UNIT SIX: MOLECULAR GENETICS AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
... d. Nucleotides form long chains, with the phosphate group of one nucleotide bonding to the deoxyribose sugar of the adjacent nucleotide. e. The amount of adenine always equals the amount of thymine, and the amount of cytosine is always equal to the amount of guanine: Chargoff’s rule (see page 329, F ...
... d. Nucleotides form long chains, with the phosphate group of one nucleotide bonding to the deoxyribose sugar of the adjacent nucleotide. e. The amount of adenine always equals the amount of thymine, and the amount of cytosine is always equal to the amount of guanine: Chargoff’s rule (see page 329, F ...
... Many mutations in Neurospora crassa are only known by a morphological or other visible phenotype. For many of these, the actual open reading frame responsible remains unknown. Among these are several temperature-sensitive lethal mutations known as unknown (Inoue and Ishikawa, 1970; Ishikawa and Perk ...
Shark Fin Forensics
... different species' DNA.) To do this, you must add primers and reagents to the unknown shark fin DNA samples as well as your great white DNA sample. First, use the pipette to load “Taq” and insert it into each tube. (You can pick up the pipette from the bench and then click on the Taq jar to generate ...
... different species' DNA.) To do this, you must add primers and reagents to the unknown shark fin DNA samples as well as your great white DNA sample. First, use the pipette to load “Taq” and insert it into each tube. (You can pick up the pipette from the bench and then click on the Taq jar to generate ...
array CGH
... Interpretation and limitations: This test will detect genomic CNVs associated with unbalanced chromosomal rearrangements. It will detect aneuploidies, deletions, and duplications, as well as unbalanced translocations of the regions represented on the array. CNVs >200-300 kb will be reported. Smaller ...
... Interpretation and limitations: This test will detect genomic CNVs associated with unbalanced chromosomal rearrangements. It will detect aneuploidies, deletions, and duplications, as well as unbalanced translocations of the regions represented on the array. CNVs >200-300 kb will be reported. Smaller ...
Sal I (R0754) - Datasheet - Sigma
... N6-methyladenine at GTCGmAC. Sal I exhibits star activity under non-optimal conditions. 100 units of Sal I can be heat inactivated after 15 minutes at 65 °C. Sal I Storage and Dilution Buffer: 10 mM Tris-HCl, 1.0 mM EDTA, 10 mM dithioerythritol, and 50% (v/v) glycerol, pH 7.5 Activity: 10,000 units/ ...
... N6-methyladenine at GTCGmAC. Sal I exhibits star activity under non-optimal conditions. 100 units of Sal I can be heat inactivated after 15 minutes at 65 °C. Sal I Storage and Dilution Buffer: 10 mM Tris-HCl, 1.0 mM EDTA, 10 mM dithioerythritol, and 50% (v/v) glycerol, pH 7.5 Activity: 10,000 units/ ...
Bio 6 – DNA & Gene Expression Lab Overview
... Before we look at translation, you need to understand the genetic code. While this may seem like yet another thing you need to learn in biology class, having knowledge of the genetic code is truly a remarkable privilege. Scientists and thinkers from the past would have given anything to know what yo ...
... Before we look at translation, you need to understand the genetic code. While this may seem like yet another thing you need to learn in biology class, having knowledge of the genetic code is truly a remarkable privilege. Scientists and thinkers from the past would have given anything to know what yo ...
Mutations Worksheet
... string of 3 or 4 nucleotides repeated over and over. A locus on the human X chromosome contains such a stretch of nucleotides in which the triplet CGG is repeated (CGGCGGCGGCGG, etc.). The number of CGGs may be as few as 5 or as many as 50 without causing a harmful phenotype. Even 100 repeats usuall ...
... string of 3 or 4 nucleotides repeated over and over. A locus on the human X chromosome contains such a stretch of nucleotides in which the triplet CGG is repeated (CGGCGGCGGCGG, etc.). The number of CGGs may be as few as 5 or as many as 50 without causing a harmful phenotype. Even 100 repeats usuall ...
Activation of Transcription
... A typical differentiated mammalian cell makes about 100,000 proteins from approximately 35,000 genes. Most of these are housekeeping proteins needed to maintain all cell types. Certain proteins can only be detected in specific cell types. How is gene expression regulated? Regulation of gene express ...
... A typical differentiated mammalian cell makes about 100,000 proteins from approximately 35,000 genes. Most of these are housekeeping proteins needed to maintain all cell types. Certain proteins can only be detected in specific cell types. How is gene expression regulated? Regulation of gene express ...
worksheet 12-3
... attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it releases the newly formed polypeptide and the mRNA molecule. 18. What is an anticodon? ...
... attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it releases the newly formed polypeptide and the mRNA molecule. 18. What is an anticodon? ...
Advanced Organic Chemistry of Nucleic Acids
... nucleic acids to Moscow University chemistry majors already with a solid organic and physical chemistry background. To teach this particular subject was most exciting at the time when virtually every year was marked by stunning discoveries in the field of nucleic acids. We still derive a great deal ...
... nucleic acids to Moscow University chemistry majors already with a solid organic and physical chemistry background. To teach this particular subject was most exciting at the time when virtually every year was marked by stunning discoveries in the field of nucleic acids. We still derive a great deal ...
NOTE slides 15-21
... Define operon. Identify the operon in this diagram and the organism it is in. What do the genes in this operon code for and how does it benefit E. coli? Study the diagram and identify the two regulatory regions. Describe and explain the function of the promoter region. Describe and explain the funct ...
... Define operon. Identify the operon in this diagram and the organism it is in. What do the genes in this operon code for and how does it benefit E. coli? Study the diagram and identify the two regulatory regions. Describe and explain the function of the promoter region. Describe and explain the funct ...
Intrastrand Self-complementary Sequences in Bacillus subtilis DNA
... 1973). This DNA reassociates with unimolecular kinetics, typical of intrastrand structures. Only the slowest eluting molecules of H strand DNA show an increased transforming activity following self-annealing (Fig. 1a). Hydroxyapatite chromatography, which can separate double- and single-stranded DNA ...
... 1973). This DNA reassociates with unimolecular kinetics, typical of intrastrand structures. Only the slowest eluting molecules of H strand DNA show an increased transforming activity following self-annealing (Fig. 1a). Hydroxyapatite chromatography, which can separate double- and single-stranded DNA ...
TheScienceofSuperAmber
... mitosis). The process of cell reproduction is called mitosis (except in sex cells; that’s called meiosis, but we’re not going to get into that). However, before a cell can divide, the DNA must be copied or replicated so that the two daughter cells will both have a complete copy of all the genetic ma ...
... mitosis). The process of cell reproduction is called mitosis (except in sex cells; that’s called meiosis, but we’re not going to get into that). However, before a cell can divide, the DNA must be copied or replicated so that the two daughter cells will both have a complete copy of all the genetic ma ...
Epigenetics - UNM Biology
... http://www.whatisepigenetics.com/dna-methylation/ accessed 9/21/2016 http://www.whatisepigenetics.com/chromatin-remodeling/ accessed 9/23/2016 http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/epigenetics/twins/ accessed 09/26/2016 http://www.naturalhistorymag.com/features/142195/beyond-dnaepigenetics/accessed ...
... http://www.whatisepigenetics.com/dna-methylation/ accessed 9/21/2016 http://www.whatisepigenetics.com/chromatin-remodeling/ accessed 9/23/2016 http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/epigenetics/twins/ accessed 09/26/2016 http://www.naturalhistorymag.com/features/142195/beyond-dnaepigenetics/accessed ...
mutations - bYTEBoss
... Chromosome Mutations Down Syndrome Chromosome 21 does not separate correctly. They have 47 chromosomes in stead of 46. Children with Down Syndrome develop slower, may have heart and stomach illnesses and vary greatly in their degree of inteligence. ...
... Chromosome Mutations Down Syndrome Chromosome 21 does not separate correctly. They have 47 chromosomes in stead of 46. Children with Down Syndrome develop slower, may have heart and stomach illnesses and vary greatly in their degree of inteligence. ...
G NOME® Whole Blood DNA Isolation Kit
... proprietary “salting-out” technique which precludes the need for phenol, chloroform, or other organic extractions. The DNA is precipitated with ethanol, pelleted by centrifugation and dissolved in TE. ...
... proprietary “salting-out” technique which precludes the need for phenol, chloroform, or other organic extractions. The DNA is precipitated with ethanol, pelleted by centrifugation and dissolved in TE. ...
S2DTimes - Science4Kids.com
... the mutant gene. By correcting the splicing error, a normal mRNA was made from a faulty pre-mRNA transcript. In addition, Krainer and Cartegni used their technology on a defective form of the SM2gene, which is associated with the neurodegenerative disease spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). The designer ...
... the mutant gene. By correcting the splicing error, a normal mRNA was made from a faulty pre-mRNA transcript. In addition, Krainer and Cartegni used their technology on a defective form of the SM2gene, which is associated with the neurodegenerative disease spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). The designer ...
See Fig. 13.1c
... incorporation (into the chromosome) of “naked” DNA from the environment…. Expression of this new DNA can alter the phenotype of the organism, e.g. converting a non-pathogen into a pathogen…. e.g. Streptococcus pneumoniae… Fig. 19.10. Streptococcus pneumoniae is pathogenic only when it produces a cap ...
... incorporation (into the chromosome) of “naked” DNA from the environment…. Expression of this new DNA can alter the phenotype of the organism, e.g. converting a non-pathogen into a pathogen…. e.g. Streptococcus pneumoniae… Fig. 19.10. Streptococcus pneumoniae is pathogenic only when it produces a cap ...
- Career Point Kota
... formation from a single megaspore is termed monosporic development. The nucleus of the functional megaspore divides mitotically to form two nuclei which move to the opposite poles, forming the 2-nucleate embryo sac. Two more sequential mitotic nuclear divisions result in the formation of the 4-nucle ...
... formation from a single megaspore is termed monosporic development. The nucleus of the functional megaspore divides mitotically to form two nuclei which move to the opposite poles, forming the 2-nucleate embryo sac. Two more sequential mitotic nuclear divisions result in the formation of the 4-nucle ...
Genomic DNA Purification Protocol
... Ten microliters of DNA isolated using each method was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. The results are shown in Figure 1. Both purification methods yielded high molecular weight DNA with little degradation. For Gram-negative strains, yield from the solution-based purification method was high ...
... Ten microliters of DNA isolated using each method was analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. The results are shown in Figure 1. Both purification methods yielded high molecular weight DNA with little degradation. For Gram-negative strains, yield from the solution-based purification method was high ...
Transposons ※ Transposons are DNA elements that can hop, or
... (5) Smaller protein made from ORFA when the frameshift does not occur regulates transcription of transposase. (6) The target site sequence that is duplicated on the insertion of IS3 is 3 bp long (ex., ATT). The length of such direct repeats is characteristic of each type of transposon. Structure of ...
... (5) Smaller protein made from ORFA when the frameshift does not occur regulates transcription of transposase. (6) The target site sequence that is duplicated on the insertion of IS3 is 3 bp long (ex., ATT). The length of such direct repeats is characteristic of each type of transposon. Structure of ...
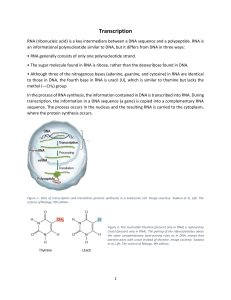
Transcription and RNA processing
... b) ELONGATION- Once RNA polymerase has bound to the promoter, it begins the process of elongation. RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA about 10 base pairs at a time and reads the template strand in the 3′-to-5′direction. Like DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase adds new nucleotides to the 3′ end of the growin ...
... b) ELONGATION- Once RNA polymerase has bound to the promoter, it begins the process of elongation. RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA about 10 base pairs at a time and reads the template strand in the 3′-to-5′direction. Like DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase adds new nucleotides to the 3′ end of the growin ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.