Biotechnology Part 1
... Plasmids typically contain antibiotic resistance (Amp) 4. Select for the bacteria you want with the plasmid. Those that grow in the presence of the antibiotic have been transformed. ...
... Plasmids typically contain antibiotic resistance (Amp) 4. Select for the bacteria you want with the plasmid. Those that grow in the presence of the antibiotic have been transformed. ...
Sex Inheritance and Multiple Allele Genetics Test Review
... What is Marfan syndrome, what are its symptoms/characteristics What causes some polydactyl people to have extra fingers and others to have extra toes 8. What is an example of plerotropic condition 9. What is the function of the SRY gene 10. Describe x-linked conditions 11. Know that males inherit an ...
... What is Marfan syndrome, what are its symptoms/characteristics What causes some polydactyl people to have extra fingers and others to have extra toes 8. What is an example of plerotropic condition 9. What is the function of the SRY gene 10. Describe x-linked conditions 11. Know that males inherit an ...
Study Island
... Development of the cell theory was made possible by advances in _______. A. physics B. chemistry C. microscopy D. anatomy 2. All living organisms use energy. They also grow and reproduce. What is another characteristic of all living organisms? A. All living organisms must consume food in order to ac ...
... Development of the cell theory was made possible by advances in _______. A. physics B. chemistry C. microscopy D. anatomy 2. All living organisms use energy. They also grow and reproduce. What is another characteristic of all living organisms? A. All living organisms must consume food in order to ac ...
Evolucijska genomika 2
... silence the mutant allele of a cancer-causing gene. The vector encodes a short RNA hairpin, which is processed in the cytoplasm by the ribonuclease Dicer into the siRNA. (b) The siRNA acts as a sequence-specific guide for the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to target cleavage of the mRNA from a ...
... silence the mutant allele of a cancer-causing gene. The vector encodes a short RNA hairpin, which is processed in the cytoplasm by the ribonuclease Dicer into the siRNA. (b) The siRNA acts as a sequence-specific guide for the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to target cleavage of the mRNA from a ...
Intro to DNA and Genetics
... A Genetic researcher can use a computer program that will organize a DNA’s chromosomes, and their matching halves in order. This is called a Karyotype. A Karyotype can be used to spot problems in the DNA, and identify the gender of the DNA donor Genetic disorders like, Down Syndrome, Klinefelter’s S ...
... A Genetic researcher can use a computer program that will organize a DNA’s chromosomes, and their matching halves in order. This is called a Karyotype. A Karyotype can be used to spot problems in the DNA, and identify the gender of the DNA donor Genetic disorders like, Down Syndrome, Klinefelter’s S ...
talk_DNAEditing
... generation of new functions! (for example: any editing in TGG creates premature stop codon). ...
... generation of new functions! (for example: any editing in TGG creates premature stop codon). ...
Mutations - Hicksville Public Schools
... the nucleus 3. Translation: tRNA reads mRNA codons (3 bases) and brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome 4. Sugar: DNA= deoxribose, RNA= ribose Bases: DNA has T and RNA has U DNA: double stranded, RNA: single stranded 5. UGG CAG UGC Try Glu Cys ...
... the nucleus 3. Translation: tRNA reads mRNA codons (3 bases) and brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome 4. Sugar: DNA= deoxribose, RNA= ribose Bases: DNA has T and RNA has U DNA: double stranded, RNA: single stranded 5. UGG CAG UGC Try Glu Cys ...
Build whatever you want - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... the nucleus 3. Translation: tRNA reads mRNA codons (3 bases) and brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome 4. Sugar: DNA= deoxribose, RNA= ribose Bases: DNA has T and RNA has U DNA: double stranded, RNA: single stranded 5. UGG CAG UGC Try Glu Cys ...
... the nucleus 3. Translation: tRNA reads mRNA codons (3 bases) and brings the correct amino acid to the ribosome 4. Sugar: DNA= deoxribose, RNA= ribose Bases: DNA has T and RNA has U DNA: double stranded, RNA: single stranded 5. UGG CAG UGC Try Glu Cys ...
Figure 1 - genomics-lab
... dye (R) is attached at the 5' end, and a quencher dye (D), which has a different emission wavelength to the reporter dye, is attached at its 3' end. Because its 3' end is blocked, primer P3 cannot by itself prime any new DNA synthesis. During the PCR reaction, Taq DNA polymerase synthesizes a new DN ...
... dye (R) is attached at the 5' end, and a quencher dye (D), which has a different emission wavelength to the reporter dye, is attached at its 3' end. Because its 3' end is blocked, primer P3 cannot by itself prime any new DNA synthesis. During the PCR reaction, Taq DNA polymerase synthesizes a new DN ...
Preg,growth,dev,genetics
... The way we inherit genes from mom and dad Autosomal dominant - masks expression of a recessive allele - it causes a trait or disease; usually an X chromosome linked trait; start in adulthood Autosomal recessive - two recessive alleles from each parent elicit a trait; early onset; X linked in females ...
... The way we inherit genes from mom and dad Autosomal dominant - masks expression of a recessive allele - it causes a trait or disease; usually an X chromosome linked trait; start in adulthood Autosomal recessive - two recessive alleles from each parent elicit a trait; early onset; X linked in females ...
Top 102 Biology Review
... 51.Traits carried on the sex chromosomes are called ___________ traits and include _______________ and colorblindness. 52.A test cross always uses the homozygous ______________ to distinguish between a homozygous dominant and a heterozygote parent. 53.What can you use to show the pattern of inherita ...
... 51.Traits carried on the sex chromosomes are called ___________ traits and include _______________ and colorblindness. 52.A test cross always uses the homozygous ______________ to distinguish between a homozygous dominant and a heterozygote parent. 53.What can you use to show the pattern of inherita ...
Obstetric physical examination
... • Grasp the lower poles of the uterus between fingers and thumbs and comment of the size, flexion and mobility of the head. • To determine the position of the vertex presentation: try to palpate the prominences (occiput @ the same side of the back & sincipital @ the opposite side of the ...
... • Grasp the lower poles of the uterus between fingers and thumbs and comment of the size, flexion and mobility of the head. • To determine the position of the vertex presentation: try to palpate the prominences (occiput @ the same side of the back & sincipital @ the opposite side of the ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • After treating long DNA molecules with a restriction enzyme, the fragments can be separated by size via gel electrophoresis. • This produces a series of bands that are characteristic of the starting molecule and that restriction enzyme. ...
... • After treating long DNA molecules with a restriction enzyme, the fragments can be separated by size via gel electrophoresis. • This produces a series of bands that are characteristic of the starting molecule and that restriction enzyme. ...
Lesson 3
... • Cells control genes by turning some genes off and turning other genes on • Each cell uses only some of the thousands of genes that it has to make proteins • For example, muscle proteins are made in muscle cells, cells in the eye produce proteins for eye color, cells in the stomach produce proteins ...
... • Cells control genes by turning some genes off and turning other genes on • Each cell uses only some of the thousands of genes that it has to make proteins • For example, muscle proteins are made in muscle cells, cells in the eye produce proteins for eye color, cells in the stomach produce proteins ...
Application of Recombinant DNA Technology.pdf
... Like other X-linked disorders, hemophilia A and B are found almost exclusively in males because they inherit just a single X chromosome, and if the gene for factor 8 (or 9) on it is defective, they will suffer from the disease. There are many different mutant versions of the genes for factors 8 and ...
... Like other X-linked disorders, hemophilia A and B are found almost exclusively in males because they inherit just a single X chromosome, and if the gene for factor 8 (or 9) on it is defective, they will suffer from the disease. There are many different mutant versions of the genes for factors 8 and ...
Definition of DNA recombinant Technology,
... Like other X-linked disorders, hemophilia A and B are found almost exclusively in males because they inherit just a single X chromosome, and if the gene for factor 8 (or 9) on it is defective, they will suffer from the disease. There are many different mutant versions of the genes for factors 8 and ...
... Like other X-linked disorders, hemophilia A and B are found almost exclusively in males because they inherit just a single X chromosome, and if the gene for factor 8 (or 9) on it is defective, they will suffer from the disease. There are many different mutant versions of the genes for factors 8 and ...
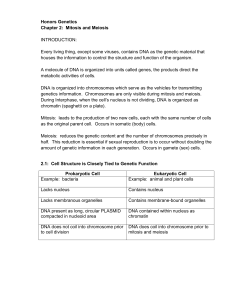
Honors Genetics Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis INTRODUCTION
... Every living thing, except some viruses, contains DNA as the genetic material that houses the information to control the structure and function of the organism. A molecule of DNA is organized into units called genes, the products direct the metabolic activities of cells. DNA is organized into chromo ...
... Every living thing, except some viruses, contains DNA as the genetic material that houses the information to control the structure and function of the organism. A molecule of DNA is organized into units called genes, the products direct the metabolic activities of cells. DNA is organized into chromo ...
Genetics - DNA
... Each of our Chromosomes is a long piece of DNA that has been tightly coiled. Each chromosome contains many genes. We inherit two copies of each chromosome (one from each parent) and this is why our chromosomes can be arranged into homologous pairs. A Gene is a section of DNA that contains a specific ...
... Each of our Chromosomes is a long piece of DNA that has been tightly coiled. Each chromosome contains many genes. We inherit two copies of each chromosome (one from each parent) and this is why our chromosomes can be arranged into homologous pairs. A Gene is a section of DNA that contains a specific ...
TM Review Genetics
... 31. If curly hair is dominant over straight hair. Draw a Punnett Square showing a cross between a homozygous dominant father and a heterozygous mother. Describe the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring, including the percentages of each. ...
... 31. If curly hair is dominant over straight hair. Draw a Punnett Square showing a cross between a homozygous dominant father and a heterozygous mother. Describe the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring, including the percentages of each. ...
File
... Genetic Testing: medical test where our DNA is examined to look for genes that can cause genetic disorders. Reasons for testing: • Finding genetic diseases in unborn babies • Finding out if people carry a gene for a disease and might pass it on to their ...
... Genetic Testing: medical test where our DNA is examined to look for genes that can cause genetic disorders. Reasons for testing: • Finding genetic diseases in unborn babies • Finding out if people carry a gene for a disease and might pass it on to their ...
lecture 2: biological diversity in organisms
... Insertion : causes a frameshift to the left the resulting sentence is non sense ...
... Insertion : causes a frameshift to the left the resulting sentence is non sense ...