Gait training facilitates central drive to ankle
... Foot drop and toe walking are frequent concerns in children with cerebral palsy. The main underlying cause of these problems is early damage and lack of maturation of the corticospinal tract. In the present study we investigated whether 4 weeks of daily treadmill training with an incline may facilit ...
... Foot drop and toe walking are frequent concerns in children with cerebral palsy. The main underlying cause of these problems is early damage and lack of maturation of the corticospinal tract. In the present study we investigated whether 4 weeks of daily treadmill training with an incline may facilit ...
Document
... The epilepsies are a group of disorders characterized by chronic recurrent paroxysmal changes in neurologic function caused by abnormalities in the electrical activity of the brain ...
... The epilepsies are a group of disorders characterized by chronic recurrent paroxysmal changes in neurologic function caused by abnormalities in the electrical activity of the brain ...
PDF
... and laterally lies the MLF. Involvement of these structures can contribute to diplopia. Careful examination of eye movements can help localize the origin of diplopia. In our patient, proximity of the MLF-related neurons to the CCN explained the clinical presentation. ...
... and laterally lies the MLF. Involvement of these structures can contribute to diplopia. Careful examination of eye movements can help localize the origin of diplopia. In our patient, proximity of the MLF-related neurons to the CCN explained the clinical presentation. ...
this PDF file - E-Journal Faculty of Medicine Universitas
... data collection, informed consent was obtained from the parents of these CP children. Inclusion criteria for this study were children diagnosed as having spastic cerebral palsy with hemiplegia, diplegia, and tetraplegia; aged 4-14 years old; and degree of Gross Motor Function Classification System ( ...
... data collection, informed consent was obtained from the parents of these CP children. Inclusion criteria for this study were children diagnosed as having spastic cerebral palsy with hemiplegia, diplegia, and tetraplegia; aged 4-14 years old; and degree of Gross Motor Function Classification System ( ...
Selective dorsal rhizotomy in children: Comparison of
... cerebral palsy. Cerebral palsy (CP) is defined as a non-progressive neurological condition that is associated with evolving motor-related impairments (Morris, 2007). CP has been attributed to brain injury occurring during the pre-natal, perinatal and post-natal periods. It may arise from birth compl ...
... cerebral palsy. Cerebral palsy (CP) is defined as a non-progressive neurological condition that is associated with evolving motor-related impairments (Morris, 2007). CP has been attributed to brain injury occurring during the pre-natal, perinatal and post-natal periods. It may arise from birth compl ...
Neuroradiology - University of Virginia School of Medicine
... brainstem contusion. •An isolated intraventricular hemorrhage may be due to rupture of subependymal veins. •As you can see, this patient also has a SAH, which, if you remember, is most commonly caused by TRAUMA! -The ruptured vessel bleeds into the space between the pia and arachnoid matter. -The mo ...
... brainstem contusion. •An isolated intraventricular hemorrhage may be due to rupture of subependymal veins. •As you can see, this patient also has a SAH, which, if you remember, is most commonly caused by TRAUMA! -The ruptured vessel bleeds into the space between the pia and arachnoid matter. -The mo ...
Thieme: Brain Imaging
... Histopathology resembles multiple sclerosis, with acute demyelinating inflammation of the brain and spinal cord In contrast to MS, the course is monophasic Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis is often difficult to differentiate from the initial episode of MS The cause is unknown but may represent a ...
... Histopathology resembles multiple sclerosis, with acute demyelinating inflammation of the brain and spinal cord In contrast to MS, the course is monophasic Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis is often difficult to differentiate from the initial episode of MS The cause is unknown but may represent a ...
Lower Extremity Orthoses in Children With Spastic Quadriplegic
... the central nervous system with an incidence of 2.5 per 1,000 live births with spastic quadriplegia being the common type of cerebral palsy (Blair & Watson, 2006). This nonprogressive neurological disorder is defined as a variation in movement, coordination, posture, and gait resulting from brain in ...
... the central nervous system with an incidence of 2.5 per 1,000 live births with spastic quadriplegia being the common type of cerebral palsy (Blair & Watson, 2006). This nonprogressive neurological disorder is defined as a variation in movement, coordination, posture, and gait resulting from brain in ...
Post-Placental Hypoxia
... can cause cellular damage that occurs within the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord). This results in an increased mortality rate, including an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Oxygen deprivation in the foetus and neonate have been implicated as either a primary ...
... can cause cellular damage that occurs within the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord). This results in an increased mortality rate, including an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Oxygen deprivation in the foetus and neonate have been implicated as either a primary ...
A Case of Isolated Middle Cerebral Artery Stenosis with Hemichorea
... Only one report has suggested that it might be an initial feature of MMD.5 Some cases with MCA stenosis associated with moyamoya pattern collateralization were reported, but the progression of a stenosis from MCA to other intreacranial vessel was not documented.6,8 MMD is a chronic, occlusive cerebr ...
... Only one report has suggested that it might be an initial feature of MMD.5 Some cases with MCA stenosis associated with moyamoya pattern collateralization were reported, but the progression of a stenosis from MCA to other intreacranial vessel was not documented.6,8 MMD is a chronic, occlusive cerebr ...
INTRACRANIAL ARTERIAL ANEURYSMS*
... of age are infrequently affected. The incidence among females is slightly higher than among males. The signs and symptoms of cerebral aneurysm vary with the type of aneurysm and with its behavior. Of the three main types, the arteriosclerotic form generally occurs in individuals beyond the age of 40 ...
... of age are infrequently affected. The incidence among females is slightly higher than among males. The signs and symptoms of cerebral aneurysm vary with the type of aneurysm and with its behavior. Of the three main types, the arteriosclerotic form generally occurs in individuals beyond the age of 40 ...
Functions of the corticospinal and corticobulbar
... how the brain works: The brain is not a painting; it is a sculpture. Michaelangelo did not create his magnificent Statue of David by starting with a massive block of crude stone and adding many more small pieces of stone. He indeed started with the block of stone, but by selectively chipping away sm ...
... how the brain works: The brain is not a painting; it is a sculpture. Michaelangelo did not create his magnificent Statue of David by starting with a massive block of crude stone and adding many more small pieces of stone. He indeed started with the block of stone, but by selectively chipping away sm ...
CEREBRAVASCULAR ANATOMY VENOUS
... • Presentation commonly with high output cardiac failure in neonates while mostly hydrocephalus in infants and children • Angiography:gold std • Classification - Lasjaunias classification: Choroidal: tend to present earlier (neonate) with more severe shunts&high output cardiac failure Mural: p ...
... • Presentation commonly with high output cardiac failure in neonates while mostly hydrocephalus in infants and children • Angiography:gold std • Classification - Lasjaunias classification: Choroidal: tend to present earlier (neonate) with more severe shunts&high output cardiac failure Mural: p ...
Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
... sinuses) with arterialized flow • (right common carotid angiogram) ...
... sinuses) with arterialized flow • (right common carotid angiogram) ...
Hypoxia/Ischemia Adult and Pediatric - Neuropathology
... Multicystic Encephalomalacia • Believed ...
... Multicystic Encephalomalacia • Believed ...
A simple novel technique to induce short
... time, middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) has been one of the models widely used to induce reversible brain ischaemia [3-6]. In most cases, a variety of intraluminar nylon filaments have been utilized in rat MCAO models. However, the extent of the lesion and its reproducibility tend to vary from ...
... time, middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) has been one of the models widely used to induce reversible brain ischaemia [3-6]. In most cases, a variety of intraluminar nylon filaments have been utilized in rat MCAO models. However, the extent of the lesion and its reproducibility tend to vary from ...
Full PDF - American Journal of Physiology
... lack of O2 and glucose, which may be a factor in triggering the hemodynamic response (3). However, the reduction in brain O2 concentration at the site of activation is small and transient and cannot account for sustained increases in flow (2). Furthermore, the CBF response to activation is not alter ...
... lack of O2 and glucose, which may be a factor in triggering the hemodynamic response (3). However, the reduction in brain O2 concentration at the site of activation is small and transient and cannot account for sustained increases in flow (2). Furthermore, the CBF response to activation is not alter ...
165 - University of Michigan
... Diplopia. Ocular misalignment created by malfunction of the ocular motor nerves or its mimickers usually evokes the symptom of diplopia, or seeing the same object in two different locations. The fixating eye will focus the object of regard on its fovea, creating a clear image. The deviating eye wil ...
... Diplopia. Ocular misalignment created by malfunction of the ocular motor nerves or its mimickers usually evokes the symptom of diplopia, or seeing the same object in two different locations. The fixating eye will focus the object of regard on its fovea, creating a clear image. The deviating eye wil ...
Botulinum Toxin in Pediatric Stiff Hips
... Bhave A, Zywiel MG, Ulrich SD, McGrath MS, Seyler TM, Marker DR, Delanois RE, Mont MA. Botulinum toxin type A injections for the management of muscle tightness following total hip arthroplasty: a case series. J Orthop Surg Res 2009; 26(4): 34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1749-799X-4-34. Huet de la Tou ...
... Bhave A, Zywiel MG, Ulrich SD, McGrath MS, Seyler TM, Marker DR, Delanois RE, Mont MA. Botulinum toxin type A injections for the management of muscle tightness following total hip arthroplasty: a case series. J Orthop Surg Res 2009; 26(4): 34. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1749-799X-4-34. Huet de la Tou ...
Revision Original Localisation in nervous system disorders
... posterior horns, and highlights the feature known as the column of Clarke at the base of the posterior horn. White matter rings these structures. Its most anterior region contains a small bundle of fibres. This is the direct pyramidal tract, otherwise known as the bundle of Türck. Laterally, we obse ...
... posterior horns, and highlights the feature known as the column of Clarke at the base of the posterior horn. White matter rings these structures. Its most anterior region contains a small bundle of fibres. This is the direct pyramidal tract, otherwise known as the bundle of Türck. Laterally, we obse ...
Clinical Features, and Nucleotide Changes in Three Families with
... muscle palsy was based on the presence of hypertropia (upward deviation of the eye) on the affected paralyzed side, which became greatest in the gaze toward the nasal field of the involved eye. The additional diagnostic feature was a positive Bielschowsky head tilt test, showing an upward deviation of ...
... muscle palsy was based on the presence of hypertropia (upward deviation of the eye) on the affected paralyzed side, which became greatest in the gaze toward the nasal field of the involved eye. The additional diagnostic feature was a positive Bielschowsky head tilt test, showing an upward deviation of ...
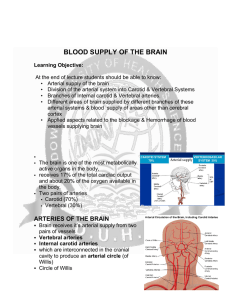
BLOOD SUPPLY OF THE BRAIN
... The corpus striatum and the internal capsule Mainly the medial and lateral striate central branches of the middle cerebral artery Central branches of the anterior cerebral arteries The thalamus Branches of the posterior communicating, basilar and the posterior cerebral arteries The midbr ...
... The corpus striatum and the internal capsule Mainly the medial and lateral striate central branches of the middle cerebral artery Central branches of the anterior cerebral arteries The thalamus Branches of the posterior communicating, basilar and the posterior cerebral arteries The midbr ...
Cerebral palsy
_2008.jpg?width=300)
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of permanent movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary between people. Often, symptoms include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sensation, vision, hearing, swallowing and speaking. Often babies with cerebral palsy do not roll over, sit, crawl, or walk as early as other children their age. Difficulty with the ability to think or reason and seizures each occurs in about one third of people with CP. While the symptoms may get more noticeable over the first few years of life, the underlying problems do not worsen over time.Cerebral palsy is caused by abnormal development or damage to the parts of the brain that control movement, balance, and posture. Most often the problems occur during pregnancy; however, they may also occur during childbirth, or shortly after birth. Often the cause is unknown. Risk factors include premature birth, being a twin, certain infections during pregnancy such as toxoplasmosis or rubella, exposure to methylmercury during pregnancy, a difficult delivery, and head trauma during the first few years of life, among others. About 2% of cases are believed to be due to an inherited genetic cause. A number of sub-types are classified based on the specific problems present. For example, those with stiff muscles have spastic cerebral palsy, those with poor coordination have ataxic cerebral palsy, and those with writhing movements have athetoid cerebral palsy. Diagnosis is based on the child's development over time. Blood tests and medical imaging may be used to rule out other possible causes.CP is partly preventable through immunization of the mother and efforts to prevent head injuries in children such as through improved safety. There is no cure for CP; however, supportive treatments, medications, and surgery may help many individuals. This may include physical therapy and speech therapy. Medications such as diazepam, baclofen, and botulinum toxin may help relax stiff muscles. Surgery may include lengthening muscles and cutting overly active nerves. Often external braces and other assistive technology are helpful. Some children have near normal adult lives with appropriate treatment. While alternative medicines are frequently used there is no evidence to support their use.CP is the most common movement disorder in children. It occurs in about 2.1 per 1,000 live births. Cerebral palsy has been documented throughout history with the first known descriptions occurring in the work of Hippocrates in the 5th century BCE. Extensive study of the condition began in the 19th century by William John Little, after whom it was called ""Little disease"". William Osler first named it ""cerebral palsy"" from the German ""zerebrale Kinderlähmung"" (cerebral child-paralysis). A number of potential treatments are being examined, including stem cell therapy. However, more research is required to determine if it is effective and safe.