Human Coelomic Divisions Coelomic Cavities Coelomic Cavities
... Human Liver Two big lobes, left & right separated by falciform ligament. Right lobe has subsidiary caudate and quadrate lobes. ...
... Human Liver Two big lobes, left & right separated by falciform ligament. Right lobe has subsidiary caudate and quadrate lobes. ...
Digestive System
... Human Liver Two big lobes, left & right separated by falciform ligament. Right lobe has subsidiary caudate and quadrate lobes. ...
... Human Liver Two big lobes, left & right separated by falciform ligament. Right lobe has subsidiary caudate and quadrate lobes. ...
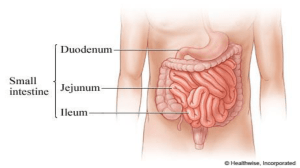
Small intestine notes
... • The intestinal enzymes are needed to break nutrients into their smallest chemical components so they can be absorbed into the • Large Molecules- such as most proteins, polysaccharides and disaccharides are too large to move into the blood stream • They must first be broken down in the small intest ...
... • The intestinal enzymes are needed to break nutrients into their smallest chemical components so they can be absorbed into the • Large Molecules- such as most proteins, polysaccharides and disaccharides are too large to move into the blood stream • They must first be broken down in the small intest ...
Digestion and Absorption
... Lymphatic tissue of the pharynx and oral cavity are arranged in a ring-like manner called Waldeyer’s ring consisting of pharyngeal, lingual, tubal and palatine tonsils. Oesophagous is a long, narrow, muscular tubular structure which connects pharynx with stomach. The oesophagus serves to convey the ...
... Lymphatic tissue of the pharynx and oral cavity are arranged in a ring-like manner called Waldeyer’s ring consisting of pharyngeal, lingual, tubal and palatine tonsils. Oesophagous is a long, narrow, muscular tubular structure which connects pharynx with stomach. The oesophagus serves to convey the ...
Stomach
... The largest gland in the body Superficially has four lobes – right, left, caudate, and quadrate The falciform ligament: Separates the right and left lobes anteriorly Suspends the liver from the diaphragm and anterior abdominal wall Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Be ...
... The largest gland in the body Superficially has four lobes – right, left, caudate, and quadrate The falciform ligament: Separates the right and left lobes anteriorly Suspends the liver from the diaphragm and anterior abdominal wall Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Be ...
Stomach - AC Reynolds High
... The largest gland in the body Superficially has four lobes – right, left, caudate, and quadrate The falciform ligament: Separates the right and left lobes anteriorly Suspends the liver from the diaphragm and anterior abdominal wall Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Be ...
... The largest gland in the body Superficially has four lobes – right, left, caudate, and quadrate The falciform ligament: Separates the right and left lobes anteriorly Suspends the liver from the diaphragm and anterior abdominal wall Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Be ...
Evaluation and Management of Patients with Acute Pancreatitis Russell Brown, MD
... Findings of acute pancreatitis by computed tomography (CT) ...
... Findings of acute pancreatitis by computed tomography (CT) ...
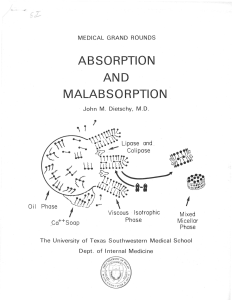
absorption and malabsorption
... to include almost any disease in which there is excessive loss of some constituent of ' the diet, including water and electrolytes, in the feces. When used in this manner, such diverse illnesses as viral gastroenteritis, the disaccharidase deficiency states, various enteric bacterial infections, dis ...
... to include almost any disease in which there is excessive loss of some constituent of ' the diet, including water and electrolytes, in the feces. When used in this manner, such diverse illnesses as viral gastroenteritis, the disaccharidase deficiency states, various enteric bacterial infections, dis ...
ch_23_lecture_outline_c
... 1 Large fat globules are emulsified (physically broken up into smaller fat droplets) by bile salts in the duodenum. ...
... 1 Large fat globules are emulsified (physically broken up into smaller fat droplets) by bile salts in the duodenum. ...
Digestion and the Digestive System
... • fatty acids, peptides stimulate release of GIF (gastric inhibitory polypeptide) and CCK (cholecystokinin) Several additional mediators have been shown to result in gastric acid secretion when infused into animals and people, including e.g. calcium. Calcium simulates gastrin release. lt is unclear ...
... • fatty acids, peptides stimulate release of GIF (gastric inhibitory polypeptide) and CCK (cholecystokinin) Several additional mediators have been shown to result in gastric acid secretion when infused into animals and people, including e.g. calcium. Calcium simulates gastrin release. lt is unclear ...
Sistrunk`s original article
... rather firm, cystic tumor in the midline of the neck, near the hyoid bone or the thyroid cartilage. When this is palpated the duct which runs from the cyst to the hyoid bone may usually be felt. If the cyst is left alone, it gradually enlarges and often is drained s ...
... rather firm, cystic tumor in the midline of the neck, near the hyoid bone or the thyroid cartilage. When this is palpated the duct which runs from the cyst to the hyoid bone may usually be felt. If the cyst is left alone, it gradually enlarges and often is drained s ...
Nipple Discharge - Tulsa OB/GYN Associates, Inc.
... This is the third most common breast complaint, and is most commonly not a serious problem. In nonlactating women, small plugs of tissue block the nipple ducts and keep the nipple from discharging fluid. Nipple discharge is often yellow, green, brown, bloody, or milky in appearance. Milky discharge ...
... This is the third most common breast complaint, and is most commonly not a serious problem. In nonlactating women, small plugs of tissue block the nipple ducts and keep the nipple from discharging fluid. Nipple discharge is often yellow, green, brown, bloody, or milky in appearance. Milky discharge ...
Exam 2 - GEOCITIES.ws
... a. low physical activity can lead to constipation B. GI Hemorrhage 1. general a. 80% of the time it stops w/o intervention b. can be life threatening c. management of GI bleed ***** 1. correct hypovolemia (most important) 2. stop bleeding 3. prevent recurrent bleeding ...
... a. low physical activity can lead to constipation B. GI Hemorrhage 1. general a. 80% of the time it stops w/o intervention b. can be life threatening c. management of GI bleed ***** 1. correct hypovolemia (most important) 2. stop bleeding 3. prevent recurrent bleeding ...
INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION
... 7. Closed-loop obstruction is a condition in which the intestinal segment is occluded at both ends, preventing either the downward passage or the regurgitation of intestinal contents. ...
... 7. Closed-loop obstruction is a condition in which the intestinal segment is occluded at both ends, preventing either the downward passage or the regurgitation of intestinal contents. ...
Teacher`s Guide for “The Digestive Tract” CT State Standards
... b. Esophagus – food travels down this tube into the stomach c. Stomach – Food enters stomach where churning occurs (mechanical) and gastric juice and HCL is released (chemical digestion) Mucus is released to prevent stomach from digesting itself. Food is now a lumpy oatmeal‐like substance calle ...
... b. Esophagus – food travels down this tube into the stomach c. Stomach – Food enters stomach where churning occurs (mechanical) and gastric juice and HCL is released (chemical digestion) Mucus is released to prevent stomach from digesting itself. Food is now a lumpy oatmeal‐like substance calle ...
Esophagus
... Digestive Processes in the Stomach • Lipid-soluble alcohol and aspirin absorbed into blood • Only stomach function essential to life – Secretes intrinsic factor for vitamin B12 absorption • B12 needed mature red blood cells • Lack of intrinsic factor ® pernicious anemia • Treated with B12 injecti ...
... Digestive Processes in the Stomach • Lipid-soluble alcohol and aspirin absorbed into blood • Only stomach function essential to life – Secretes intrinsic factor for vitamin B12 absorption • B12 needed mature red blood cells • Lack of intrinsic factor ® pernicious anemia • Treated with B12 injecti ...
ch_23_lecture_outline_b
... Absorptive cells Lacteal Goblet cell Blood capillaries Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue Intestinal crypt Muscularis mucosae Duodenal gland (b) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Absorptive cells Lacteal Goblet cell Blood capillaries Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue Intestinal crypt Muscularis mucosae Duodenal gland (b) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Part b
... Absorptive cells Lacteal Goblet cell Blood capillaries Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue Intestinal crypt Muscularis mucosae Duodenal gland (b) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Absorptive cells Lacteal Goblet cell Blood capillaries Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue Intestinal crypt Muscularis mucosae Duodenal gland (b) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Chapter 23 PowerPoint
... Absorptive cells Lacteal Goblet cell Blood capillaries Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue Intestinal crypt Muscularis mucosae Duodenal gland (b) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Absorptive cells Lacteal Goblet cell Blood capillaries Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue Intestinal crypt Muscularis mucosae Duodenal gland (b) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
D25 - 1 UNIT 25. DISSECTION: PERITONEAL CAVITY, STOMACH
... Move the small intestines as far to the left as possible, exposing the right side of the mesentery proper. Remove the entire layer of peritoneum covering this surface and expose the superior mesenteric vessels (N. plates 306, 310; G. plate 2.35, 2.36) and their branches. In cleaning the vessels, the ...
... Move the small intestines as far to the left as possible, exposing the right side of the mesentery proper. Remove the entire layer of peritoneum covering this surface and expose the superior mesenteric vessels (N. plates 306, 310; G. plate 2.35, 2.36) and their branches. In cleaning the vessels, the ...
Frog External Anatomy
... fat frog, these fat bodies may need to be removed to see the other structures. Peritoneum A spider web like membrane that covers many of the organs, you may have to carefully pick it off to get a clear view Liver--The largest structure of the body cavity. This brown colored organ is composed of thre ...
... fat frog, these fat bodies may need to be removed to see the other structures. Peritoneum A spider web like membrane that covers many of the organs, you may have to carefully pick it off to get a clear view Liver--The largest structure of the body cavity. This brown colored organ is composed of thre ...
BI 233 Laboratory Package winter 2013 - PCC
... Students who do not comply with these safety guidelines and directions will be excluded from the Laboratory ...
... Students who do not comply with these safety guidelines and directions will be excluded from the Laboratory ...
Ascending cholangitis

Ascending cholangitis or acute cholangitis (or sometimes cholangitis without a modifier - from Greek chol-, bile + ang-, vessel + itis-, inflammation) is an infection of the bile duct (cholangitis), usually caused by bacteria ascending from its junction with the duodenum (first part of the small intestine). It tends to occur if the bile duct is already partially obstructed by gallstones.Cholangitis can be life-threatening, and is regarded as a medical emergency. Characteristic symptoms include yellow discoloration of the skin or whites of the eyes, fever, abdominal pain, and in severe cases, low blood pressure and confusion. Initial treatment is with intravenous fluids and antibiotics, but there is often an underlying problem (such as gallstones or narrowing in the bile duct) for which further tests and treatments may be necessary, usually in the form of endoscopy to relieve obstruction of the bile duct.