Slide 1
... Jaenisch, R. & Bird, A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals Nature Genetics, 2003, 33, 245-254 Schwarz, G. (1978). "Estimating the Dimension of a Model." The Annals of Statistics 6(2): 461-464. Barski, A., S. Cuddapah, et al. (2007) ...
... Jaenisch, R. & Bird, A. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression: how the genome integrates intrinsic and environmental signals Nature Genetics, 2003, 33, 245-254 Schwarz, G. (1978). "Estimating the Dimension of a Model." The Annals of Statistics 6(2): 461-464. Barski, A., S. Cuddapah, et al. (2007) ...
Inheritance Intro
... division. This is why there are two types of cell division. Sex cells are produced by meiosis. In which organs does meiosis take place? ...
... division. This is why there are two types of cell division. Sex cells are produced by meiosis. In which organs does meiosis take place? ...
TUTORIAL 8 – DNA - Molecular Movies
... In this section of the tutorial we’ll import a PDB file for an entire strand of B-DNA using Tom Doeden’s pdbReader script that creates NURBS spheres at every PDB coordinate point. The original script has been around for while and can be downloaded form www.highend3d.com. We will actually be using a ...
... In this section of the tutorial we’ll import a PDB file for an entire strand of B-DNA using Tom Doeden’s pdbReader script that creates NURBS spheres at every PDB coordinate point. The original script has been around for while and can be downloaded form www.highend3d.com. We will actually be using a ...
QUESTIONS AND ANSWER TO PROBLEM SETS
... Concept check: Is DNA a small molecule, a macromolecule, or an organelle? Answer: DNA is a macromolecule. FIGURE 1.5 Concept check: Which types of macromolecules are found in chromosomes? Answer: DNA and proteins are found in chromosomes. A small amount of RNA may also be associated with chromosomes ...
... Concept check: Is DNA a small molecule, a macromolecule, or an organelle? Answer: DNA is a macromolecule. FIGURE 1.5 Concept check: Which types of macromolecules are found in chromosomes? Answer: DNA and proteins are found in chromosomes. A small amount of RNA may also be associated with chromosomes ...
Biology 2006 Answers
... Describes why either the cloned offspring looks identical to biological parent OR why it looks different to the parent in sexual reproduction, eg: cloned offspring is genetically identical to the biological parent cloned offspring gets all of its’ DNA from only one parent mitosis is used to pr ...
... Describes why either the cloned offspring looks identical to biological parent OR why it looks different to the parent in sexual reproduction, eg: cloned offspring is genetically identical to the biological parent cloned offspring gets all of its’ DNA from only one parent mitosis is used to pr ...
Bitter-Tasting Ability
... 1,000 nucleotides. Although some have a biological effect on the individual, most have no effect. However, they may be used as genetic markers in order to locate genes that cause or predispose to disease or influence other traits.! Haplotype - a set of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on a sin ...
... 1,000 nucleotides. Although some have a biological effect on the individual, most have no effect. However, they may be used as genetic markers in order to locate genes that cause or predispose to disease or influence other traits.! Haplotype - a set of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) on a sin ...
THE CHASM BETWEEN THE HUMAN AND CHIMPANZEE GENOMES
... genes. To accomplish this, a fair amount of re-sequencing was required because the chimp sequence in this area was fragmented and incomplete. The end result was 25,800,000 bases of highly accurate chimp Y-chromosome sequence distributed among eight contiguous segments, the longest of which was 10,10 ...
... genes. To accomplish this, a fair amount of re-sequencing was required because the chimp sequence in this area was fragmented and incomplete. The end result was 25,800,000 bases of highly accurate chimp Y-chromosome sequence distributed among eight contiguous segments, the longest of which was 10,10 ...
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma
... 2. hybridized to several thousand probes. The probes are derived from most of the known genes and non-coding regions of the genome, printed on a glass slide. 3. The fluorescence intensity of the test and of the reference DNA is then measured, to calculate the ratio between them and subsequently the ...
... 2. hybridized to several thousand probes. The probes are derived from most of the known genes and non-coding regions of the genome, printed on a glass slide. 3. The fluorescence intensity of the test and of the reference DNA is then measured, to calculate the ratio between them and subsequently the ...
Classification of Bears
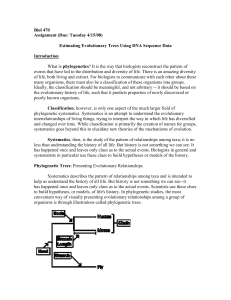
... unrooted. In rooted trees, there is a particular node, called the root--representing a common ancestor--from which a unique path leads to any other node. An unrooted tree only specifies the relationship among species, without identifying a common ancestor, or evolutionary path. Molecular phylogeneti ...
... unrooted. In rooted trees, there is a particular node, called the root--representing a common ancestor--from which a unique path leads to any other node. An unrooted tree only specifies the relationship among species, without identifying a common ancestor, or evolutionary path. Molecular phylogeneti ...
Life Science Content Review for the Science HSPE
... ergy flows from the sun to an animal cell where it is used for cellular work? A. Sun → Plants → Sugars → Animal cell → ATP B. Sun → Plants → Food → Animal cell → Sugar C. Sun → ATP → Plants → Animal cell → Sugar D. Sun → Sugars → Plants → Animal cell → ATP 10. Plants transform energy from ...
... ergy flows from the sun to an animal cell where it is used for cellular work? A. Sun → Plants → Sugars → Animal cell → ATP B. Sun → Plants → Food → Animal cell → Sugar C. Sun → ATP → Plants → Animal cell → Sugar D. Sun → Sugars → Plants → Animal cell → ATP 10. Plants transform energy from ...
ECA Review ANSWER KEY
... 6. What is ATP and why is it important to all living things? ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the functional unit of energy for all living organisms. Organisms get energy by breaking off the last phosphate group and using the energy stored in that bond. During cellular respiration, organisms can c ...
... 6. What is ATP and why is it important to all living things? ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is the functional unit of energy for all living organisms. Organisms get energy by breaking off the last phosphate group and using the energy stored in that bond. During cellular respiration, organisms can c ...
D melanogaster - GEP Community Server
... Considerations for Genome Sequencing 1. Satellite DNA, a sequence of tandem repeats, is very difficult to sequence, as there are few markers to help order subclones; hence centromeric regions of the chromosomes are usually left unsequenced. 2. Other repetitious DNA, derived from transposable elemen ...
... Considerations for Genome Sequencing 1. Satellite DNA, a sequence of tandem repeats, is very difficult to sequence, as there are few markers to help order subclones; hence centromeric regions of the chromosomes are usually left unsequenced. 2. Other repetitious DNA, derived from transposable elemen ...
Classification Chapter 18 - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
... concluded that barnacles are more closely related to crabs than to MOLLUSKS http://siena.earth.rochester.edu/ees207/Gastropoda/ ...
... concluded that barnacles are more closely related to crabs than to MOLLUSKS http://siena.earth.rochester.edu/ees207/Gastropoda/ ...
Global MAPS Metabolomic Assisted Pathway Screen
... The Proband Whole Exome Sequencing test is a highly complex test that is newly developed for the identification of changes in a patient’s DNA that are causative or related to their medical concerns. In contrast to current sequencing tests that analyze one gene or small groups of related genes at a t ...
... The Proband Whole Exome Sequencing test is a highly complex test that is newly developed for the identification of changes in a patient’s DNA that are causative or related to their medical concerns. In contrast to current sequencing tests that analyze one gene or small groups of related genes at a t ...
Chapter 12 Molecular Genetics
... diffraction, a technique that involved aiming X rays at the DNA molecule. In 1951, Franklin joined the staff at King's College. There she took the now famous Photo 51 and collected data eventually used by Watson and Crick. Photo 51, shown in Figure 12.6, indicated that DNA was a double helix, or twi ...
... diffraction, a technique that involved aiming X rays at the DNA molecule. In 1951, Franklin joined the staff at King's College. There she took the now famous Photo 51 and collected data eventually used by Watson and Crick. Photo 51, shown in Figure 12.6, indicated that DNA was a double helix, or twi ...
6.1 Mutation
... do some people have lighter skin and other have darker skin? Why would a cuckoo bird lay her eggs in another birds’ nest? Why did white moths become less common and gray moths become more common near a factory? ...
... do some people have lighter skin and other have darker skin? Why would a cuckoo bird lay her eggs in another birds’ nest? Why did white moths become less common and gray moths become more common near a factory? ...
Mitochondrial point mutations do not limit the natural lifespan of mice
... embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) derived from 2.5-month-old animals Polg mice argues against a substantial role for Polg misinsertions in completely deficient in the proofreading activity of DNA polymerase g the absence of DNA damage (Supplementary Fig. 5). The muta(Polg), the mitochondrial replicative ...
... embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) derived from 2.5-month-old animals Polg mice argues against a substantial role for Polg misinsertions in completely deficient in the proofreading activity of DNA polymerase g the absence of DNA damage (Supplementary Fig. 5). The muta(Polg), the mitochondrial replicative ...
Analysis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis mutations in the
... loci, although three of the five loci were located on the same 330-kb SmaI fragment of the wild-type strain Eagan chromosome. This fragment also contains several important virulence determinants, including the capb locus, and one of the five constitutive mutants had concomitantly lost the ability to ...
... loci, although three of the five loci were located on the same 330-kb SmaI fragment of the wild-type strain Eagan chromosome. This fragment also contains several important virulence determinants, including the capb locus, and one of the five constitutive mutants had concomitantly lost the ability to ...
Chapter 12
... Chapter 12 - DNA Technology and the Human Genome How can we use bacteria to manipulate DNA and protein? Recall how a bacterium defends itself when a bacteriophage injects its DNA into a bacterium… The bacterium has enzymes called restriction enzymes that attempt to cut up the bacteriophage DNA befo ...
... Chapter 12 - DNA Technology and the Human Genome How can we use bacteria to manipulate DNA and protein? Recall how a bacterium defends itself when a bacteriophage injects its DNA into a bacterium… The bacterium has enzymes called restriction enzymes that attempt to cut up the bacteriophage DNA befo ...
lecture notes - Fountain University, Osogbo
... gene activity can cause disease. The scientists expected that their project would lead to the development of new drugs targeted to specific disorders. 1. 1 Cell division This the replication of cells for the growth and development the reproduction during because of the cell of organism could not gro ...
... gene activity can cause disease. The scientists expected that their project would lead to the development of new drugs targeted to specific disorders. 1. 1 Cell division This the replication of cells for the growth and development the reproduction during because of the cell of organism could not gro ...
Chromosomal Microarray: Test Information for Families
... multiple birth defects or autism spectrum disorders. It is sometimes referred to as “microarray” or “array CGH”. Chromosomal microarrays have the ability to find small changes in genetic material (DNA). It is more detailed than a regular chromosome test (karyotype). It specifically looks for extra a ...
... multiple birth defects or autism spectrum disorders. It is sometimes referred to as “microarray” or “array CGH”. Chromosomal microarrays have the ability to find small changes in genetic material (DNA). It is more detailed than a regular chromosome test (karyotype). It specifically looks for extra a ...
Replication Protein A (RPA1a) Is Required for Meiotic and Somatic
... during repair of other kinds of DNA lesions by NER or BER (West et al., 2004; Bleuyard et al., 2006). The past decade has witnessed an explosion in understanding of this complex process by using yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) as a model organism (Aylon and Kupiec, 2004). Cells can repair DSBs by t ...
... during repair of other kinds of DNA lesions by NER or BER (West et al., 2004; Bleuyard et al., 2006). The past decade has witnessed an explosion in understanding of this complex process by using yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) as a model organism (Aylon and Kupiec, 2004). Cells can repair DSBs by t ...
Gene7-21
... 11. Acetylation of histones occurs at both replication and transcription and could be necessary to form a less compact chromatin structure. 12. Active chromatin and inactive chromatin are not in equilibrium. 13. A group of hypersensitive sites upstream of the cluster of -globin genes forms a locus c ...
... 11. Acetylation of histones occurs at both replication and transcription and could be necessary to form a less compact chromatin structure. 12. Active chromatin and inactive chromatin are not in equilibrium. 13. A group of hypersensitive sites upstream of the cluster of -globin genes forms a locus c ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.