping inflation – 1 to 3% per year • Galloping inflation – 100 to 300% per year • Hyperinflation – 500% and up – Ex. Hungary’s currency inflation went up to 828 octillion to 1 because it printed money to pay its bills. – What currency rule does that violate? ...
The Effects of the Recent Oil Price Shock on the US Economy
... predominantly coming from a booming Asia, from the US perspective, it is a supply problem, not Demand ...
... predominantly coming from a booming Asia, from the US perspective, it is a supply problem, not Demand ...
Marx_and_the_Macroeconomy
... 3. Think of a particular industrial commodity, and draw the circuit of industrial capital associated with it, giving specific examples of the various inputs (C) and the output (C'). (Assume at first that the industrial capitalist has the initial money capital (no banks, stockholders or bondholders), ...
... 3. Think of a particular industrial commodity, and draw the circuit of industrial capital associated with it, giving specific examples of the various inputs (C) and the output (C'). (Assume at first that the industrial capitalist has the initial money capital (no banks, stockholders or bondholders), ...
FRBSF L CONOMIC
... the economy always changed instantaneously, monetary policy would have little effect on the economy other than to cause prices to change. This is the classic argument that “money is a veil”—if the central bank were to double the quantity of money in circulation and the monetary doubling were perfect ...
... the economy always changed instantaneously, monetary policy would have little effect on the economy other than to cause prices to change. This is the classic argument that “money is a veil”—if the central bank were to double the quantity of money in circulation and the monetary doubling were perfect ...
AS/AD Model part 2
... Increasing share of GDP & growth is slower, recoveries taking longer. Benefits of G may not be worth the costs. ...
... Increasing share of GDP & growth is slower, recoveries taking longer. Benefits of G may not be worth the costs. ...
Macro Economic Issues In International Business (1)
... That can be purchased with 1 unit of country’s currency ...
... That can be purchased with 1 unit of country’s currency ...
PDF Download
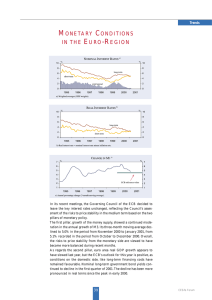
... In its recent meetings, the Governing Council of the ECB decided to leave the key interest rates unchanged, reflecting the Council’s assessment of the risks to price stability in the medium term based on the two pillars of monetary policy. The first pillar, growth of the money supply, showed a conti ...
... In its recent meetings, the Governing Council of the ECB decided to leave the key interest rates unchanged, reflecting the Council’s assessment of the risks to price stability in the medium term based on the two pillars of monetary policy. The first pillar, growth of the money supply, showed a conti ...
MACROECONOMICS
... We assume flexible prices, bat nominal wages are considered to be rigid Nominal wage contracts set wages for a lenghty time period The process can be modelled explicitly, but we do not do it Simply assume: wages are rigid Consequence: labor market does not clear, there is unemployment Short run and ...
... We assume flexible prices, bat nominal wages are considered to be rigid Nominal wage contracts set wages for a lenghty time period The process can be modelled explicitly, but we do not do it Simply assume: wages are rigid Consequence: labor market does not clear, there is unemployment Short run and ...
ECO 2013 Performance Standards
... 5. Identify those factors which cause demand and supply to change and determine the effect of such change on market price and quantity (output) equilibriums. 6. Define and understand the calculation of GDP and other related measures of economic performance. 7. Define and describe the various types o ...
... 5. Identify those factors which cause demand and supply to change and determine the effect of such change on market price and quantity (output) equilibriums. 6. Define and understand the calculation of GDP and other related measures of economic performance. 7. Define and describe the various types o ...
Chapter 6: An Introduction to Macroeconomics Learning objectives
... which invest in equipment, factories, and other capital goods Uncertainty, expectations, shocks, and short-run fluctuations Both saving and investment depend on expectations about the future. Expectations are the anticipations of consumers, firms, and others about future economic conditions. Expecta ...
... which invest in equipment, factories, and other capital goods Uncertainty, expectations, shocks, and short-run fluctuations Both saving and investment depend on expectations about the future. Expectations are the anticipations of consumers, firms, and others about future economic conditions. Expecta ...
Chapter 6 - FIU Faculty Websites
... If the price of a good rises, sometimes consumers substitute a different good instead of buying less of the good with the new price. Therefore, the CPI may overstate increases in the cost of living. 2. Introduction of new goods – New goods mean more choices and more choices mean that the purchasing ...
... If the price of a good rises, sometimes consumers substitute a different good instead of buying less of the good with the new price. Therefore, the CPI may overstate increases in the cost of living. 2. Introduction of new goods – New goods mean more choices and more choices mean that the purchasing ...
Year Cost of Basket CPI
... what part stems from a change in prices (inflation)? Item Nominal GDP in: ...
... what part stems from a change in prices (inflation)? Item Nominal GDP in: ...
Chapter 11 Keynesianism: The Macroeconomics of Wage and
... • (2) Blinder and his students found a high degree of price stickiness in their survey of firms • (a) The main reason for price stickiness was managers’ fear that if they raised their prices, they’d lose customers to rivals • (3) But catalog prices also don’t seem to change much from one issue to th ...
... • (2) Blinder and his students found a high degree of price stickiness in their survey of firms • (a) The main reason for price stickiness was managers’ fear that if they raised their prices, they’d lose customers to rivals • (3) But catalog prices also don’t seem to change much from one issue to th ...
PROBLEM SET 3 14.02 Macroeconomics March 15, 2006 Due March 22, 2006
... 3. The aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because firms produce more goods at higher prices. 4. The US unemployment rate will not increase as long as there is positive output growth. 5. If Lucas and Sargent were right, it would be possible to decrease inflation without an increase in unemploym ...
... 3. The aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because firms produce more goods at higher prices. 4. The US unemployment rate will not increase as long as there is positive output growth. 5. If Lucas and Sargent were right, it would be possible to decrease inflation without an increase in unemploym ...
Sticky wages and prices
... the expectations of both firms and workers. During the period in which the preset wage holds, firms are then free to determine their employment level such that marginal product of labour equals the preset nominal wage. The wage that is set one period in advance is based on rational expectations of n ...
... the expectations of both firms and workers. During the period in which the preset wage holds, firms are then free to determine their employment level such that marginal product of labour equals the preset nominal wage. The wage that is set one period in advance is based on rational expectations of n ...
GDP Worksheet Answer Key
... 1. What is GDP? Name a couple of things that would be included in GDP. Name a couple of things that would NOT be included. Gross Domestic Product is the total of all final goods and services produced in a country within a given period of time. Items included in GDP is almost infinite. It must have a ...
... 1. What is GDP? Name a couple of things that would be included in GDP. Name a couple of things that would NOT be included. Gross Domestic Product is the total of all final goods and services produced in a country within a given period of time. Items included in GDP is almost infinite. It must have a ...
Unemployment - New Paltz Central School District
... - everybody who wants a job has one In a market economy (ours) there will never be 0 unemployment, 4-6% always Underemployment – working at a job when your overqualified, or working parttime when you want to work full-time ...
... - everybody who wants a job has one In a market economy (ours) there will never be 0 unemployment, 4-6% always Underemployment – working at a job when your overqualified, or working parttime when you want to work full-time ...