Create analogies and similes Long-term Memory Summary
... When new information enters the hippocampus, if the brain recognizes anything “familiar” or related to memories already stored in the cortex, these existing memory storage networks are activated. These related memories are stored in different parts of the cortex depending on which sensory receptors ...
... When new information enters the hippocampus, if the brain recognizes anything “familiar” or related to memories already stored in the cortex, these existing memory storage networks are activated. These related memories are stored in different parts of the cortex depending on which sensory receptors ...
Remembering What Matters
... encoding has garnered much interest; however, the role of the posteromedial regions remains to be fully elucidated.… Our results provide further evidence that posteromedial regions constitute critical nodes in the large-scale cortical network subserving episodic memory. The article is part of a larg ...
... encoding has garnered much interest; however, the role of the posteromedial regions remains to be fully elucidated.… Our results provide further evidence that posteromedial regions constitute critical nodes in the large-scale cortical network subserving episodic memory. The article is part of a larg ...
Readings
... High expectations are based on associations and context. (examples on p.125) Human Factors Guidelines in Perception – pp. 126 -127 Perception versus comprehension ...
... High expectations are based on associations and context. (examples on p.125) Human Factors Guidelines in Perception – pp. 126 -127 Perception versus comprehension ...
Learning skills - Personal web pages for people of Metropolia
... events, especially if they are connected to strong feelings. Memories do change. ...
... events, especially if they are connected to strong feelings. Memories do change. ...
Economic Attention Networks: Associative Memory and Resource
... • conserved quantities (except for unusual circumstances – e.g. Economic Stimulus Package) • STI: the immediate urgency of an Atom • LTI: measure of importance for quick recall of Atom • Forgetting process: uses low-LTI and other factors to remove Atoms from quick memory ...
... • conserved quantities (except for unusual circumstances – e.g. Economic Stimulus Package) • STI: the immediate urgency of an Atom • LTI: measure of importance for quick recall of Atom • Forgetting process: uses low-LTI and other factors to remove Atoms from quick memory ...
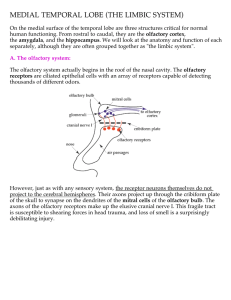
MEDIAL TEMPORAL LOBE (THE LIMBIC SYSTEM)
... amygdala is the nucleus responsible for the lurch you feel in your stomach when you turn around in a dark alley and notice someone following you. It couples a learned sensory stimulus (man in ski mask in alley = danger) to an adaptive response (fight or flight). On the basis of this information, yo ...
... amygdala is the nucleus responsible for the lurch you feel in your stomach when you turn around in a dark alley and notice someone following you. It couples a learned sensory stimulus (man in ski mask in alley = danger) to an adaptive response (fight or flight). On the basis of this information, yo ...
Functional Framework for Cognition
... sketchpad, interact constantly with the long-term stores. Verbal rehearsal/inner speech is for rehearsing and memorizing information and commentary on our current ...
... sketchpad, interact constantly with the long-term stores. Verbal rehearsal/inner speech is for rehearsing and memorizing information and commentary on our current ...
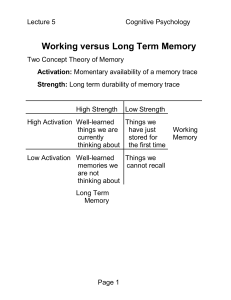
Working Memory
... sketchpad, interact constantly with the long-term stores. Verbal rehearsal/inner speech is for rehearsing and memorizing information and commentary on our current ...
... sketchpad, interact constantly with the long-term stores. Verbal rehearsal/inner speech is for rehearsing and memorizing information and commentary on our current ...
Functional Framework for Cognition
... Hippocampus is involved with episodic memory, while subcortical basal ganglia and cerebellum are responsible for motor learning. ...
... Hippocampus is involved with episodic memory, while subcortical basal ganglia and cerebellum are responsible for motor learning. ...
Biology of Learning and Memory
... long-term declarative memories, although they can still recall events from before the damage and can still form new procedural memories. • The hippocampus is critical for consolidating some forms of memory but not all. It is especially important for declarative memory and spatial memory. ...
... long-term declarative memories, although they can still recall events from before the damage and can still form new procedural memories. • The hippocampus is critical for consolidating some forms of memory but not all. It is especially important for declarative memory and spatial memory. ...
How we make Memories - Boone County Schools
... it again. For example, taking a multiple-choice quiz requires that you recognize the correct answer. Relearning: This type of memory retrieval involves relearning information that has been previously learned. ...
... it again. For example, taking a multiple-choice quiz requires that you recognize the correct answer. Relearning: This type of memory retrieval involves relearning information that has been previously learned. ...
Lecture05
... Impact of Background Knowledge on Memory Mnemonics Expertise and Memory Memory for a Baseball Game (Hi vs Low Knowledge) The Self-Reference Effect ...
... Impact of Background Knowledge on Memory Mnemonics Expertise and Memory Memory for a Baseball Game (Hi vs Low Knowledge) The Self-Reference Effect ...
Posttraumatic stress disorder
... “PTSD symptoms may include: nightmares, flashbacks, emotional detachment or numbing of feelings (emotional selfmortification or dissociation), insomnia, avoidance of reminders and extreme distress when exposed to the reminders ("triggers"), loss of appetite, irritability, hypervigilance, memory loss ...
... “PTSD symptoms may include: nightmares, flashbacks, emotional detachment or numbing of feelings (emotional selfmortification or dissociation), insomnia, avoidance of reminders and extreme distress when exposed to the reminders ("triggers"), loss of appetite, irritability, hypervigilance, memory loss ...
Learning Skill
... This self-discovery of more efficient movements eventually leads to an array of somewhat efficient movements that are stored as motor memories and integrated with the sensory memories of those movements. ...
... This self-discovery of more efficient movements eventually leads to an array of somewhat efficient movements that are stored as motor memories and integrated with the sensory memories of those movements. ...
Memory Retrieval
... it again. For example, taking a multiple-choice quiz requires that you recognize the correct answer. Relearning: This type of memory retrieval involves relearning information that has been previously learned. ...
... it again. For example, taking a multiple-choice quiz requires that you recognize the correct answer. Relearning: This type of memory retrieval involves relearning information that has been previously learned. ...
Learning, remembering and forgetting in the mammalian brain
... permanent storage. The reasons for this reconsolidation are not clear but it has been suggested that this mechanism provides the opportunity to update stored memories based on new information. These results also suggest that procedures may be able to be implemented that enhance the second round of c ...
... permanent storage. The reasons for this reconsolidation are not clear but it has been suggested that this mechanism provides the opportunity to update stored memories based on new information. These results also suggest that procedures may be able to be implemented that enhance the second round of c ...
Learning, Memory and Amnesia
... recognize that stimulus again (it is remembered). – H. M. shows very limited signs of recognizing prior stimuli without cognitively realizing it. ...
... recognize that stimulus again (it is remembered). – H. M. shows very limited signs of recognizing prior stimuli without cognitively realizing it. ...
Silva & White - Walker Bioscience
... (e.g., 85 dB, 2800 Hz), and lesions in the amygdala, but not the hippocampus, appear to disrupt this type of conditioning. • - In "contextual conditioning", rodents become conditioned to the "context" in which they were exposed, such as a particular location. Contextual conditioning is thought to de ...
... (e.g., 85 dB, 2800 Hz), and lesions in the amygdala, but not the hippocampus, appear to disrupt this type of conditioning. • - In "contextual conditioning", rodents become conditioned to the "context" in which they were exposed, such as a particular location. Contextual conditioning is thought to de ...
Chap 5: The Cognitive Approach II
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
Ch07a
... the emotional arousal associated with an event, the greater the likelihood that the event will be remembered. • This does not mean that all components of the memory will be accurate! ...
... the emotional arousal associated with an event, the greater the likelihood that the event will be remembered. • This does not mean that all components of the memory will be accurate! ...
The Physiology of Memory Craig E. Geis, MBA, Management
... to be completely done to be done at all and so requires a higher degree of organization and competency which involves over learning. ...
... to be completely done to be done at all and so requires a higher degree of organization and competency which involves over learning. ...
Body Position Affects Access to Memories Katinka Dijkstra ()
... Autobiographical memories can be considered experiences that are stored in highly distributed memory traces, which include perceptual details that were part of the original experience. Retrieval of autobiographical memories has been conceptualized as a process in which the original experience is rec ...
... Autobiographical memories can be considered experiences that are stored in highly distributed memory traces, which include perceptual details that were part of the original experience. Retrieval of autobiographical memories has been conceptualized as a process in which the original experience is rec ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... 1. Increase in vesicle release site for secretion of transmitters 2. Increase in number of transmitter vesicles released 3. Increase in the number of presynaptic terminals 4. Changes in the structure of dendritic spines that permit transmission of stronger signals ...
... 1. Increase in vesicle release site for secretion of transmitters 2. Increase in number of transmitter vesicles released 3. Increase in the number of presynaptic terminals 4. Changes in the structure of dendritic spines that permit transmission of stronger signals ...
Lec 18 - Forgetting
... Forgetting (retention loss) refers to apparent loss of information already encoded and stored in an individual's long term memory. It is a spontaneous or gradual process in which oldmemories are unable to be recalled from memory storage. It is subject to delicately balanced optimization that ensures ...
... Forgetting (retention loss) refers to apparent loss of information already encoded and stored in an individual's long term memory. It is a spontaneous or gradual process in which oldmemories are unable to be recalled from memory storage. It is subject to delicately balanced optimization that ensures ...
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder? Motivation and Emotion are
... degree that usual psychological defenses are incapable of coping. It is important to make a distinction between PTSD and Traumatic stress, which is a similar condition, but of less intensity and duration.” ...
... degree that usual psychological defenses are incapable of coping. It is important to make a distinction between PTSD and Traumatic stress, which is a similar condition, but of less intensity and duration.” ...