GI Tract - review anatomy of upper and lower GI tract
... - identify the regions of the small intestine; define ‘law of intestine’; describe the organization of the intestinal villus -- where is the lamina propria? What is the lacteal? - what are intestinal crypts? What substances are released from intestinal glands? - describe regional secretion and abso ...
... - identify the regions of the small intestine; define ‘law of intestine’; describe the organization of the intestinal villus -- where is the lamina propria? What is the lacteal? - what are intestinal crypts? What substances are released from intestinal glands? - describe regional secretion and abso ...
watering eye
... and also due to the negative pressure created by the sac. • As the sac is surrounded by the orbicularis muscle, normal blinking movements result in negative pressure in the sac when the lids are open and positive pressure when, the lids are closed. ...
... and also due to the negative pressure created by the sac. • As the sac is surrounded by the orbicularis muscle, normal blinking movements result in negative pressure in the sac when the lids are open and positive pressure when, the lids are closed. ...
pdf - Open Assembly
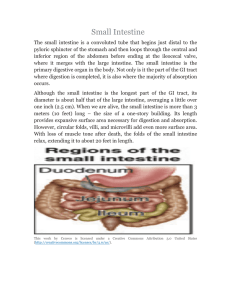
... The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine; it is less than 1 foot of the 10 foot intestine (30 cm of the 3 m). The duodenum receives the stomach contents, pancreatic juice and bile. Chemical digestion continues in the duodenum. The jejunum is the nex ...
... The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine; it is less than 1 foot of the 10 foot intestine (30 cm of the 3 m). The duodenum receives the stomach contents, pancreatic juice and bile. Chemical digestion continues in the duodenum. The jejunum is the nex ...
Lecture 7
... The gallbladder is a sac located in a depression on the posterior surface of the liver ...
... The gallbladder is a sac located in a depression on the posterior surface of the liver ...
7.Medical Helminthology flatworms
... Localization: bile ducts, gallbladder and liver of mammals (cattle, horses). Very rare in humans. Morphology: the worms are 1 cm long with lanceolate form of the body; the ...
... Localization: bile ducts, gallbladder and liver of mammals (cattle, horses). Very rare in humans. Morphology: the worms are 1 cm long with lanceolate form of the body; the ...
Digestion Fizz
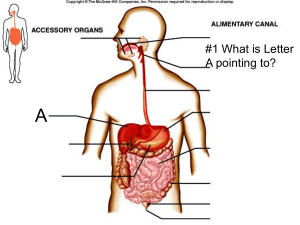
... picture of the stomach and small intestine. B Which letter is closest to the esophageal sphincter? ...
... picture of the stomach and small intestine. B Which letter is closest to the esophageal sphincter? ...
The mannitol fermentation test.
... Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak) ...
... Bacitracin resistant CAMP positive Growth on Mac (weak) ...
Physiology of Digestive System I - كلية طب الاسنان
... Secretions of the small intestine Secretion of Mucus by Brunner’s Glands in the Duodenum An extensive array of compound mucous glands, called Brunner’s glands, is located in the wall of the first few centimeters of the duodenum, mainly between the pylorus of the stomach and the papilla of Vater wh ...
... Secretions of the small intestine Secretion of Mucus by Brunner’s Glands in the Duodenum An extensive array of compound mucous glands, called Brunner’s glands, is located in the wall of the first few centimeters of the duodenum, mainly between the pylorus of the stomach and the papilla of Vater wh ...
cystic fibrosis case study
... parents who were both carries for the disease. Some symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis are frequent lung infections, salty skin, wheezing, greasy stool and poor weight gain. 2. Cystic Fibrosis affects the lungs, pancreas, liver, gallbladder, intestines, sinuses, sex organs and the epithelial tissue (simple ...
... parents who were both carries for the disease. Some symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis are frequent lung infections, salty skin, wheezing, greasy stool and poor weight gain. 2. Cystic Fibrosis affects the lungs, pancreas, liver, gallbladder, intestines, sinuses, sex organs and the epithelial tissue (simple ...
chapter_16_digestion_and_absorption
... The digestion of proteins begins in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine. The digestive juice secreted in the gastric glands present on the stomach walls is called gastric juice. The food that enters the stomach becomes acidic on mixing with this gastric juice. The main components of ...
... The digestion of proteins begins in the stomach and is completed in the small intestine. The digestive juice secreted in the gastric glands present on the stomach walls is called gastric juice. The food that enters the stomach becomes acidic on mixing with this gastric juice. The main components of ...
Eye Infections: Neonatal - Women and Newborn Health Service
... spilling of tears without conjunctivitis may indicate nasal lacrimal duct obstruction, which is usually ...
... spilling of tears without conjunctivitis may indicate nasal lacrimal duct obstruction, which is usually ...
Quiz 4 Practice - philipdarrenjones.com
... 2. Which of the following best describes bone remodeling? a. bone growth through adolescence b. a balance between deposition and absorption of bone minerals c. joint replacement d. plastic surgery after an accident 3. Which of the following activities would lead to the strongest bones? a. bicycling ...
... 2. Which of the following best describes bone remodeling? a. bone growth through adolescence b. a balance between deposition and absorption of bone minerals c. joint replacement d. plastic surgery after an accident 3. Which of the following activities would lead to the strongest bones? a. bicycling ...
Stomach
... Figure 23.16 Photographs of a gastric ulcer and the H. pylori bacteria that most commonly cause it. ...
... Figure 23.16 Photographs of a gastric ulcer and the H. pylori bacteria that most commonly cause it. ...
Thomas
... Small intestine Partially digested food is passed into the small intestine so that it can be further digested as well as absorb nutrients from the food. The small intestine consists of the Duodenum, Jejunum and Ileum. ...
... Small intestine Partially digested food is passed into the small intestine so that it can be further digested as well as absorb nutrients from the food. The small intestine consists of the Duodenum, Jejunum and Ileum. ...
Nutrition & Digestion Review Power Point
... •Mouth – teeth grind up food 37. Where does chemical digestion begin? ...
... •Mouth – teeth grind up food 37. Where does chemical digestion begin? ...
`Oh no it`s Physio!` - Gastrointestinal System and Nutrition
... Acts as valve → closed when food not being swallowed, therefore prevents regurgitation of food, acid & air Relaxes just before peristaltic wave (& food) reaches end of esophagus Proximal stomach = fundus + body → act as temporary reservoir of food → can accommodate ↑ volume with no ↑ in intragastric ...
... Acts as valve → closed when food not being swallowed, therefore prevents regurgitation of food, acid & air Relaxes just before peristaltic wave (& food) reaches end of esophagus Proximal stomach = fundus + body → act as temporary reservoir of food → can accommodate ↑ volume with no ↑ in intragastric ...
Airway obstruction
... May be impaired for similar reasons May decompensate with addition of varied bolus sizes and consistencies ...
... May be impaired for similar reasons May decompensate with addition of varied bolus sizes and consistencies ...
2. SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACT
... bacteria. All these actions maintain the health of the oral cavity and the teeth of the animals. The last role of saliva is thermoregulation. There are many animals that are not capable of sweating, dogs for example. These animals depend on the evaporation taking place over the tongue, oral cavity a ...
... bacteria. All these actions maintain the health of the oral cavity and the teeth of the animals. The last role of saliva is thermoregulation. There are many animals that are not capable of sweating, dogs for example. These animals depend on the evaporation taking place over the tongue, oral cavity a ...
Medical Terminology
... Jaundice / Icterus : yellow discoloration of the skin, sclera,and other tissues caused by excessive bilirubin in the blood Ascites: Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the abdomen; can be a symptom of neoplasm or inflammatory disorders in the abdomen, venous hypertension caused by liver disease and he ...
... Jaundice / Icterus : yellow discoloration of the skin, sclera,and other tissues caused by excessive bilirubin in the blood Ascites: Abnormal accumulation of fluid in the abdomen; can be a symptom of neoplasm or inflammatory disorders in the abdomen, venous hypertension caused by liver disease and he ...
GI Physiology IV: Early Intestinal Phase of
... Delivery of acid and nutrients into the small intestine initiates signaling that slows gastric motility and secretion which allows adequate time for digestion and absorption in the duodenum. ...
... Delivery of acid and nutrients into the small intestine initiates signaling that slows gastric motility and secretion which allows adequate time for digestion and absorption in the duodenum. ...
Cirrhosis of the Liver
... sample of liver tissue, then examines it under the microscope for scarring or other signs of disease. Treatment Liver damage from cirrhosis cannot be reversed, but treatment can stop or delay further progression and reduce complications. Treatment depends on the cause of cirrhosis and any complicati ...
... sample of liver tissue, then examines it under the microscope for scarring or other signs of disease. Treatment Liver damage from cirrhosis cannot be reversed, but treatment can stop or delay further progression and reduce complications. Treatment depends on the cause of cirrhosis and any complicati ...
Part B
... Absorptive cells Lacteal Goblet cell Blood capillaries Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue Intestinal crypt Muscularis mucosae Duodenal gland (b) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Absorptive cells Lacteal Goblet cell Blood capillaries Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue Intestinal crypt Muscularis mucosae Duodenal gland (b) Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
... in controlling IBD and IBS • Currently all uses for FMT outside of CDI treatment are considered investigational and must take place in the setting of a clinical trial • FMT does NOT alter liver transplant status, may resolve recurrent infections that delay transplantation. ...
... in controlling IBD and IBS • Currently all uses for FMT outside of CDI treatment are considered investigational and must take place in the setting of a clinical trial • FMT does NOT alter liver transplant status, may resolve recurrent infections that delay transplantation. ...
What`s In Your Probiotic? A probiotic is only as good as its bacterial
... Health Benefits ● May improve specific immune response* ● Beneficial modulation of immune function* ● Competes for adhesion sites with pathogens, stimulates immunoglobulin A (IgA)* Strain Name: Lactobacillus rhamnosus Characteristics ● One of the most common species in breast-fed infants. Also found ...
... Health Benefits ● May improve specific immune response* ● Beneficial modulation of immune function* ● Competes for adhesion sites with pathogens, stimulates immunoglobulin A (IgA)* Strain Name: Lactobacillus rhamnosus Characteristics ● One of the most common species in breast-fed infants. Also found ...
Ascending cholangitis

Ascending cholangitis or acute cholangitis (or sometimes cholangitis without a modifier - from Greek chol-, bile + ang-, vessel + itis-, inflammation) is an infection of the bile duct (cholangitis), usually caused by bacteria ascending from its junction with the duodenum (first part of the small intestine). It tends to occur if the bile duct is already partially obstructed by gallstones.Cholangitis can be life-threatening, and is regarded as a medical emergency. Characteristic symptoms include yellow discoloration of the skin or whites of the eyes, fever, abdominal pain, and in severe cases, low blood pressure and confusion. Initial treatment is with intravenous fluids and antibiotics, but there is often an underlying problem (such as gallstones or narrowing in the bile duct) for which further tests and treatments may be necessary, usually in the form of endoscopy to relieve obstruction of the bile duct.