bio-of-cells-lent-restriction-enzymes-information-for-exam
... Restriction enzyme mapping - determining the order of fragments produced by cutting a DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme. RFLP - restriction fragment length polymorphism, a difference in the size of a genomic DNA fragment produced by digestion with a particular enzyme. A useful DNA marker. RFLPs ...
... Restriction enzyme mapping - determining the order of fragments produced by cutting a DNA molecule with a restriction enzyme. RFLP - restriction fragment length polymorphism, a difference in the size of a genomic DNA fragment produced by digestion with a particular enzyme. A useful DNA marker. RFLPs ...
Genetic Disorders
... weaker and slowly stop working because of a lack of a certain protein (see the relationship to genetics?) Can be passed on by one or both parents, depending on the form of MD (therefore it could be autosomal dominant and/or recessive) ...
... weaker and slowly stop working because of a lack of a certain protein (see the relationship to genetics?) Can be passed on by one or both parents, depending on the form of MD (therefore it could be autosomal dominant and/or recessive) ...
Name: page1 of 7 pages MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIO372S January
... 11. Which of the following isotopes would be the most appropriate for the end-labeling of a DNA strand with a radioactive phosphate via polynucleotide kinase? A. α-32P B. 35S C. β -32P D. γ -32P E. 14C ...
... 11. Which of the following isotopes would be the most appropriate for the end-labeling of a DNA strand with a radioactive phosphate via polynucleotide kinase? A. α-32P B. 35S C. β -32P D. γ -32P E. 14C ...
Slide 1
... • Who made the discovery/invention? • How long did it take to develop? • Were there any problems in the beginning? • What are important dates in its history? • How useful is the discovery/ invention now? Give an example. • What could happen with it in the future? ...
... • Who made the discovery/invention? • How long did it take to develop? • Were there any problems in the beginning? • What are important dates in its history? • How useful is the discovery/ invention now? Give an example. • What could happen with it in the future? ...
Guidelines and Assignments
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
... 1. (MT1) A. How is the 5-mC distributed within the human genome? B. Do all human genes have CpG island at their promoters? C. How bisulfite treatment may affect the CpG methylation status? D. What methods can be used to detect the methylation status of DNA? Please describe at least four different me ...
DNA PROFILING
... A technique used by scientists to distinguish between individuals of the same species using only samples of their DNA ...
... A technique used by scientists to distinguish between individuals of the same species using only samples of their DNA ...
No Slide Title
... • Proteins: macromolecules composed of one or more chains of amino acids • Amino acids: class of 20 different organic compounds containing a basic amino group (NH2) and an acidic carboxyl group (-COOH) • The order of amino acids is determined by the base sequence of nucleotides in the gene coding fo ...
... • Proteins: macromolecules composed of one or more chains of amino acids • Amino acids: class of 20 different organic compounds containing a basic amino group (NH2) and an acidic carboxyl group (-COOH) • The order of amino acids is determined by the base sequence of nucleotides in the gene coding fo ...
Chapter 13: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... ● Hershey and Chase’s experiment labeled the proteins and DNA with different radioactive markers. They then let them infect E. Coli cells and spun the mixture in a centrifuge to remove the proteins from the outside. ○ Seeing that the DNA was left in the cell, not the protein, Hershey and Chase concl ...
... ● Hershey and Chase’s experiment labeled the proteins and DNA with different radioactive markers. They then let them infect E. Coli cells and spun the mixture in a centrifuge to remove the proteins from the outside. ○ Seeing that the DNA was left in the cell, not the protein, Hershey and Chase concl ...
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS
... cells are removed; but ! Mutations in germ cells and embryos can cause developmental defects; mutations in adult cells can cause cancer ! The genetic code has apparently evolved to minimize the effects of mutation ...
... cells are removed; but ! Mutations in germ cells and embryos can cause developmental defects; mutations in adult cells can cause cancer ! The genetic code has apparently evolved to minimize the effects of mutation ...
IB Biology 11 SL (H) - Anoka
... Outline the use of polymerase chain reaction to copy and amplify minute quantities of DNA State that in gel electrophoresis, fragments of DNA move in an electric field and are separated according to their size State that gel electrophoresis of DNA is used in DNA profiling, and describe the applicati ...
... Outline the use of polymerase chain reaction to copy and amplify minute quantities of DNA State that in gel electrophoresis, fragments of DNA move in an electric field and are separated according to their size State that gel electrophoresis of DNA is used in DNA profiling, and describe the applicati ...
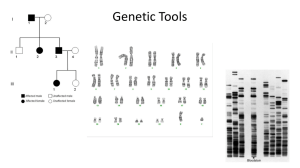
Genetic Tools
... • Mr. and Mrs. Raider are deeply worried about their child who seems to be developing at a slower rate. They are concerned for the child’s health just like any other parent and have come to you for help. ...
... • Mr. and Mrs. Raider are deeply worried about their child who seems to be developing at a slower rate. They are concerned for the child’s health just like any other parent and have come to you for help. ...
Lecture 2: Biology Review II
... Definition: Natural populations are those where mating is not controlled by the experimenter, though the experimenter can choose who to observe. Only phenotype observable, genotype sometimes unknown, phase is unknown. Knowns: allele frequencies, genotype frequencies, amount of disequilibrium. ...
... Definition: Natural populations are those where mating is not controlled by the experimenter, though the experimenter can choose who to observe. Only phenotype observable, genotype sometimes unknown, phase is unknown. Knowns: allele frequencies, genotype frequencies, amount of disequilibrium. ...
CH 9 cont
... What is it? __________ When does it occur? _____ Where does it occur ______? See p 286 and Draw ...
... What is it? __________ When does it occur? _____ Where does it occur ______? See p 286 and Draw ...
3.5 Genetic modification and biotechnology
... - Gel electrophoresis is used to separate proteins of fragments of DNA according to size - PCR can be used to amplify small amounts of DNA - DNA profiling involves comparison of DNA - Genetic modification is carried out by gene transfer between species - Clones are groups of genetically identical or ...
... - Gel electrophoresis is used to separate proteins of fragments of DNA according to size - PCR can be used to amplify small amounts of DNA - DNA profiling involves comparison of DNA - Genetic modification is carried out by gene transfer between species - Clones are groups of genetically identical or ...
GENETICS EOCT STUDY GUIDE 1. DNA Bases: Guanine RNA
... female cat: BbSs (male) and bbSS (female). B Black fur The phenotype of the offspring from these parents willb White fur a. All have black fur S Short fur b. All have white fur s Long fur c. All have long fur d. All have short fur 16. The process of DNA replication is necessary before a cell can – a ...
... female cat: BbSs (male) and bbSS (female). B Black fur The phenotype of the offspring from these parents willb White fur a. All have black fur S Short fur b. All have white fur s Long fur c. All have long fur d. All have short fur 16. The process of DNA replication is necessary before a cell can – a ...
Slide 1 - KREISELMANBIOLOGY
... changes can lead to kinks in the DNA that prevent genes from being correctly read or deletions that alter the type of proteins produced. Thanks to constant biochemical repair work most mutations are corrected before that have any effect. But in rare cases mutations can accumulate and this can give r ...
... changes can lead to kinks in the DNA that prevent genes from being correctly read or deletions that alter the type of proteins produced. Thanks to constant biochemical repair work most mutations are corrected before that have any effect. But in rare cases mutations can accumulate and this can give r ...
EPIGENETICS Textbook
... – INDIRECT/LONGER REGIONS: mediated by “methyl binding domain” proteins acting in multicomplex units that also have histone modifying components, HMT, HDAC ...
... – INDIRECT/LONGER REGIONS: mediated by “methyl binding domain” proteins acting in multicomplex units that also have histone modifying components, HMT, HDAC ...
GENETICS EOCT STUDY GUIDE 1. DNA Bases: Guanine RNA
... female cat: BbSs (male) and bbSS (female). B Black fur The phenotype of the offspring from these parents willb White fur a. All have black fur S Short fur b. All have white fur s Long fur c. All have long fur d. All have short fur 16. The process of DNA replication is necessary before a cell can – a ...
... female cat: BbSs (male) and bbSS (female). B Black fur The phenotype of the offspring from these parents willb White fur a. All have black fur S Short fur b. All have white fur s Long fur c. All have long fur d. All have short fur 16. The process of DNA replication is necessary before a cell can – a ...
... - Gains/losses of >50 Kb within custom clinically significant gene set. On request candidate genes can be analyzed at a much lower threshold, depending on gene specific marker density. - UPD testing is recommended for patient results demonstrating a long contiguous region of homozygosity in a single ...