The Indivisible Now: why time must be discrete. - Philsci
... considered individually as being determinate. The entangled system for a pair of photons for example is a non-divisible system. Secondly, as previously discussed, time being connected with physical properties implies various properties time itself must have, and in the case of non-reducible properti ...
... considered individually as being determinate. The entangled system for a pair of photons for example is a non-divisible system. Secondly, as previously discussed, time being connected with physical properties implies various properties time itself must have, and in the case of non-reducible properti ...
Full text in PDF form
... In the year nineteen hundred, in the course of a purely theoretic investigation, Max Planck made a very remarkable discovery: the law of radiation of bodies as a function of temperature could not be derived solely from the laws of Maxwellian electrodynamics. To arrive at results consistent with the ...
... In the year nineteen hundred, in the course of a purely theoretic investigation, Max Planck made a very remarkable discovery: the law of radiation of bodies as a function of temperature could not be derived solely from the laws of Maxwellian electrodynamics. To arrive at results consistent with the ...
Large Quantum Superpositions and Interference of Massive
... in [23]. In Fig. 2 the operational parameter regime is shown for different sphere sizes and superposition distances with the particular set of experimental parameters given in the caption. The interference pattern simulated by solving the master equation numerically, which describes the evolution of ...
... in [23]. In Fig. 2 the operational parameter regime is shown for different sphere sizes and superposition distances with the particular set of experimental parameters given in the caption. The interference pattern simulated by solving the master equation numerically, which describes the evolution of ...
Commutative Operators and Common Basis
... In other words, B |ai is an eigenstate of A with eigenvalue a. Since |ai is nondegenerate, B |ai has to be proportional to |ai, or B |ai = b |ai ...
... In other words, B |ai is an eigenstate of A with eigenvalue a. Since |ai is nondegenerate, B |ai has to be proportional to |ai, or B |ai = b |ai ...
Solution key to exam 1 - University of Rochester
... ____ Charles Coulomb discovered the fundamental nature of light in terms of electric and magnetic fields. ____ For any two people, time flows at exactly the same rate. ____ Albert Einstein invented Newton’s Laws. ____ The New York Yankees baseball players are heavily overpaid. ____ An object can be ...
... ____ Charles Coulomb discovered the fundamental nature of light in terms of electric and magnetic fields. ____ For any two people, time flows at exactly the same rate. ____ Albert Einstein invented Newton’s Laws. ____ The New York Yankees baseball players are heavily overpaid. ____ An object can be ...
File
... The spin quantum number of an electron can be thought of as describing a. the direction of electron spin. b. whether the electron's charge is positive or negative. c. the electron's exact location in orbit. d. the number of revolutions the electron makes about the nucleus per second. ...
... The spin quantum number of an electron can be thought of as describing a. the direction of electron spin. b. whether the electron's charge is positive or negative. c. the electron's exact location in orbit. d. the number of revolutions the electron makes about the nucleus per second. ...
Lecture Notes and Solved Problems
... However, one of the problems with Newton's particle theory of light is the observation that two light beams can pass through each other unaffected. This is very hard to explain with the corpuscular theory (there ought to be an enormous amount of scattering going on as the little particles smash agai ...
... However, one of the problems with Newton's particle theory of light is the observation that two light beams can pass through each other unaffected. This is very hard to explain with the corpuscular theory (there ought to be an enormous amount of scattering going on as the little particles smash agai ...
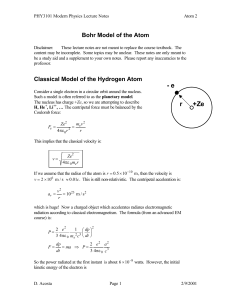
Atom 2 - UF Physics
... Thus, new laws of physics must be derived for atomic physics. The Bohr Model of the atom is the first step towards the new Quantum Mechanics ...
... Thus, new laws of physics must be derived for atomic physics. The Bohr Model of the atom is the first step towards the new Quantum Mechanics ...
Chapter 7_01042016
... • Principal quantum number (n) – size and energy of the orbital. • Angular momentum quantum number (l) shape of atomic orbitals (sometimes called a ...
... • Principal quantum number (n) – size and energy of the orbital. • Angular momentum quantum number (l) shape of atomic orbitals (sometimes called a ...
Bohr–Einstein debates

The Bohr–Einstein debates were a series of public disputes about quantum mechanics between Albert Einstein and Niels Bohr. Their debates are remembered because of their importance to the philosophy of science. An account of the debates was written by Bohr in an article titled ""Discussions with Einsteinon Epistemological Problems in Atomic Physics"". Despite their differences of opinion regarding quantum mechanics, Bohr and Einstein had a mutual admiration that was to last the rest of their lives.The debates represent one of the highest points of scientific research in the first half of the twentieth century because it called attention to an element of quantum theory, quantum non-locality, which is absolutely central to our modern understanding of the physical world. The consensus view of professional physicists has been that Bohr proved victorious, and definitively established the fundamental probabilistic character of quantum measurement.