CHM 441: QUANTUM CHEMISTRY
... called quantum mechanics, It challenged classical mechanics which states that the position and momentum of a particle can be calculated precisely at all times from knowledge of the forces on the particle. Photons which have energies given by E = hѵ are usual particles in that they have zero rest mas ...
... called quantum mechanics, It challenged classical mechanics which states that the position and momentum of a particle can be calculated precisely at all times from knowledge of the forces on the particle. Photons which have energies given by E = hѵ are usual particles in that they have zero rest mas ...
Quantum mechanics of light dispersion: does the photon have mass?
... mutually exclusive. Nonetheless, it is argued that because of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, there can be no such thing as a perfectly localized particle. In this view, a ”particle” is simply a particularly localized wave packet (a quantized state of the electromagnetic field), so from a pure ...
... mutually exclusive. Nonetheless, it is argued that because of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, there can be no such thing as a perfectly localized particle. In this view, a ”particle” is simply a particularly localized wave packet (a quantized state of the electromagnetic field), so from a pure ...
visible Ultra violet Infra red Longer line ? Energy? Wavelength
... Dual nature of ma@er (par2cle and/or wave ) was confirmed by Davisson and Germer and independently by G. P. Thomson both in 1927 ...
... Dual nature of ma@er (par2cle and/or wave ) was confirmed by Davisson and Germer and independently by G. P. Thomson both in 1927 ...
Unit 2 Intro Worksheet - Coral Gables Senior High
... 1. What is the explanation for the discrete lines in atomic emission spectra? 2. Why are you unable to observe the wavelike motion of a soccer ball as it is kicked toward a goal? 3. What is the quantum mechanical model? 4. Explain what is meant by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. 5. Explain the ...
... 1. What is the explanation for the discrete lines in atomic emission spectra? 2. Why are you unable to observe the wavelike motion of a soccer ball as it is kicked toward a goal? 3. What is the quantum mechanical model? 4. Explain what is meant by the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. 5. Explain the ...
Chemistry 1 Concept 5 “Electrons in Atoms” Study Guide
... 18. The spin quantum number indicates that the number of possible spin states for an electron in an orbital is __________ 19. The angular momentum quantum number indicates the ________________________ 20. What is the energy of a photon whose frequency is 5.0 x 1020 Hz? ______________ 21. What state ...
... 18. The spin quantum number indicates that the number of possible spin states for an electron in an orbital is __________ 19. The angular momentum quantum number indicates the ________________________ 20. What is the energy of a photon whose frequency is 5.0 x 1020 Hz? ______________ 21. What state ...
Lecture 24: Quantum mechanics
... Non-classical Explanation: Planck hypothesis. Planck assumed that the radiating substance was composed of electric dipoles that acted as simple harmonic oscillators. His suggestion was as follows: The energy of an oscillator must be discrete. E = n h where n is an integer, h is a constant of propo ...
... Non-classical Explanation: Planck hypothesis. Planck assumed that the radiating substance was composed of electric dipoles that acted as simple harmonic oscillators. His suggestion was as follows: The energy of an oscillator must be discrete. E = n h where n is an integer, h is a constant of propo ...
Lecture Notes, Feb 29
... The idea of the position of an object seems so obvious that the concept of position is generally taken for granted in classical physics. Knowing the position of a particle means knowing the values of its coordinates in some coordinate system. The precision of those values, in classical physics, is l ...
... The idea of the position of an object seems so obvious that the concept of position is generally taken for granted in classical physics. Knowing the position of a particle means knowing the values of its coordinates in some coordinate system. The precision of those values, in classical physics, is l ...
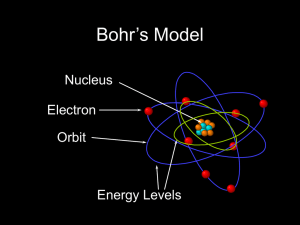
03-02BohrAtom
... • Did not explain • Spectral fine structure • Brightness of lines • Molecular bonds • Theory was not complete. • But otherwise it generally kicked tuckus ...
... • Did not explain • Spectral fine structure • Brightness of lines • Molecular bonds • Theory was not complete. • But otherwise it generally kicked tuckus ...
Wave-Particle Duality - the Principle of Complementarity The
... De Broglie’s hypothesis is the one associating a wavelength with the momentum of a particle. He proposed that only those orbits where the wave would be a circular standing wave will occur. This yields the same relation that Bohr had proposed. In addition, it makes more reasonable the fact that the e ...
... De Broglie’s hypothesis is the one associating a wavelength with the momentum of a particle. He proposed that only those orbits where the wave would be a circular standing wave will occur. This yields the same relation that Bohr had proposed. In addition, it makes more reasonable the fact that the e ...
2710 PS3 1 Problem Set #3 Comparing classical electromagnetic
... Problem 2 refers to: A single photon in a quantum wire stretching between x = 0 and x = L is described by the wavefunction Ψ(x,t) = Ψ max sin(3π x L)exp(− ic3π t L) . Let L= 900 nm. 2.(a) How does the photon kinetic energy vary in space and time? What is the average photon kinetic energy measured ma ...
... Problem 2 refers to: A single photon in a quantum wire stretching between x = 0 and x = L is described by the wavefunction Ψ(x,t) = Ψ max sin(3π x L)exp(− ic3π t L) . Let L= 900 nm. 2.(a) How does the photon kinetic energy vary in space and time? What is the average photon kinetic energy measured ma ...
Pre-AP Chemistry
... 1. What kind of proportion is shown by the equation c = λ ν? 2. Who stated that electromagnetic radiation has a dual nature? 3. How many meters are 665 nm equal to? 4. What wave measure is identified by the unit Hz? 5. What wave property is known as distance between similar points on a wave? 6. What ...
... 1. What kind of proportion is shown by the equation c = λ ν? 2. Who stated that electromagnetic radiation has a dual nature? 3. How many meters are 665 nm equal to? 4. What wave measure is identified by the unit Hz? 5. What wave property is known as distance between similar points on a wave? 6. What ...
Quantum Mechanics
... arbitrary accuracy momentum (p) and position (x) of a particle cannot be known exactly at the same time ...
... arbitrary accuracy momentum (p) and position (x) of a particle cannot be known exactly at the same time ...
BasicQuantumMechanics18And20January2017
... • It is impossible to simultaneously describe with absolute accuracy the energy of a particle and the instant of time the particle has this energy ...
... • It is impossible to simultaneously describe with absolute accuracy the energy of a particle and the instant of time the particle has this energy ...
Announcements
... constructive interference and dark for destructive interference. The same pattern appears even if you cut down the light intensity so that only one photon goes through at a time. But the photon has to go through either the top slit or the bottom slit, but it still interferes with itself. somehow it ...
... constructive interference and dark for destructive interference. The same pattern appears even if you cut down the light intensity so that only one photon goes through at a time. But the photon has to go through either the top slit or the bottom slit, but it still interferes with itself. somehow it ...
Line Spectra and the Bohr Model
... Line Spectra and the Bohr Model Limitations of the Bohr Model • Can only explain the line spectrum of hydrogen adequately. • Can only work for (at least) one electron atoms. • Cannot explain multi-lines with each color. • Electrons are not completely described as small particles. • Electrons can ha ...
... Line Spectra and the Bohr Model Limitations of the Bohr Model • Can only explain the line spectrum of hydrogen adequately. • Can only work for (at least) one electron atoms. • Cannot explain multi-lines with each color. • Electrons are not completely described as small particles. • Electrons can ha ...
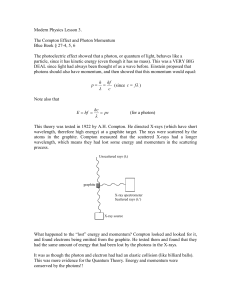
Modern Physics Lesson 3
... This can obviously only be used for objects with mass (i.e., NOT photons). It is usually used for electrons and protons, since they are the only objects that display noticeable wave-like properties. Normal sized objects (like a book or a basketball) also have a deBroglie wavelength, but it is so sma ...
... This can obviously only be used for objects with mass (i.e., NOT photons). It is usually used for electrons and protons, since they are the only objects that display noticeable wave-like properties. Normal sized objects (like a book or a basketball) also have a deBroglie wavelength, but it is so sma ...
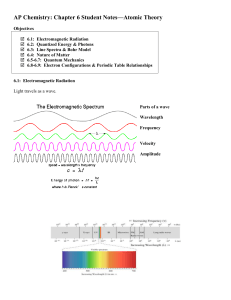
Ch. 6 notes
... 6.5-6.7: Quantum Mechanics Developed by Werner Heisenberg (1901-1976), Louis De Broglie (1892-1987), Erwin Schrodinger (1887-1961) This answers the question: Where is the _____________ in the atom? The answer is complex. We can’t say exactly where the atom is. We can only say where we think it _____ ...
... 6.5-6.7: Quantum Mechanics Developed by Werner Heisenberg (1901-1976), Louis De Broglie (1892-1987), Erwin Schrodinger (1887-1961) This answers the question: Where is the _____________ in the atom? The answer is complex. We can’t say exactly where the atom is. We can only say where we think it _____ ...
Bohr–Einstein debates

The Bohr–Einstein debates were a series of public disputes about quantum mechanics between Albert Einstein and Niels Bohr. Their debates are remembered because of their importance to the philosophy of science. An account of the debates was written by Bohr in an article titled ""Discussions with Einsteinon Epistemological Problems in Atomic Physics"". Despite their differences of opinion regarding quantum mechanics, Bohr and Einstein had a mutual admiration that was to last the rest of their lives.The debates represent one of the highest points of scientific research in the first half of the twentieth century because it called attention to an element of quantum theory, quantum non-locality, which is absolutely central to our modern understanding of the physical world. The consensus view of professional physicists has been that Bohr proved victorious, and definitively established the fundamental probabilistic character of quantum measurement.