a copy of the Candy DNA Replication
... 2. Why is it important that DNA replicates? ______________________________________ 3. Why is it necessary for DNA to replicate accurately in a cell in order for an organism to survive? ____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________ ...
... 2. Why is it important that DNA replicates? ______________________________________ 3. Why is it necessary for DNA to replicate accurately in a cell in order for an organism to survive? ____________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________ ...
Structure and Role of DNA Genetic and DNA Genetics
... o DNA polymerase checks the arrangement of bases in the new DNA strands and fix errors Chromosomes and Genes Chromosomes(contain genetic information) wraps around proteins and become tightly coiled Every species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in its cells Traits are dertermined by ...
... o DNA polymerase checks the arrangement of bases in the new DNA strands and fix errors Chromosomes and Genes Chromosomes(contain genetic information) wraps around proteins and become tightly coiled Every species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in its cells Traits are dertermined by ...
biotechnology
... (1) Short segments of DNA that repeat over and over in the non-coding regions of a chromosome (2) Short segments of DNA that repeat over and over in the coding regions of a chromosome (3) Short segments of DNA that repeat over and over in both the coding and non-coding regions of a chromosome (4) Sh ...
... (1) Short segments of DNA that repeat over and over in the non-coding regions of a chromosome (2) Short segments of DNA that repeat over and over in the coding regions of a chromosome (3) Short segments of DNA that repeat over and over in both the coding and non-coding regions of a chromosome (4) Sh ...
Genetics and Genetic Engineering
... change the function of cells by inserting their DNA into the DNA of the cell ...
... change the function of cells by inserting their DNA into the DNA of the cell ...
From DNA to Protein Name: What does DNA stand for? What is DNA
... 12. If the sequence of nucleotides on the original DNA strand was A-G-G-C-T-A, what would the nucleotide sequence on the complementary strand of DNA? ...
... 12. If the sequence of nucleotides on the original DNA strand was A-G-G-C-T-A, what would the nucleotide sequence on the complementary strand of DNA? ...
Chemistry 5.50 Site Directed Mutagenesis Methods. Site directed
... methods are described below. All of these methods are now available in "kit" form were the details of the biology are described. A generic overview of the method is described in Figure 1. This figure was redrawn based on the figure from Cosby and Lesley (1997) Promega Notes Magazine Number 61, 12. I ...
... methods are described below. All of these methods are now available in "kit" form were the details of the biology are described. A generic overview of the method is described in Figure 1. This figure was redrawn based on the figure from Cosby and Lesley (1997) Promega Notes Magazine Number 61, 12. I ...
Organization of Eukaryotic DNA Dr: Hussein abdelaziz
... female or XY in male. In gametes (ova, sperm): genome is haploid. Thus the human gametes contain 22 autosomal chromosomes and one sex chromosome, X in female gamete or Y in male gamete ...
... female or XY in male. In gametes (ova, sperm): genome is haploid. Thus the human gametes contain 22 autosomal chromosomes and one sex chromosome, X in female gamete or Y in male gamete ...
Term
... person, [which can then be used to distinguish that persons DNA from other DNA] One allele masks the expression of the other. Biological catalyst ...
... person, [which can then be used to distinguish that persons DNA from other DNA] One allele masks the expression of the other. Biological catalyst ...
Object 4: Genetic fingerprinting
... Although over 99% of human DNA is the same, he discovered short sequences of DNA called minisatellites that vary from one person to another and are passed on from parent to child. How is it used? The most well known use of genetic fingerprinting is in helping to solve crimes. Scientists analyse tiny ...
... Although over 99% of human DNA is the same, he discovered short sequences of DNA called minisatellites that vary from one person to another and are passed on from parent to child. How is it used? The most well known use of genetic fingerprinting is in helping to solve crimes. Scientists analyse tiny ...
Lecture 2 PSY391S John Yeomans
... • Behavior = Genes <=> Environment • Psychologists have studied environmental effects on behavior best for a century. • Human genome project now gives us all the genes. What an opportunity! • Most of these genes are found in lower animals such as mice. • Behavioral effects of single genes can be stu ...
... • Behavior = Genes <=> Environment • Psychologists have studied environmental effects on behavior best for a century. • Human genome project now gives us all the genes. What an opportunity! • Most of these genes are found in lower animals such as mice. • Behavioral effects of single genes can be stu ...
study guide - cloudfront.net
... 7. What cells and where in the body does mitosis occur (hint: somatic or sex cells)?(notes) 8. What cells and where in the body does meiosis occur? (use the hint from #7) (notes) 9. What are gametes?(p.266) ...
... 7. What cells and where in the body does mitosis occur (hint: somatic or sex cells)?(notes) 8. What cells and where in the body does meiosis occur? (use the hint from #7) (notes) 9. What are gametes?(p.266) ...
downloadable file
... nucleotides and an enzyme called DNA polymerase which incorporates new nucleotide bases making a new piece of DNA which is a copy of the original piece. In Sanger’s original method, four different sequencing reactions are performed. Each reaction contains a different modified nucleotide that once in ...
... nucleotides and an enzyme called DNA polymerase which incorporates new nucleotide bases making a new piece of DNA which is a copy of the original piece. In Sanger’s original method, four different sequencing reactions are performed. Each reaction contains a different modified nucleotide that once in ...
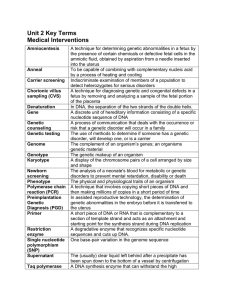
Unit 2 Terms
... then making millions of copies in a short period of time In assisted reproductive technology, the determination of genetic abnormalities in the embryo before it is transferred to the uterus A short piece of DNA or RNA that is complementary to a section of template strand and acts as an attachment an ...
... then making millions of copies in a short period of time In assisted reproductive technology, the determination of genetic abnormalities in the embryo before it is transferred to the uterus A short piece of DNA or RNA that is complementary to a section of template strand and acts as an attachment an ...
Transgenic Organisms
... 2. Whatever gene is taken up is then expressed by the plant cell 3. What are some advantages and disadvantages of this technology? ...
... 2. Whatever gene is taken up is then expressed by the plant cell 3. What are some advantages and disadvantages of this technology? ...
15.3_Applications_of_Genetic_Engineering
... To compare the genes in cancer cells with genes in normal cells, the mRNA would first be isolated from both types of cells Enzymes are used to copy the mRNA base sequence into single-stranded DNA labeled with fluorescent colors -red for the cancer cell and green for the normal cell. ...
... To compare the genes in cancer cells with genes in normal cells, the mRNA would first be isolated from both types of cells Enzymes are used to copy the mRNA base sequence into single-stranded DNA labeled with fluorescent colors -red for the cancer cell and green for the normal cell. ...
Ch 15 Genetic Engineering
... To compare the genes in cancer cells with genes in normal cells, the mRNA would first be isolated from both types of cells Enzymes are used to copy the mRNA base sequence into single-stranded DNA labeled with fluorescent colors -red for the cancer cell and green for the normal cell. ...
... To compare the genes in cancer cells with genes in normal cells, the mRNA would first be isolated from both types of cells Enzymes are used to copy the mRNA base sequence into single-stranded DNA labeled with fluorescent colors -red for the cancer cell and green for the normal cell. ...
1.3. Identity: Molecules and Cells Study Guide (Fisher)
... 1.3.d How can tools of molecular biology be used to compare the DNA of two individuals? DNA can be extracted from a person & then scientists can perform PCR (polymerase chain reactions) to amplify the DNA, making a sample millions of times bigger than the original sample. They can then cut the DNA w ...
... 1.3.d How can tools of molecular biology be used to compare the DNA of two individuals? DNA can be extracted from a person & then scientists can perform PCR (polymerase chain reactions) to amplify the DNA, making a sample millions of times bigger than the original sample. They can then cut the DNA w ...
Variation exists within individuals, within populations, and among
... Review guidelines for discussion test in WFB 224 Examples of types of questions are given in italics Basic terminology – review terms in genetics (Hardy-Weinberg, Mendel, molecular genetics); you should not only be able to define the terms, but understand the concepts behind them Define F1, homozygo ...
... Review guidelines for discussion test in WFB 224 Examples of types of questions are given in italics Basic terminology – review terms in genetics (Hardy-Weinberg, Mendel, molecular genetics); you should not only be able to define the terms, but understand the concepts behind them Define F1, homozygo ...