BLOOD SUPPLY OF THE BRAIN
... The corpus striatum and the internal capsule Mainly the medial and lateral striate central branches of the middle cerebral artery Central branches of the anterior cerebral arteries The thalamus Branches of the posterior communicating, basilar and the posterior cerebral arteries The midbr ...
... The corpus striatum and the internal capsule Mainly the medial and lateral striate central branches of the middle cerebral artery Central branches of the anterior cerebral arteries The thalamus Branches of the posterior communicating, basilar and the posterior cerebral arteries The midbr ...
REVIEWARTICLES Pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury
... detection, 133Xe computed tomography (CT), stable xenon CT, or 15O2 positron emission CT to assess CBF within a temporal range from ultra-early to late stages after TBI, many investigations have revealed that focal or global cerebral ischaemia occurs frequently.6 13 26 52 Although the total ischaemi ...
... detection, 133Xe computed tomography (CT), stable xenon CT, or 15O2 positron emission CT to assess CBF within a temporal range from ultra-early to late stages after TBI, many investigations have revealed that focal or global cerebral ischaemia occurs frequently.6 13 26 52 Although the total ischaemi ...
Approaches to Therapeutic Exercise and Activity for Neurological
... Principles of treatment: Adult hemiplegia • Treatment should avoid movements and activities that increase muscle tone or produce abnormal reflex patterns in the involved side • Treatment should be directed toward the development of normal patterns of posture and movement (movement patterns are not ...
... Principles of treatment: Adult hemiplegia • Treatment should avoid movements and activities that increase muscle tone or produce abnormal reflex patterns in the involved side • Treatment should be directed toward the development of normal patterns of posture and movement (movement patterns are not ...
Fatty acid methyl esters as a potential therapy against cerebral
... of time neurological symptoms may be transient. However, at times, brain damage may be permanent and irreversible if a significant amount of time passes (more than 5 min) before restoration of CBF. The most common causes of cardiac arrest in 60–70% of cases are ventricular fibrillation or ventricula ...
... of time neurological symptoms may be transient. However, at times, brain damage may be permanent and irreversible if a significant amount of time passes (more than 5 min) before restoration of CBF. The most common causes of cardiac arrest in 60–70% of cases are ventricular fibrillation or ventricula ...
STROKE
... MRI usually detects evolving infarction within hours. Diffusion-weighted MRI is the most accurate imaging test to rule out an infarct in patients with presumed TIA but is not always available. ...
... MRI usually detects evolving infarction within hours. Diffusion-weighted MRI is the most accurate imaging test to rule out an infarct in patients with presumed TIA but is not always available. ...
Effectiveness of Treatment of Cerebral Palsy Form Newborn To
... Despite this, it was felt necessary to clarify certain areas that have been known to cause quite a bit of confusion in the literature. In this thesis is based on the definition compiled by an executive committee in April 2004. This is now widely recognised as the most descriptive description as for ...
... Despite this, it was felt necessary to clarify certain areas that have been known to cause quite a bit of confusion in the literature. In this thesis is based on the definition compiled by an executive committee in April 2004. This is now widely recognised as the most descriptive description as for ...
jpndds-2017-105-ed_w
... with the front line therapy that modifies altered physiological processes during malaria is referred as adjunctive therapy. These therapies may act directly on specific biological pathways altered by malaria or more generally on end-stage factors produced in malaria by a number of different specific ...
... with the front line therapy that modifies altered physiological processes during malaria is referred as adjunctive therapy. These therapies may act directly on specific biological pathways altered by malaria or more generally on end-stage factors produced in malaria by a number of different specific ...
Ischemic Stroke
... Strokes of the perforating branches cause complete contralateral hemianesthesia with loss of all sensation and complete ipsilateral hemianopsia. Macular (central) vision may be spared because of collateral blood supply from the MCA. Difficulty reading (dyslexia) and performing calculations (dyscalcu ...
... Strokes of the perforating branches cause complete contralateral hemianesthesia with loss of all sensation and complete ipsilateral hemianopsia. Macular (central) vision may be spared because of collateral blood supply from the MCA. Difficulty reading (dyslexia) and performing calculations (dyscalcu ...
Cranial nerves palsy as an initial feature of an early onset distal
... At the age of 8 months stridor and dyspnoea by bilateral recurrent nerve palsy with live threatening vocal cord paresis was reported and was later treated by a chordectomy at the age of 10 years. During the first decade of life she developed mild distal muscular atrophy predominantly in her hands, wh ...
... At the age of 8 months stridor and dyspnoea by bilateral recurrent nerve palsy with live threatening vocal cord paresis was reported and was later treated by a chordectomy at the age of 10 years. During the first decade of life she developed mild distal muscular atrophy predominantly in her hands, wh ...
Zoophilic behavior in a patient with posterior cerebral arterial
... aneurysms, defined as greater than 25 mm in diameter, represent 3-5% of all intracranial aneurysms. Although giant aneurysms may cause SAH, these lesions frequently produce mass effects and result in distal thromboembolism (1). Symptoms associated with cerebral aneurysms producing SAH are related to ...
... aneurysms, defined as greater than 25 mm in diameter, represent 3-5% of all intracranial aneurysms. Although giant aneurysms may cause SAH, these lesions frequently produce mass effects and result in distal thromboembolism (1). Symptoms associated with cerebral aneurysms producing SAH are related to ...
Lecture4 RADIOLOGY EXAMINATION OF THE BRAIN AND SPINAL
... often associated with skull fractures, usually develop within hours after injury. Associated massive cerebral or brainstem contusions or both contribute to a high mortality rate. Common signs are depressed consciousness, ipsilateral pupillary dilatation, and contralateral hemiparesis. Chronic subdur ...
... often associated with skull fractures, usually develop within hours after injury. Associated massive cerebral or brainstem contusions or both contribute to a high mortality rate. Common signs are depressed consciousness, ipsilateral pupillary dilatation, and contralateral hemiparesis. Chronic subdur ...
Lecture04 RADIOLOGY EXAMINATION OF THE BRAIN AND
... often associated with skull fractures, usually develop within hours after injury. Associated massive cerebral or brainstem contusions or both contribute to a high mortality rate. Common signs are depressed consciousness, ipsilateral pupillary dilatation, and contralateral hemiparesis. Chronic subdur ...
... often associated with skull fractures, usually develop within hours after injury. Associated massive cerebral or brainstem contusions or both contribute to a high mortality rate. Common signs are depressed consciousness, ipsilateral pupillary dilatation, and contralateral hemiparesis. Chronic subdur ...
CODING CLARIFICATION FOR CNS TUMORS
... that have a behavior code of /0 OR malignant meningiomas that have a behavior code of /3. Do not use this code for multiple meningiomas except in rare circumstances (about 1-2% of all meningiomas). Multiple meningiomas (also called meningiomatosis), is a rare condition strongly associated with neuro ...
... that have a behavior code of /0 OR malignant meningiomas that have a behavior code of /3. Do not use this code for multiple meningiomas except in rare circumstances (about 1-2% of all meningiomas). Multiple meningiomas (also called meningiomatosis), is a rare condition strongly associated with neuro ...
regulation of cerebral blood flow
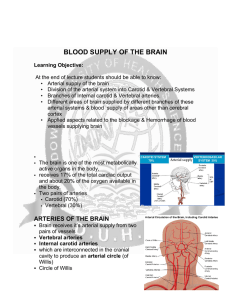
... The Circle of Willis is a vital formation of arteries at the base of the brain Brain receives its blood supply from four main arteries, the two internal carotid arteries and the two vertebral arteries. Normal blood flow through the brain of the adult person averages 50 to 65 milliliters per 100 gram ...
... The Circle of Willis is a vital formation of arteries at the base of the brain Brain receives its blood supply from four main arteries, the two internal carotid arteries and the two vertebral arteries. Normal blood flow through the brain of the adult person averages 50 to 65 milliliters per 100 gram ...
24 Cerebral blood flow2012-10-01 04:03788 KB
... The Circle of Willis is a vital formation of arteries at the base of the brain Brain receives its blood supply from four main arteries, the two internal carotid arteries and the two vertebral arteries. Normal blood flow through the brain of the adult person averages 50 to 65 milliliters per 100 gram ...
... The Circle of Willis is a vital formation of arteries at the base of the brain Brain receives its blood supply from four main arteries, the two internal carotid arteries and the two vertebral arteries. Normal blood flow through the brain of the adult person averages 50 to 65 milliliters per 100 gram ...
A Healthy Pregnancy
... What Are Birth Defects? •Birth defects: an abnormality of the baby’s bodily structure, function or metabolism that is present at birth. •These abnormalities may be fatal or lead to mental or physical disabilities. •150,000 babies are born each year with birth defects (1 out of 28 babies) ...
... What Are Birth Defects? •Birth defects: an abnormality of the baby’s bodily structure, function or metabolism that is present at birth. •These abnormalities may be fatal or lead to mental or physical disabilities. •150,000 babies are born each year with birth defects (1 out of 28 babies) ...
3. Centro nervous system
... The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic pole, presumably representing the fluid-filled rhombencephalic vesicle. At 9 weeks, demonstration of the convoluted pattern of the three primary cerebral ves ...
... The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic pole, presumably representing the fluid-filled rhombencephalic vesicle. At 9 weeks, demonstration of the convoluted pattern of the three primary cerebral ves ...
Chapter 24 - wcunurs207and217
... after acute or nontraumatic brain injury or has lasted for 1 month in children with degenerative or metabolic disorders or developmental malformations Family support is needed ...
... after acute or nontraumatic brain injury or has lasted for 1 month in children with degenerative or metabolic disorders or developmental malformations Family support is needed ...
Phenotypic plasticity and the perception–action–cognition
... © 2015 The Authors. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology © 2015 Mac Keith Press, 57 (Suppl. 2): 52–54 ...
... © 2015 The Authors. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology © 2015 Mac Keith Press, 57 (Suppl. 2): 52–54 ...
Cerebral Protection, EEG End
... The EEG may exhibit changes intraoperatively with no demonstrable neurologic deficit during postoperative examination. Cerebral ischemia can produce electrical dysfunction without causing neuronal cell damage because the blood flow threshold for electrical failure is higher than that needed to maint ...
... The EEG may exhibit changes intraoperatively with no demonstrable neurologic deficit during postoperative examination. Cerebral ischemia can produce electrical dysfunction without causing neuronal cell damage because the blood flow threshold for electrical failure is higher than that needed to maint ...
Prolonged unconsciousness after anaesthesia
... A number of authors report causes and hypothesize that, after exclusion of organs and pharmacological causes, coma may be attributed to a disassociative stupor. Reported delays in return to consciousness span time periods from 2 to 30 h, and longer periods of amnesia thereafter. There are four repor ...
... A number of authors report causes and hypothesize that, after exclusion of organs and pharmacological causes, coma may be attributed to a disassociative stupor. Reported delays in return to consciousness span time periods from 2 to 30 h, and longer periods of amnesia thereafter. There are four repor ...
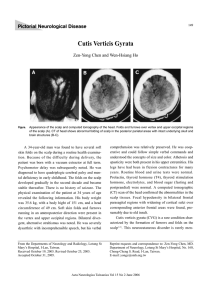
Cutis Verticis Gyrata
... tioned in the literature of neurology, but is often recognized by dermatologist. The CVG is classified into two major categories. Primary CVG has no specific recognized cause and is frequently associated with neurological manifestations; secondary CVG is due to infiltration or inflammation of the sc ...
... tioned in the literature of neurology, but is often recognized by dermatologist. The CVG is classified into two major categories. Primary CVG has no specific recognized cause and is frequently associated with neurological manifestations; secondary CVG is due to infiltration or inflammation of the sc ...
baby watch early intervention vision screening training
... into three types - by the number of joints involved, the symptoms, and the presence or absence of certain antibodies found by a blood test. Eye inflammation is a potentially severe complication that sometimes occurs in children with JRA. Eye diseases such as iritis and uveitis often are not present ...
... into three types - by the number of joints involved, the symptoms, and the presence or absence of certain antibodies found by a blood test. Eye inflammation is a potentially severe complication that sometimes occurs in children with JRA. Eye diseases such as iritis and uveitis often are not present ...
notes - Austin Community College
... Certain criteria must be met, depending on which State the individual resides. It includes such criteria as flat EEG, negative cerebral blood flow studies, absent ocular and pupils response, apnea, etc Prognosis a. Outcome varies according to underlying cause and pathologic process b. Recovery withi ...
... Certain criteria must be met, depending on which State the individual resides. It includes such criteria as flat EEG, negative cerebral blood flow studies, absent ocular and pupils response, apnea, etc Prognosis a. Outcome varies according to underlying cause and pathologic process b. Recovery withi ...
with concussion injuries
... 30 minutes after a lateral FPI there is a 30-40% increase in glucose metabolism At 6 hours there is a reduction to 50% of normal Reduction is due to oxidative dysfunction of mitochondria who cannot keep up with energy demands There is also production of superoxide free radicals which can create furt ...
... 30 minutes after a lateral FPI there is a 30-40% increase in glucose metabolism At 6 hours there is a reduction to 50% of normal Reduction is due to oxidative dysfunction of mitochondria who cannot keep up with energy demands There is also production of superoxide free radicals which can create furt ...
Cerebral palsy
_2008.jpg?width=300)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of permanent movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary between people. Often, symptoms include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sensation, vision, hearing, swallowing and speaking. Often babies with cerebral palsy do not roll over, sit, crawl, or walk as early as other children their age. Difficulty with the ability to think or reason and seizures each occurs in about one third of people with CP. While the symptoms may get more noticeable over the first few years of life, the underlying problems do not worsen over time.Cerebral palsy is caused by abnormal development or damage to the parts of the brain that control movement, balance, and posture. Most often the problems occur during pregnancy; however, they may also occur during childbirth, or shortly after birth. Often the cause is unknown. Risk factors include premature birth, being a twin, certain infections during pregnancy such as toxoplasmosis or rubella, exposure to methylmercury during pregnancy, a difficult delivery, and head trauma during the first few years of life, among others. About 2% of cases are believed to be due to an inherited genetic cause. A number of sub-types are classified based on the specific problems present. For example, those with stiff muscles have spastic cerebral palsy, those with poor coordination have ataxic cerebral palsy, and those with writhing movements have athetoid cerebral palsy. Diagnosis is based on the child's development over time. Blood tests and medical imaging may be used to rule out other possible causes.CP is partly preventable through immunization of the mother and efforts to prevent head injuries in children such as through improved safety. There is no cure for CP; however, supportive treatments, medications, and surgery may help many individuals. This may include physical therapy and speech therapy. Medications such as diazepam, baclofen, and botulinum toxin may help relax stiff muscles. Surgery may include lengthening muscles and cutting overly active nerves. Often external braces and other assistive technology are helpful. Some children have near normal adult lives with appropriate treatment. While alternative medicines are frequently used there is no evidence to support their use.CP is the most common movement disorder in children. It occurs in about 2.1 per 1,000 live births. Cerebral palsy has been documented throughout history with the first known descriptions occurring in the work of Hippocrates in the 5th century BCE. Extensive study of the condition began in the 19th century by William John Little, after whom it was called ""Little disease"". William Osler first named it ""cerebral palsy"" from the German ""zerebrale Kinderlähmung"" (cerebral child-paralysis). A number of potential treatments are being examined, including stem cell therapy. However, more research is required to determine if it is effective and safe.