Period 2 - Digestive System
... 1. Oral Cavity, PharynxThe oral cavity is where food is chewed and saliva is produced to help propel food toward the stomach. The upper portion of the oral cavity is where the hard and soft palates are located, with the tongue serving as the primary organ in the area.The Pharynx muscular walls funct ...
... 1. Oral Cavity, PharynxThe oral cavity is where food is chewed and saliva is produced to help propel food toward the stomach. The upper portion of the oral cavity is where the hard and soft palates are located, with the tongue serving as the primary organ in the area.The Pharynx muscular walls funct ...
Digestion
... • Labial frenulum – median fold that joins the internal aspect of each lip to the gum • Vestibule – bounded by the lips and cheeks externally, and teeth and gums internally • Oral cavity proper – area that lies within the teeth and gums ...
... • Labial frenulum – median fold that joins the internal aspect of each lip to the gum • Vestibule – bounded by the lips and cheeks externally, and teeth and gums internally • Oral cavity proper – area that lies within the teeth and gums ...
Preview Sample 2
... d. the type of lipoproteins made primarily by liver cells to transport lipids to various tissues in the body; composed primarily of triglycerides. e. the type of lipoproteins derived from VLDL as cells remove triglycerides from them; composed primarily of cholesterol. f. the type of lipoproteins tha ...
... d. the type of lipoproteins made primarily by liver cells to transport lipids to various tissues in the body; composed primarily of triglycerides. e. the type of lipoproteins derived from VLDL as cells remove triglycerides from them; composed primarily of cholesterol. f. the type of lipoproteins tha ...
Digestive System Packet
... • Because your liver has so many vital functions, you would die within 24 hours if it stopped working. • A common sign of a damaged liver is jaundice, a yellowness of your eyes and skin. This happens when bilirubin, a yellow breakdown product of your red blood cells, builds up in your blood. Gallbla ...
... • Because your liver has so many vital functions, you would die within 24 hours if it stopped working. • A common sign of a damaged liver is jaundice, a yellowness of your eyes and skin. This happens when bilirubin, a yellow breakdown product of your red blood cells, builds up in your blood. Gallbla ...
Emergency Medical Training Services
... Localized tearing is associated with rupture of the organ. Dull pain may be obstruction. Sharp pain, (in flank) kidney stones. Shoulder or neck pain associated with diaphragm. IE Cholecystitis. Any abdominal pain lasting over 6 hours considered surgical emergency. Vomit – coffee grounds or clots. Lo ...
... Localized tearing is associated with rupture of the organ. Dull pain may be obstruction. Sharp pain, (in flank) kidney stones. Shoulder or neck pain associated with diaphragm. IE Cholecystitis. Any abdominal pain lasting over 6 hours considered surgical emergency. Vomit – coffee grounds or clots. Lo ...
Lipid Digestion and Transport: Objectives
... 1. Short and medium chain FAs are transported to the liver via the portal vein (NOT via the chylomicrons!) 2. Transported as micelles (along with Cholesterol) 3. Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) hydrolyzes FAs from TGs a. Which allows FAs to be transported into fat cell and consequently re-esterified with g ...
... 1. Short and medium chain FAs are transported to the liver via the portal vein (NOT via the chylomicrons!) 2. Transported as micelles (along with Cholesterol) 3. Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) hydrolyzes FAs from TGs a. Which allows FAs to be transported into fat cell and consequently re-esterified with g ...
Biliary Intervention - What`s New in Medicine
... • Upsize for pericatheter leakage if necessary • Convert to internal biliary stent for malignant stricture if appropriate • DO NOT place metal stent for benign strictures unless life expectancy is less than 3-6 months ...
... • Upsize for pericatheter leakage if necessary • Convert to internal biliary stent for malignant stricture if appropriate • DO NOT place metal stent for benign strictures unless life expectancy is less than 3-6 months ...
I. DEFINITIONS THE DEGLUTITION PROCESS 2) Peristalsis
... with the gastric juice forming a thin fluid called the chyme. The muscular wall of the stomach is stronger in the pyloric region, and the peristalsis waves here force several milliliters of chyme into the duodenum through the pyloric sphincter. The later opens to permit the passage of chyme into the ...
... with the gastric juice forming a thin fluid called the chyme. The muscular wall of the stomach is stronger in the pyloric region, and the peristalsis waves here force several milliliters of chyme into the duodenum through the pyloric sphincter. The later opens to permit the passage of chyme into the ...
Digestive System
... new research shows it may make digestive enzymes produced no where else in the body • Features – 7-9 cm (varies); redish, wormlike sac; open only at one end; attached to cecum ...
... new research shows it may make digestive enzymes produced no where else in the body • Features – 7-9 cm (varies); redish, wormlike sac; open only at one end; attached to cecum ...
DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY
... • HYDROGEN IONS ARE DISSOCIATED FROM WATER MOLECULES • ACTIVELY TRANSPORTED FROM INTERIOR OF PARIETAL CELLS TO STOMACH LUMEN ...
... • HYDROGEN IONS ARE DISSOCIATED FROM WATER MOLECULES • ACTIVELY TRANSPORTED FROM INTERIOR OF PARIETAL CELLS TO STOMACH LUMEN ...
Dear Notetaker:
... Acid in duodenum causes secretin release Fat and protein cause CCK release CCK will cause acinar cells to release enzymes to break down those components ...
... Acid in duodenum causes secretin release Fat and protein cause CCK release CCK will cause acinar cells to release enzymes to break down those components ...
Digestive System
... • It stores excess bile produced by the liver and when needed, it releases bile into the duodenum • The passage of the stones may block the common bile duct and cause jaundice, a yellowish tint of the whites of the eyes and skin. Jaundice is caused by abnormal amounts of bilirubin in the blood. At t ...
... • It stores excess bile produced by the liver and when needed, it releases bile into the duodenum • The passage of the stones may block the common bile duct and cause jaundice, a yellowish tint of the whites of the eyes and skin. Jaundice is caused by abnormal amounts of bilirubin in the blood. At t ...
Mouth
... Bile breaks down fats into large fat droplets so juices from the small intestine and enzymes from the pancreas mix more easily with the fat Fats are eventually broken down into fatty acids and ...
... Bile breaks down fats into large fat droplets so juices from the small intestine and enzymes from the pancreas mix more easily with the fat Fats are eventually broken down into fatty acids and ...
The Digestion of Food
... Complete the flowchart about the digestion of food. These terms may be used more than once: esophagus, feces, large intestine, liver, mechanical digestion, mouth, pancreas, pepsin, stomach. ...
... Complete the flowchart about the digestion of food. These terms may be used more than once: esophagus, feces, large intestine, liver, mechanical digestion, mouth, pancreas, pepsin, stomach. ...
Pharyngeal Apparatus
... • It begins to form about 24 days after fertilization • It develops from a median endodermal thickening in the floor of a primordial pharynx • Thickening soon forms a small outpouching called thyroid primordium ...
... • It begins to form about 24 days after fertilization • It develops from a median endodermal thickening in the floor of a primordial pharynx • Thickening soon forms a small outpouching called thyroid primordium ...
The digestive system consists of
... When your stomach fills the rugae flattens out. When its full the rugae almost disappears. When full: it can expand to contain 1-1.5 liters of material. ...
... When your stomach fills the rugae flattens out. When its full the rugae almost disappears. When full: it can expand to contain 1-1.5 liters of material. ...
BIOL242DigestiveObjChap23,24SEP2012
... 7. Know the functions of the stomach. Know the anatomy of the stomach including the regions (cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus) and what is unique to each region of the stomach. What is distinctive to the histology of the stomach? 8. Know the purpose of the gastric glands in the stomach. What types ...
... 7. Know the functions of the stomach. Know the anatomy of the stomach including the regions (cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus) and what is unique to each region of the stomach. What is distinctive to the histology of the stomach? 8. Know the purpose of the gastric glands in the stomach. What types ...
BIOL242DigestiveObjChap23,24SEP2012
... 7. Know the functions of the stomach. Know the anatomy of the stomach including the regions (cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus) and what is unique to each region of the stomach. What is distinctive to the histology of the stomach? 8. Know the purpose of the gastric glands in the stomach. What types ...
... 7. Know the functions of the stomach. Know the anatomy of the stomach including the regions (cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus) and what is unique to each region of the stomach. What is distinctive to the histology of the stomach? 8. Know the purpose of the gastric glands in the stomach. What types ...
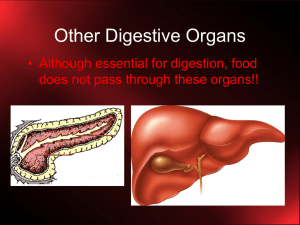
Other Digestive Organs
... • secretes enzymes into small intestine for chemical digestion • responsible for neutralization of acidic chyme from the stomach ...
... • secretes enzymes into small intestine for chemical digestion • responsible for neutralization of acidic chyme from the stomach ...
Class – XI Biology Chapter – 16 Human
... The other two digestive enzyme secreted by its source gland is amylase and lipases. Answer 9: The polysaccharides and disaccharides are partially digested by the amylase enzyme present in the pancreatic juice. The remaining digestion takes place by enzymes in the succus entericus. The enzyme maltase ...
... The other two digestive enzyme secreted by its source gland is amylase and lipases. Answer 9: The polysaccharides and disaccharides are partially digested by the amylase enzyme present in the pancreatic juice. The remaining digestion takes place by enzymes in the succus entericus. The enzyme maltase ...
Digestive System Notes (PPT)
... ______________________________ that is about 25 cm (10 inches) long and in most people can hold over 2 liters of food When empty, its inner linings form deep folds known as _______________ (ROO-JE) The convex lateral margin of the stomach is called the ______________________________ The greater omen ...
... ______________________________ that is about 25 cm (10 inches) long and in most people can hold over 2 liters of food When empty, its inner linings form deep folds known as _______________ (ROO-JE) The convex lateral margin of the stomach is called the ______________________________ The greater omen ...
Review
... 2. What is the middle section of the small intestine: 3. The “gatekeeper” of the small intestine that regulates food movement into it is the: 4. The primary function of the small intestine is: 5. Amylase is an enzyme that digests what? 6. Pancreatic enzymes for digestion are secreted into which sect ...
... 2. What is the middle section of the small intestine: 3. The “gatekeeper” of the small intestine that regulates food movement into it is the: 4. The primary function of the small intestine is: 5. Amylase is an enzyme that digests what? 6. Pancreatic enzymes for digestion are secreted into which sect ...
Ascending cholangitis

Ascending cholangitis or acute cholangitis (or sometimes cholangitis without a modifier - from Greek chol-, bile + ang-, vessel + itis-, inflammation) is an infection of the bile duct (cholangitis), usually caused by bacteria ascending from its junction with the duodenum (first part of the small intestine). It tends to occur if the bile duct is already partially obstructed by gallstones.Cholangitis can be life-threatening, and is regarded as a medical emergency. Characteristic symptoms include yellow discoloration of the skin or whites of the eyes, fever, abdominal pain, and in severe cases, low blood pressure and confusion. Initial treatment is with intravenous fluids and antibiotics, but there is often an underlying problem (such as gallstones or narrowing in the bile duct) for which further tests and treatments may be necessary, usually in the form of endoscopy to relieve obstruction of the bile duct.